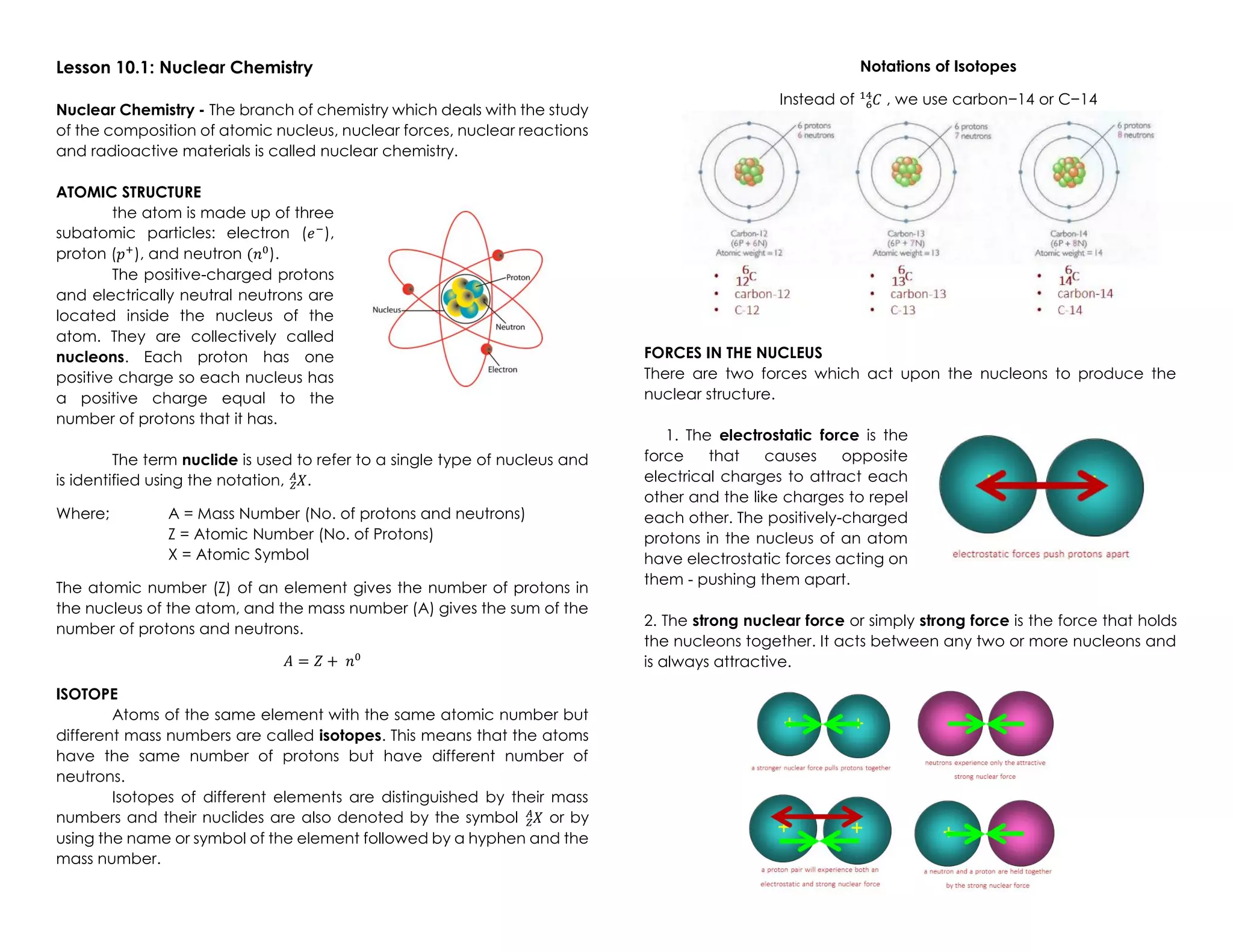
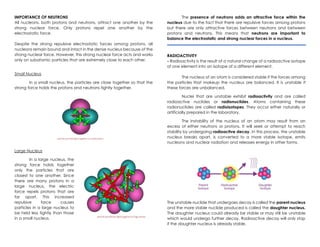
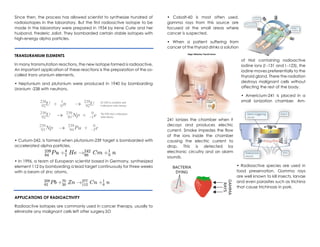
Nuclear chemistry deals with the composition of atomic nuclei, nuclear forces, reactions, and radioactive materials. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons, which are held together by the strong nuclear force balancing the electromagnetic repulsion between protons. Unstable nuclei undergo radioactive decay through processes like alpha decay (emitting an alpha particle), beta decay (emitting an electron), gamma decay (emitting gamma rays), or other rarer types of decay, becoming more stable nuclides over time until reaching a stable configuration. Nuclear reactions involve changes to nuclei and preserve the total number of nucleons.