Embed presentation
Download to read offline

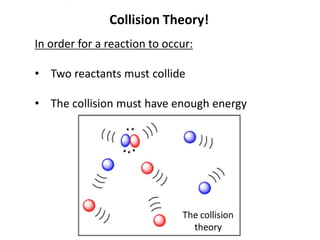


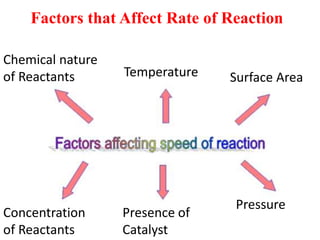
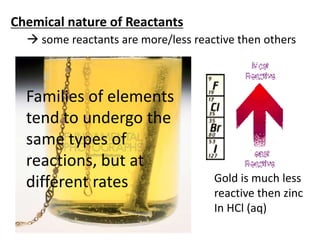
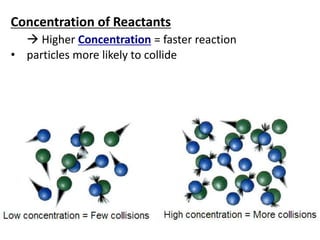
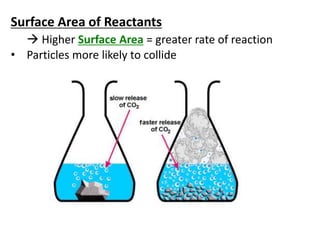
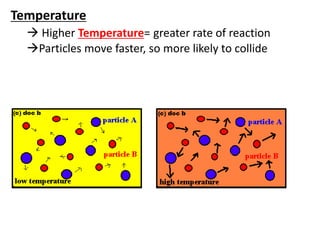
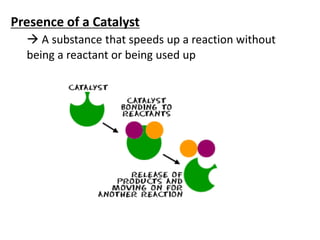
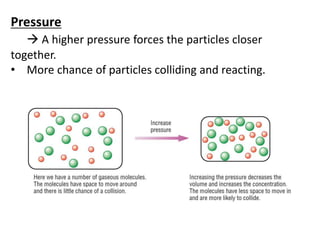
Collision theory states that for a reaction to occur, reactants must collide with sufficient energy. The rate of reaction depends on factors that increase the probability of successful collisions between reactants, such as higher concentrations, temperatures, pressures, surface areas, and the presence of catalysts. These factors relate to collision theory because they influence whether reactants collide and the likelihood that collisions will be energetic enough to trigger chemical reactions.










