This document discusses several key concepts in research ethics including:
- The four main principles of ethics in research are respect for persons, beneficence, justice, and respect for communities.
- Standards of care in research must consider local contexts and not exploit vulnerable groups.
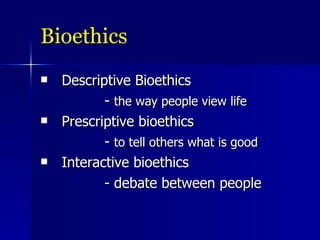
- Bioethics examines life science morality through descriptive, prescriptive, and interactive approaches.
- Research ethics frameworks like the Nuremberg Code and Declaration of Helsinki provide guidelines on informed consent, honesty, and protecting human subjects.