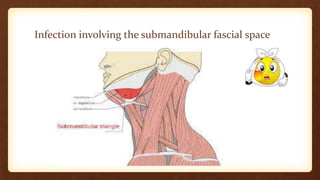
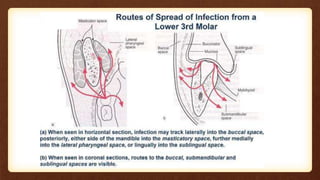
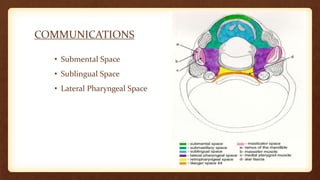
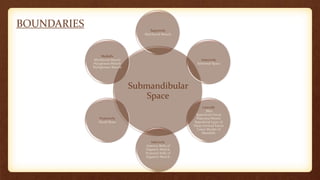
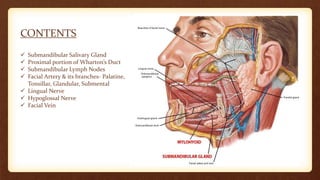
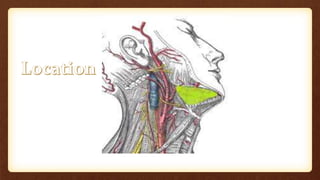
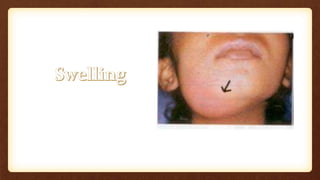
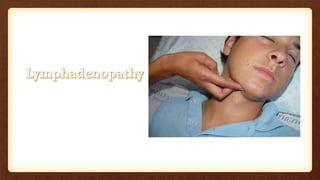
This document discusses submandibular space infections, including their classification, etiology, boundaries, contents, clinical features, diagnosis, and management. Submandibular space infections can be primary, related to teeth, or spread from other areas. They are commonly caused by infections of the lower molars. Clinically, they present as swelling and pain in the angle of the jaw, with trismus. Treatment involves airway protection, hydration, nutrition, treating any underlying conditions, analgesics, antiseptics, antibiotics, and potentially extraction or incision and drainage. Complications can include sialadenitis, Ludwig's angina, and lymphadenitis.