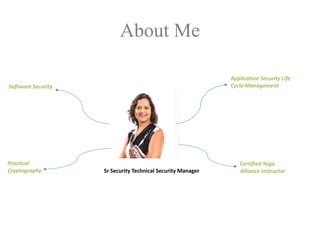
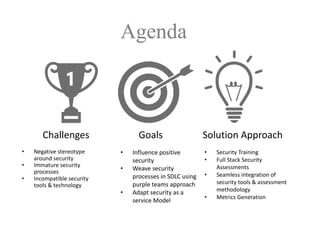
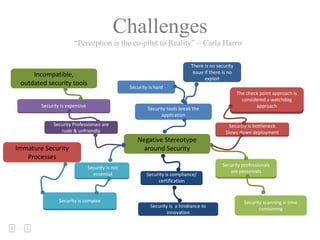
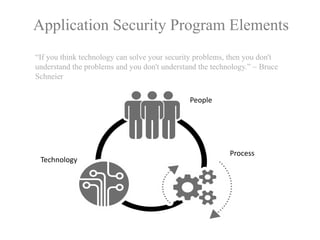
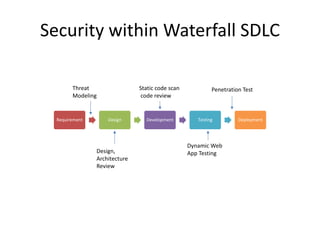
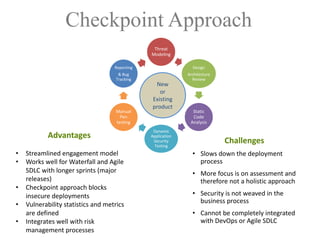
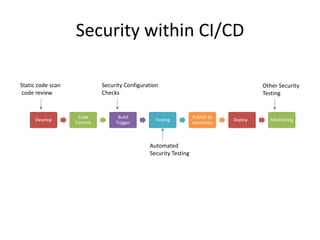
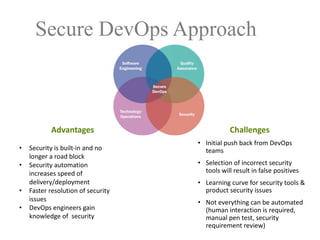
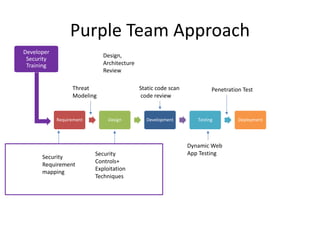
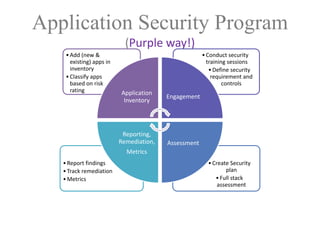
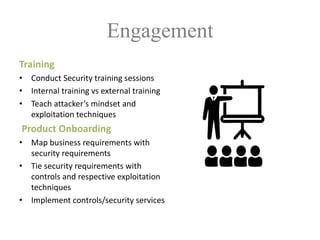
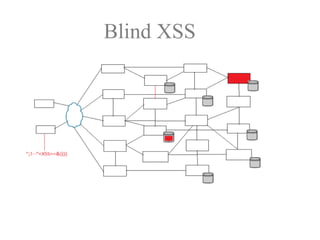
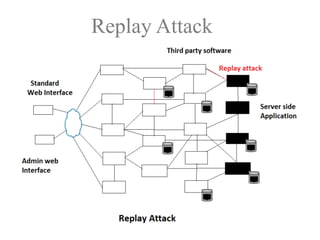
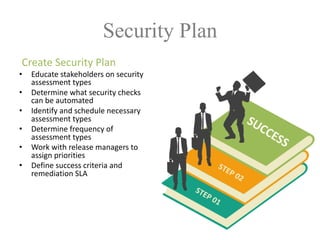
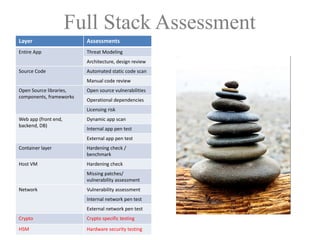
The document discusses a purple team strategy for enhancing application security by addressing common challenges and stereotypes associated with security practices. It emphasizes the integration of security processes throughout the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and presents various methods to foster collaboration between development and security teams. The aim is to create a holistic security program that improves processes, training, and risk management while overcoming deployment obstacles.