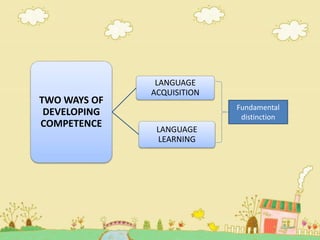
1. The document discusses Stephen Krashen's acquisition-learning hypothesis, which distinguishes between language acquisition and language learning.
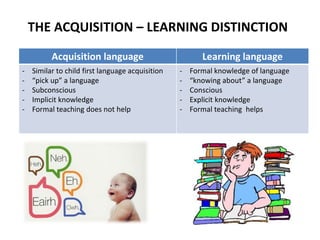
2. Language acquisition is a subconscious process that occurs through meaningful interaction and communication, similar to how children learn their first language. Language learning is a conscious process involving formal study and attention to language rules.
3. Acquisition results in implicit practical language ability while learning provides explicit knowledge about the language. Formal teaching is more helpful for learning than acquisition according to Krashen.