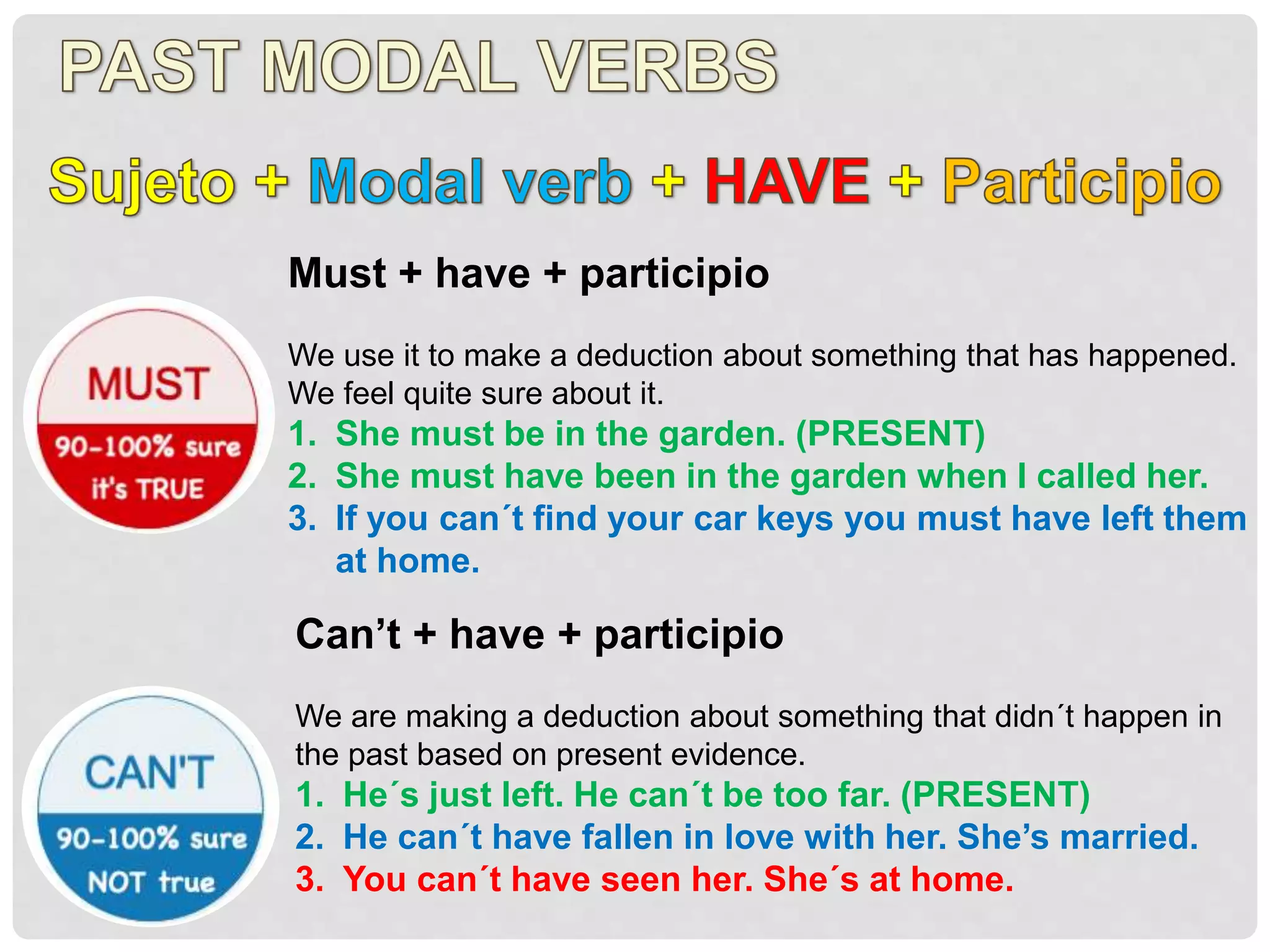
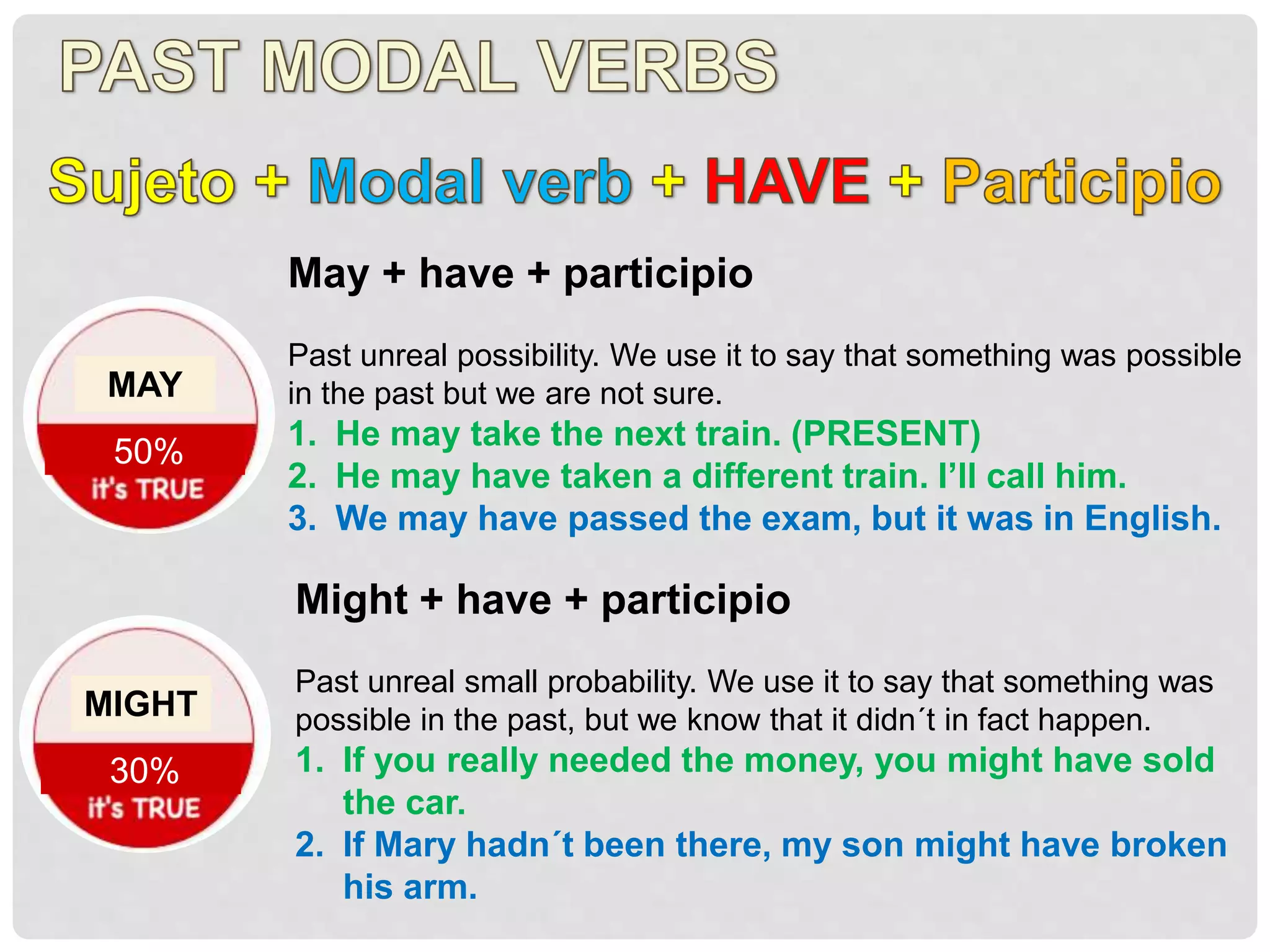
This document discusses the different types of conditional sentences in English. There are four main types: zero conditional, first conditional, second conditional, and third conditional. Each type uses a different verb tense combination and serves a different grammatical function. The zero conditional refers to general truths using present tense. The first conditional refers to possible future events using present and future tenses. The second conditional refers to unlikely present or future situations using past tense. The third conditional refers to imagined past events using past perfect tense. Mixed conditionals combine tenses to discuss past situations with present results or vice versa.