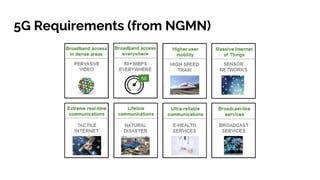
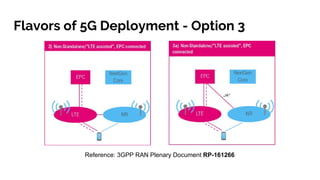
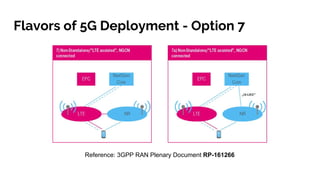
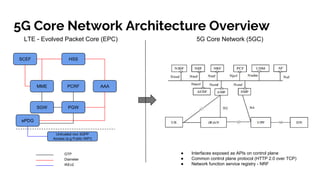
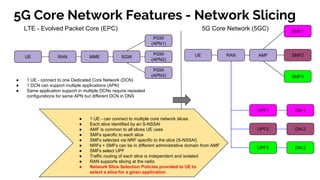
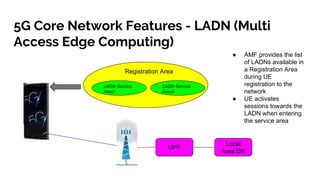
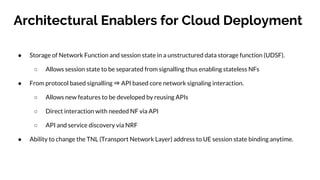
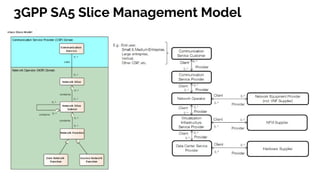
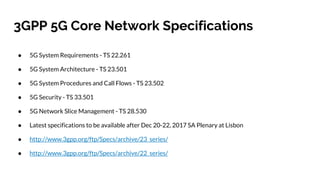
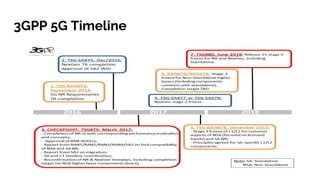
The document discusses the 5G core network, focusing on its characteristics, deployment flavors, and the necessary standards from 3GPP and ETSI. Key features include network slicing, cloud deployment enablers, and the differentiation between user and control planes. It emphasizes the need for standards for cross-domain orchestration and the role of APIs in the evolution towards a truly converged, cloud-native architecture.