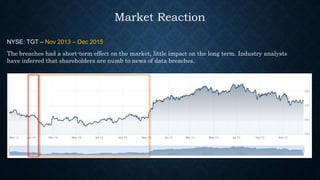
Target suffered a major data breach in late 2013 that compromised the payment card and personal information of up to 110 million customers. Hackers were able to gain access to Target's systems by phishing a vendor for credentials and installing malware that stole payment card data. Target failed to properly respond to warnings from its security systems about the breach. The breach had short-term negative impacts for Target's stock price and brand reputation, and resulted in lawsuits and settlements totaling tens of millions of dollars. Key lessons highlighted include the need for strong network segmentation, oversight of third party vendors, effective log monitoring and analytics, and accountability from executives for cybersecurity practices.