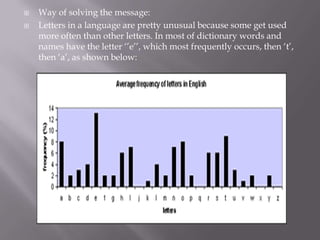
This document discusses various types of codes and ciphers used throughout history for secure communication. It explains that codes operate at the word or phrase level by assigning whole words or phrases to symbols, while ciphers operate at the letter level by substituting letters for other letters, numbers, or symbols. Examples of codes and ciphers discussed include the Caesar cipher, Morse code, Enigma machines, and the code used by Mary Queen of Scots. Frequency analysis is introduced as an effective method for cracking ciphers by analyzing which symbols appear most frequently and mapping them to the most common letters in a language.