Urinary Tract Infection
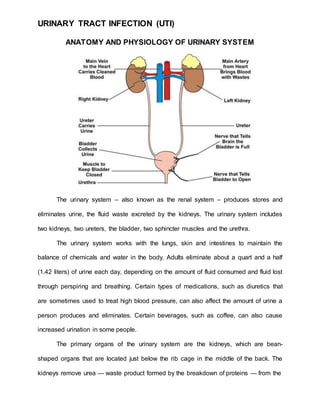
- 1. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system – also known as the renal system – produces stores and eliminates urine, the fluid waste excreted by the kidneys. The urinary system includes two kidneys, two ureters, the bladder, two sphincter muscles and the urethra. The urinary system works with the lungs, skin and intestines to maintain the balance of chemicals and water in the body. Adults eliminate about a quart and a half (1.42 liters) of urine each day, depending on the amount of fluid consumed and fluid lost through perspiring and breathing. Certain types of medications, such as diuretics that are sometimes used to treat high blood pressure, can also affect the amount of urine a person produces and eliminates. Certain beverages, such as coffee, can also cause increased urination in some people. The primary organs of the urinary system are the kidneys, which are bean- shaped organs that are located just below the rib cage in the middle of the back. The kidneys remove urea — waste product formed by the breakdown of proteins — from the
- 2. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) blood through small filtering units called nephrons. Each nephron consists of a ball formed of small blood capillaries, called a glomerulus, and a small tube called a renal tubule. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney. From the kidneys, urine travels down two thin tubes, called ureters, to the bladder. The ureters are about 8 to 10 inches long (20 to 25 centimeters). Muscles in the ureter walls continuously tighten and relax to force urine away from the kidneys. A backup of urine can cause a kidney infection. Small amounts of urine are emptied into the bladder from the ureters about every 10 to 15 seconds. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ shaped like a balloon. It sits in the pelvis and is held in place by ligaments attached to other organs and the pelvic bones. The bladder stores urine until you are ready to empty it. A normal, healthy bladder can hold up to 16 ounces (almost half a liter) of urine comfortably for 2 to 5 hours. To prevent leakage, circular muscles called sphincters close tightly around the opening of the bladder into the urethra, the tube that allows urine to pass outside the body. The only difference between the female and male urinary system is the length of the urethra. In females, the urethra is about 1.5 inches (3.8 cm) to 2 inches (5.1 cm) long and sits between the clitoris and the vagina. In males, it runs the length of the penis, is about 8 inches (20 cm) long and opens at the end of the penis. The male urethra is used to eliminate urine as well as semen during ejaculation.
- 3. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) Nerves in the bladder send signals when it needs to be emptied. The sensation to urinate becomes stronger as the bladder reaches its limit. At that point, nerves from the bladder send a message to the brain that the bladder is full, and your urge to empty your bladder intensifies. When you urinate, the brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten while simultaneously signaling the sphincter muscles to relax. Reference: Kim Ann Zimmermann, Live Science Contributor | February 11, 2013 01:53pm ET. Urinary System: Facts, Functions & Diseases. Retrieved: (November 07, 2014) http://www.livescience.com/27012-urinary-system.html
- 4. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) OVERVIEW OF DISEASE The urinary tract is commonly divided into two areas. The upper urinary tract consists of the kidneys and the delicate tubular structure (ureter) that runs from the kidney to the bladder. The lower tract includes the bladder and the urethra (the tube from the bladder to the outside of the body). Bacteria cause the large majority of urinary tract infections in children. Viral infection of the bladder is less common, while fungal infections of the urinary tract are rare and occur most commonly in immunocompromised individuals. Normally urine travels this path without a hitch, but if bacteria get in the urine – from the skin around the genitals or rectum or via the bloodstream – they can create infection and inflammation at any point along the way. About 8 percent of girls and 2 percent of boys will have at least one urinary tract infection during childhood. Characteristic symptoms of a urinary tract infection include pain with urination (dysuria), urinary frequency (needing to urinate frequently) and urgency (feeling a
- 5. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) compelling urge to urinate) and loss of previously established urinary control (for example, bedwetting). Nonspecific but common symptoms include fever (especially >102.2 F or 39 C) and abdominal pain. For some children less than 2 years of age, these more subtle problems may be the only indicator of a UTI. Associated symptoms of concern include flank pain, fever, and vomiting. Obvious blood in the urine (gross hematuria) as well as a positive family history for childhood urinary tract infections (especially in siblings) are also red flags and should raise the level of concern. Interestingly, the odor and color (with the exception of obvious blood) of the urine are not predictors of a UTI. In some cases, a child may show other symptoms – with or without a fever – including: Crying or another indication that urination is painful Frequent, urgent need to urinate Difficulty emptying bladder Pain or burning while urinating Daytime or nighttime accidents in a child who's toilet trained Odd-smelling urine Cloudy or bloody urine Unexplained, persistent irritability Vomiting Refusal to eat Abdominal, side, or back pain Fatigue
- 6. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) Chills Diarrhea The physical examination of a child with suspected urinary tract infection should start with the vital signs (temperature, pulse, breathing rate, and blood pressure, which is often measured with the vital signs). The presence of fever (especially over 102.2 F or 39 C) is highly correlated with the presence of a UTI. Blood pressure and assessment of height and weight provide helpful reassurance if normal or stable long-term renal function. Visual examination of the abdomen for enlargement related to potentially oversized kidney(s) or bladder is important. Tenderness during palpation of the abdomen (especially the suprapubic region containing the bladder) or the flank area (where the kidneys are situated) is very helpful in establishing the diagnosis. Examination of the genitalia is also very important to see if there is evidence of vaginal irritation (redness, discharge, evidence of trauma or foreign body). An uncircumcised male (especially with a foreskin which is difficult to retract) is more likely to experience a UTI when compared to a population of similar infant boys who have been circumcised. Lastly, consideration of other conditions that might be responsible for fever and abdominal pain is important. Reference: John Mersch, MD, FAAP,. Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD,. (Medically Reviewed by a Doctor on 12/20/2013). MedicineNet.com. Urinary Tract Infections in Children. Retrieved: (November 07, 2014) http://www.medicinenet.com/urinary_tract_infections_in_children/page3.htm
- 7. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) ASSESSMENT If you have symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI), your initial evaluation by your doctor will include a medical history and physical exam. A medical history includes an evaluation of your current urinary tract symptoms, history of urinary tract infections or other urinary tract problems, family health history, and sexual history. You and your doctor will discuss your general health and the results of previous testing. For women, your doctor will: Evaluate the possibility of pregnancy and any history of reproductive problems. Include a pelvic exam if symptoms indicate a possible pelvic infection or urethritis. Examine your lower back, abdomen, and the area just above where the pelvic bone and the lower abdomen meet for tenderness, pain, or abnormalities. Take temperature. For men, your doctor will: Evaluate any history of prostate problems. Examine your genitals, lower back, and abdomen. Examine your rectum and rectal area to check for prostate enlargement, growths, or inflammation. Take temperature.
- 8. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) Findings of the medical history and physical exam include the following: Normal No pain, growths, or abnormalities No prostate enlargement or tenderness (men only) No discharge from the urethra Abnormal Pain or discomfort in response to pressure on the lower back, abdomen, or the area above the pelvic bone Growths or abnormalities detected during pelvic or rectal exam Enlarged or tender prostate gland (men only) Discharge from the urethra Reference: E. Gregory Thompson, MD - Internal Medicine,. Avery L. Seifert, MD – Urology,. (May 13, 2013). Information and Resources: Medical History and Physical Exam for Urinary Tract Infections. Retrieved: (November 07, 2014) http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/medical-history-and-physical-exam-for-urinary- tract-infections
- 9. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) Reference:Niall F.Davis.,The Pathogenesisof UrinaryTract Infection.Chapter7. Retrieved:(November08,2014) http://www.intechopen.com/books/clinical-management-of-complicated-urinary-tract-infection/the-pathogenesis-of-urinary-tract-infections ASCENDING ROUTE HAEMATOGENOUS/ DESCENDING ROUTE LYMPHATIC ROUTE FACTORS Youngerage Female Uncircumcisedboys Improperperineal hygiene Maternal historyof UTI Urinary Tract abnormalities BlockagesinUrinaryTract Suppressedimmune system (Diabeticpatient) Use of Urinary Catheters Decreasedinvaginal pH Decreasedinoestrogen Decreasedinvaginal lactobacilli Increasedcolonizationof bacteria(E.coli, enterobacteriaceae)fromthe rectum UTI IN FEMALE PATIENT Lower UTIs are infections of the urethra and bladder. Their symptoms include: -burning with urination -increased frequency of urination with scant amounts of urine being passed -bloody urine -cloudy urine -urine that looks like cola or tea -strong odor to urine -pelvic pain (women) Upper UTIs are infections of the kidneys. -pain and tenderness in the upper back and sides -chills -fever -nausea -vomiting
- 10. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) MEDICAL MANAGEMENT Doctors typically use antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections. Which drugs are prescribed and for how long depend on your health condition and the type of bacterium found in your urine. Simple infection Drugs commonly recommended for simple UTIs include: Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (Bactrim, Septra, others) Amoxicillin (Amoxil, Augmentin, others) Nitrofurantoin (Furadantin, Macrodantin, others) Ampicillin Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) Levofloxacin (Levaquin) Usually, symptoms clear up within a few days of treatment. But you may need to continue antibiotics for a week or more. Take the entire course of antibiotics prescribed by your doctor to ensure that the infection is completely gone. For an uncomplicated UTI that occurs when you're otherwise healthy, your doctor may recommend a shorter course of treatment, such as taking an antibiotic for one to three days. But whether this short course of treatment is adequate to treat your infection depends on your particular symptoms and medical history.
- 11. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) The doctor may also prescribe a pain medication (analgesic) that numbs your bladder and urethra to relieve burning while urinating. One common side effect of urinary tract analgesics is discolored urine — orange or red. Frequent infections If you experience frequent UTIs, your doctor may make certain treatment recommendations, such as: Longer course of antibiotic treatment or a program with short courses of antibiotics at the start of your urinary symptoms. Home urine tests, in which you dip a test stick into a urine sample, to check for infection a single dose of antibiotic after sexual intercourse if your infections are related to sexual activity. Vaginal estrogen therapy if you're postmenopausal, to minimize your chance of recurrent UTIs. Severe infection For a severe UTI, you may need treatment with intravenous antibiotics in a hospital. Reference: Mayo Clinic Staff,. August 29, 2012. Disease and Conditions: Urinary Tract Infections (UTI). Retrieved: (November 07, 2014) http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases- conditions/urinary-tract-infection/basics/treatment/con-20037892
- 12. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) SURGICAL MANAGEMENT Surgical Therapy The goal of surgical intervention is to completely relieve the urinary tract obstruction. This can be evaluated with reimaging to ensure that the obstruction is resolved, as well as renal function monitoring with a creatinine laboratory test. The recovery of renal function depends on the severity and duration of the obstruction. Different interventions can be performed to temporarily relieve the point of obstruction. Surgical intervention is usually obtained once the point of obstruction is identified with radiographic imaging. Lower urinary tract obstruction (bladder, urethra) can be relieved with the following: Urethral catheter: A urethral catheter (size 8F-24F) is a flexible external catheter that extends from the bladder through the urethra. A physician or nurse can place it. If catheter placement is difficult, a urologist may be needed to avoid urethral trauma. The urologist may need to perform urethral dilation, cystoscopy, or both to pass the catheter. The catheter can be left indwelling, or, as an alternative, the patient can perform clean intermittent catheterization. If blood is present at the urethral meatus after pelvic trauma and suspicion of urethral injury exists, a urologist should be consulted prior to catheter placement. Retrograde urethrography needs to be performed to rule out urethral injury. Suprapubic tube or catheter: If a Foley catheter cannot be passed, a suprapubic tube can be placed percutaneously (at the bedside) or in an open fashion (in
- 13. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) the operating room). A suprapubic tube is placed on the lower anterior abdominal wall, approximately 2 finger-breadths above the pubic symphysis. Ultrasound guidance should be used for bedside procedures to ensure proper placement without injury to adjacent structures. In patients with previous abdominal surgery, adhesions and scar tissue may have changed the normal bowel location, so an open approach may be preferred. Upper urinary tract obstruction (ureter, kidney) can be relieved with the following: Ureteral stent (see the image below): A ureteral stent is a flexible tube that extends from the renal pelvis to the bladder. It can be placed during cystoscopy to relieve obstruction along any point in the ureter. A ureteral stent generally needs to be changed every 3 months. Kidney-ureter-bladder (KUB): image displaying a large right-sided renal stone and an indwelling ureteral stent. Nephrostomy tube: A nephrostomy tube is a flexible tube that is placed through the back directly into the renal pelvis. If a ureteral stent cannot be placed cystoscopically in a retrograde fashion, a percutaneous nephrostomy tube can be inserted for relief of hydronephrosis. If needed, a ureteral stent can then be passed in an antegrade fashion through the nephrostomy tube tract. Reference: Edward David Kim, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Division of Urology, University of Tennessee Graduate School of Medicine; Consulting Staff, University of Tennessee Medical Center,. May 2, 2013. Urinary Tract Obstruction Treatment and Management. Retrieved: (November 07, 2014) http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/438890-treatment#a1128
- 14. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) NURSING DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1. Acute Pain related to inflammation and infection of the urethra, bladder and other urinary tract structures. Goal: Pain is reduced / lost, the spasms can be controlled. Expected outcomes: client reported no pain on urination, no pain in the suprapubic region. INTERVENTION 1. Monitor urine color changes, monitor the voiding pattern, input and output every 8 hours and monitor the results of urinalysis repeated. Rationale: To identify the indications of progress or deviations from expected results 2. Note the location, time intensity scale (1-10) pain. Rationale: To help evaluate the place of obstruction and cause pain. 3 .Provide convenient measures, such as massage. Rationale: Increase relaxation, reduce muscle tension. 4. Give perineal care. Rational: To prevent contamination of the urethra. 5. If using a catheter, catheter treatment 2 times per day. Rationale: The catheter provides a way for bacteria to enter the bladder and urinary tract up to. 6. Divert attention to the fun. Rationale: Relaxation, avoid too feel the pain. 7. Collaboration of analgesics. Rational: to control the pain.
- 15. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) 2. Impaired Urinary Elimination related to frequent urination, urgency, and hesitancy. Goal: improve urinary elimination pattern. Expected outcomes: clients reported a reduction in frequency (frequent urination), urgency, and hesitance. INTERVENTION 1. Assess the patient's pattern of elimination. Rationale: as a basis for determining interventions. 2. Encourage the patient to drink as much as possible and reduce drinking in the afternoon. Rationale: To support the renal blood flow and to flush bacteria from the urinary tract. The liquid that can irritate the bladder (e.g, coffee, tea, alcohol) is avoided. In order not to wake up frequently at night to urinate. 3. Encourage the patient to urinate every 2-3 hours and when it suddenly felt. Rationale: Because it significantly lowers the number of bacteria in the urine, reduced urine status and prevent recurrence of infection. 4. Prepare / encouragement do perineal care every day. Rationale: Reduce the risk of contamination / infection increased.
- 16. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) 2. Disturbed Sleep Pattern related to pain and nocturia. Goal: to improve sleep patterns. Expected outcomes: clients reported being able to sleep, clients seem fresh. INTERVENTION 1. Determine the usual sleeping habits and changes. Rationale: Assess and identify appropriate interventions. 2. Provide a comfortable bed. Rationale: Improve sleeping comfort and support of physiological / psychological. 3. Increase comfort bedtime regimen, for example, a warm bath and a massage, a glass of warm milk. Rationale: Increases the effect of relaxation. Note: The milk has sopofik quality, boost the synthesis of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps patients and sleep longer. 4. Reduce noise and light. Rationale: Provide a situation conducive to sleep. 5. Instruct relaxation measures. Rationale: Helps induce sleep.
- 17. URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI) 3. Hyperthermia related to the inflammatory reaction. Goal: body temperature back to normal. Expected outcomes: client reported no fever, no palpable heat, vital signs within normal limits. INTERVENTION 1. Assess any complaints or signs of increased body temperature changes. Rationale: Increased body temperature will shows a variety of symptoms such as red eyes and the body feels warm. 2. Observation of vital signs, especially temperature, as indicated. Rationale: To determine interventions. 3. Warm water compress on the forehead and both axilla. Rationale: To stimulate the hypothalamus to the temperature control center. 4. Collaboration of antipyretic drugs. Rationale: Controlling fever. Reference: Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) – 4 Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions,. Copyright 2012 NCP NANDA. Retrieved: (November 07, 2014) http://ncpnanda.blogspot.com/2013/02/urinary-tract-infection-uti-4-nursing.html
