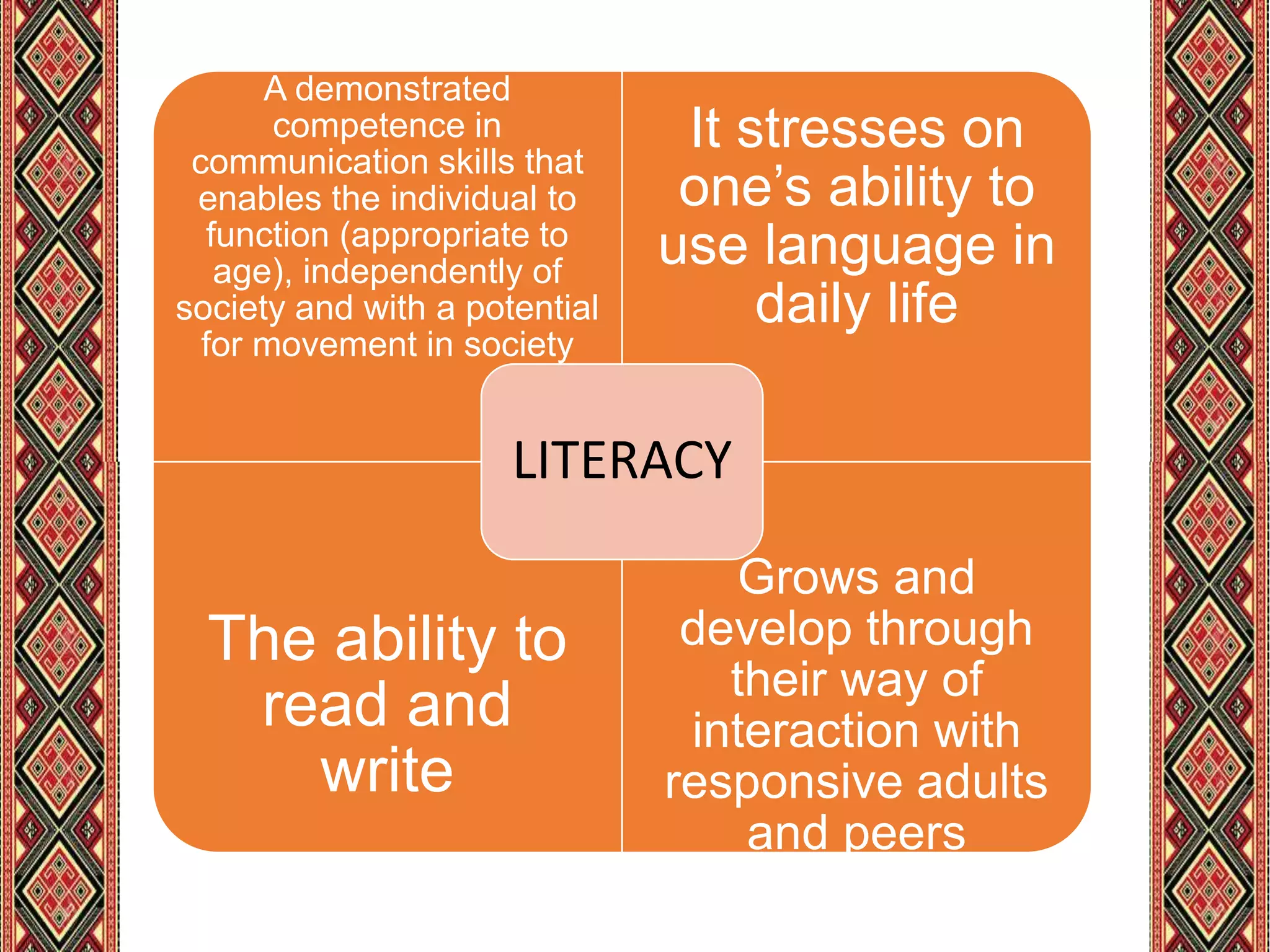
The document discusses strategies for promoting numeracy and literacy. It defines key concepts like literacy and numeracy and identifies essential components of teaching reading like oral language, phonological awareness, phonemic awareness, and comprehension. The presentation also provides examples of appropriate activities for teaching mathematics and demonstrates applying reading and math strategies through a teaching demonstration.