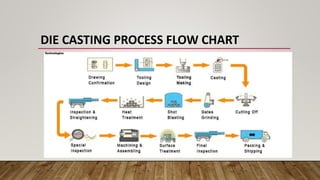
This presentation summarizes the die casting process. It discusses that die casting involves forcing molten metal under high pressure into a mold cavity created by hardened steel dies. It describes the main steps of the die casting process as well as the two primary types - gravity die casting and pressure die casting (cold chamber and hot chamber processes). The presentation outlines the key advantages of die casting as high production rates, dimensional accuracy, and ability to cast intricate parts. It also notes some disadvantages such as limitations on hollow shapes, size of parts, and alloy selection.