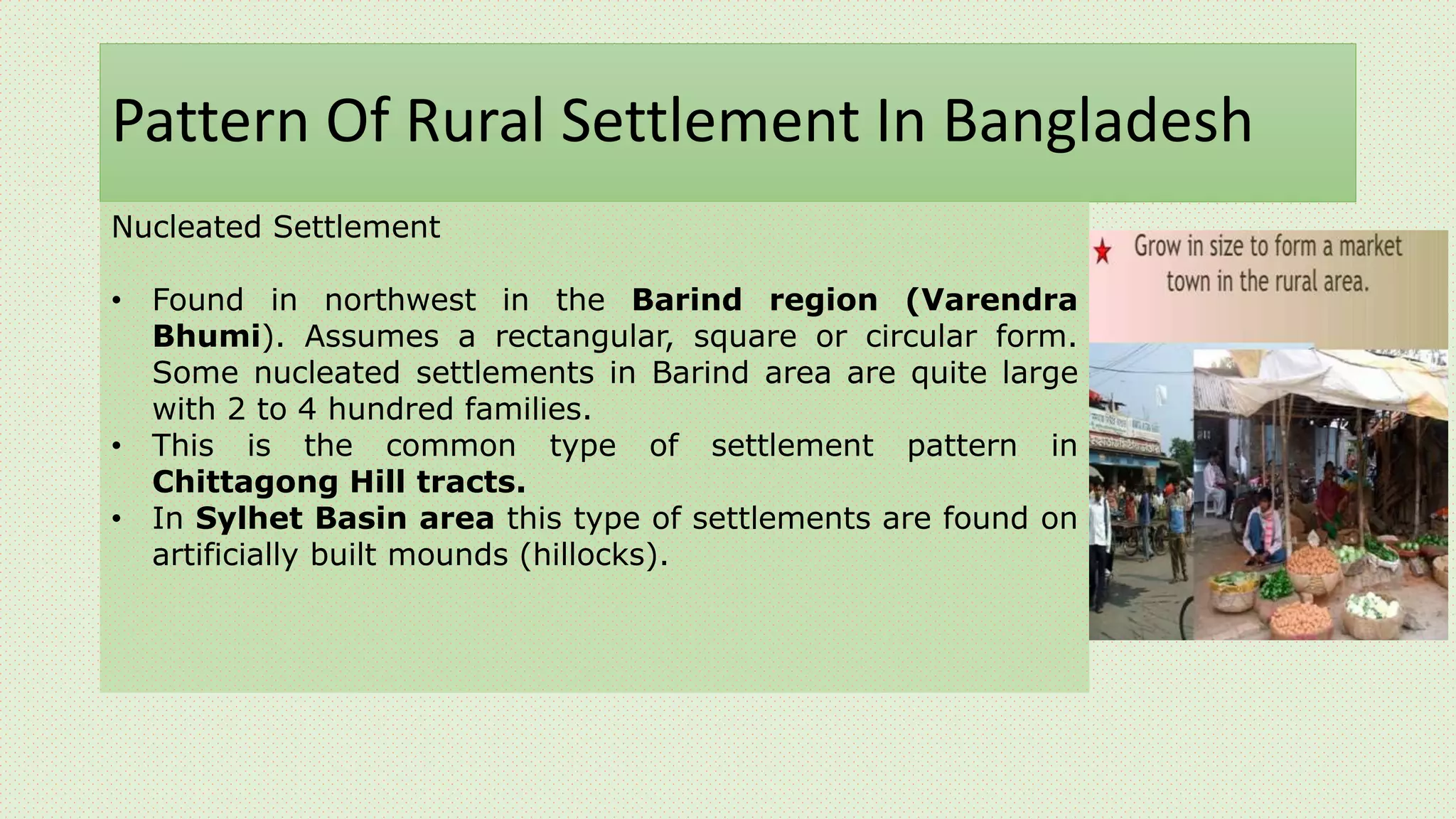
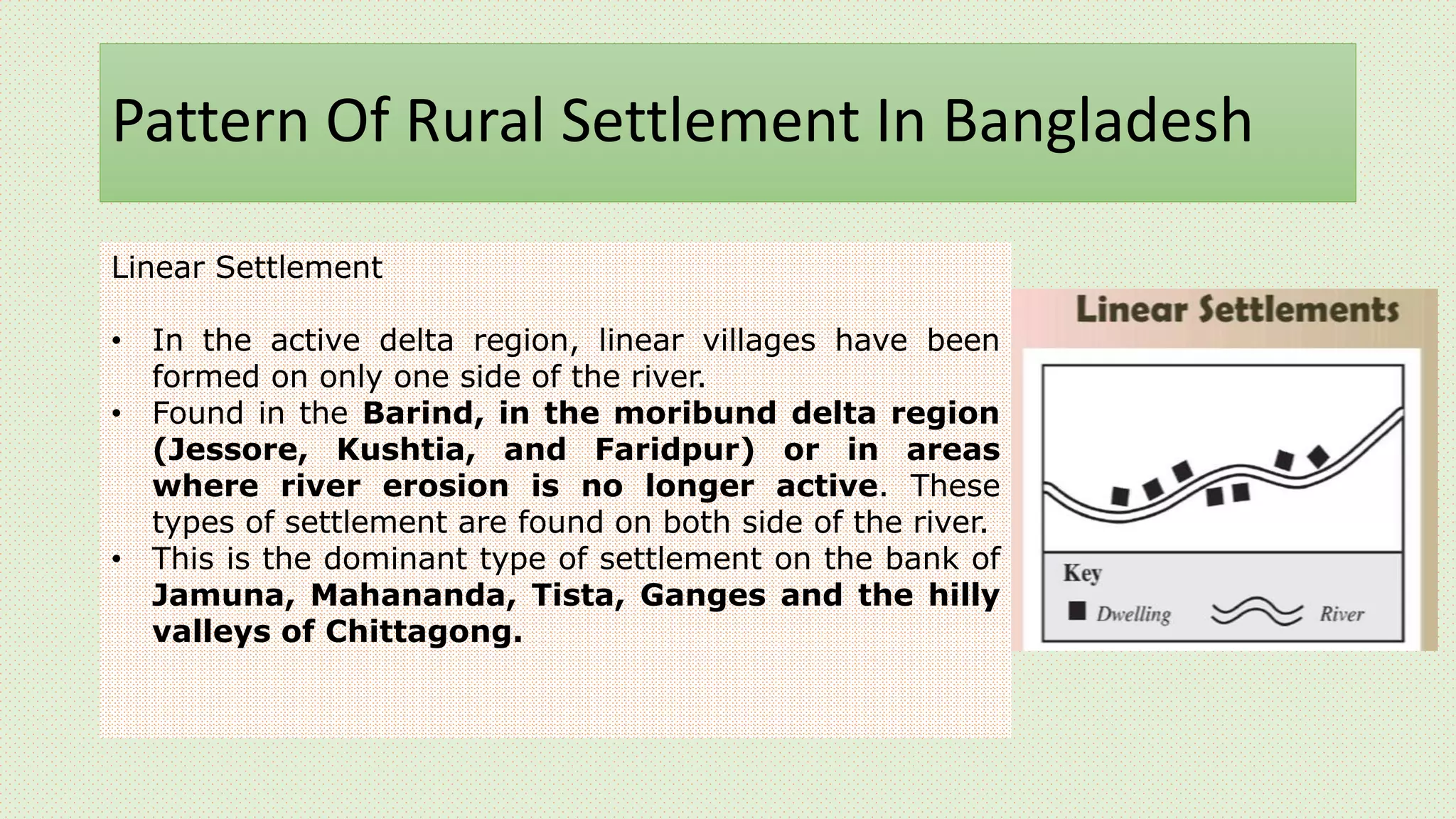
This document discusses rural settlement patterns in Asia, focusing on patterns found in Bangladesh. It describes the main types of rural settlements as nucleated, dispersed, elongated, and cluster villages. For Bangladesh specifically, it outlines the nucleated, linear, and dispersed settlement patterns found in different regions, including the Barind region, active delta region, and haor areas. It also provides examples of different house types found across Asia, including India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka.