Tetrahedron compound angles example
- 1. Making a Regular Tetrahedron Compound Angle / Solid Trigonometry Example – Quinn Morley
- 2. Whether you are making a regular tetrahedron in a CAD program or in real life, the technique is the same. Start with a triangular log. If you were doing this in real life you would want to cut a piece of wood down to this shape. In CAD we start with a sketch of an equilateral triangle and extrude it. Recall that the faces of a regular tetrahedron are equilateral triangles, so each angle on the face is 60°. Note: The length of the log needs to be greater than the length of each edge of the triangular face. From here we will cut this piece into the tetrahedron. The only face that is “final” is the bottom face. Isometric view Rotated for Clarity
- 3. Three cuts are needed to finish the tetrahedron. If you were cutting this on a band saw, you would need to know what angle to tilt the log in order to make the cut. In the CAD program, we will do something similar, by rotating a plane around one of the edges. The plane then acts as our saw blade when we use the split tool. Here are what the 3 cuts would look like. The final result is the bottom right picture. It is hard to visualize this. Note that the only point where all 3 of the cuts intersect is the tip of the tetrahedron.
- 4. Here is our regular tetrahedron with the excess from the cuts removed. Now, what angle do we need to make those cuts at, and how do we do the math to find out our rotation angle for the cuts? It will be the same angle for all three cuts, but we will rotate around a different leg of the base triangle for each cut. Hint: it isn’t 60°. The best way to figure out is to imagine drawing a pencil line on one of the faces using a carpenter’s square, and then cut into that line (going to the center of the tetrahedron) with the band saw. You can see below that this creates a right angle directly under the point of the tetrahedron. This is called an altitude. Next we are going to “cut off” the front right corner of the tetrahedron and analyze this part of it to solve for the angle. This is done with another band saw cut from the front right corner to the top corner and is shown below. Imagining making a cut with a knife or saw into geometric shapes is really helpful when trying to set up this type of problem.
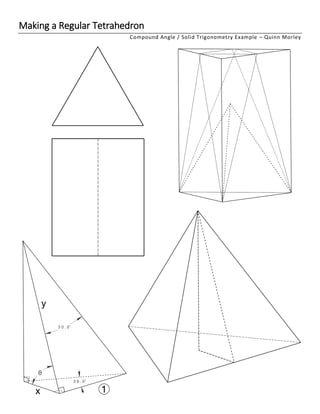
- 5. This is the section of the tetrahedron we will use to setup our math problem. The right angles are identified. The front two right angles were made by the use of the carpenter square, and the back two right angles were locked in by the depth of the cut stopping exactly at the altitude (directly under the tip of the tetrahedron). The next step is to take what we know about the tetrahedron and add that information to our drawing of this pyramid. Since we added the right angles already, there are only two unknowns left on this whole pyramid. Recall that each angle on the face of a tetrahedron is 60°, so the front face of our pyramid has that in the bottom right corner. The top of the front face has been cut in half, so it is at 30°. The bottom face has also been cut in half, so it has a 60° angle on the left rear corner, and a 30° on the right side. See below right. We don’t need to put all of the angles on there, so for simplicity let’s just add the 30° angles to the pyramid. We can also add the location of our unknown, theta (symbol θ). The method we will use to solve for theta is called the “unity method.” This allows us to use what we know about the front and bottom faces, and apply that to the face with our unknown angle in a logical way. To use the unity method, first assign a length of 1 unit to the edge connecting the two faces that are known triangles. It could be 1 inch or 1mm; it doesn’t matter. This is called the unity. Since the front and bottom are the known triangles, unity is identified on the next page with an encircled 1. See the image on the next page. This is also a good time to label the sides of our unknown triangle (the triangle that contains θ). The easiest way to do this is to label the sides that are shared with the known triangles with the variables x and y. It doesn’t matter which one you label x and which you label y. Once you have identified the unity, and chosen x and y, you are ready to start solving for θ.
- 6. The Unity Method • The edge common to the known faces is given a length of 1 o The unit of 1 itself doesn’t matter o If it helps, imagine it as 1 inch, 1 mm, etc. • Figure out which two legs of the unknown triangle you will use to solve for θ. Label them x and y o It doesn’t matter which one is x and which is y
- 7. Equation Set-up and Solving Now that we have everything identified we want to create an equation for our unknown angle, θ. We can see that y is the hypotenuse of the unknown triangle, and x is adjacent to θ. That means we can say x/y is the cosine of θ. cos(𝜃) = 𝑥 𝑦 If we solve for θ by taking the inverse cosine of both sides, we get: 𝜃 = cos−1 ( 𝑥 𝑦 ) Now we need to come up with a substitution for x and y that relates them back to the known faces of this pyramid via the unity. If you look at just the bottom face of the pyramid to the right, you can see that x is the leg opposite the 30° angle. This is where setting the unity to 1 comes in handy. Divide x by unity. We are actually dividing the opposite leg (x) by the adjacent leg (1). 𝑥 1 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 If we simplify the denominator and recognize that opposite/adjacent is the tangent function, we have our substation for x. When looking at the 30° angle on the bottom face, the length of x is the tangent of 30°. 𝑥 = 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 = tan(30°) Similarly, look at the front face of the pyramid. With the unity as the leg opposite the 30° angle and y as the adjacent leg, you could say that y/1 is the adjacent over the opposite. We are dividing y by the unity. 𝑦 1 = 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 Simplifying, and remember that adjacent/opposite is cotangent: 𝑦 = 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑜𝑝𝑝𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑒 = cot(30°) Now plug both x and y into our original formula for 𝜃: cos−1(𝜃) = 𝑥 𝑦 𝜃 = cos−1 ( tan(30°) cot(30°) ) 𝜃 = cos−1 ( 0.57735027 1.73205081 ) = 70.52877936551° 𝜽 = 𝟕𝟎. 𝟓𝟑°