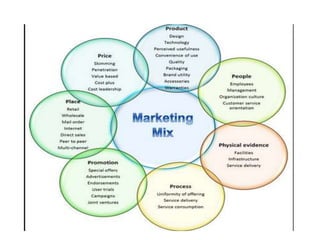
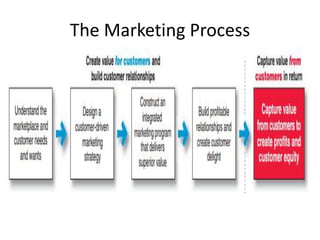
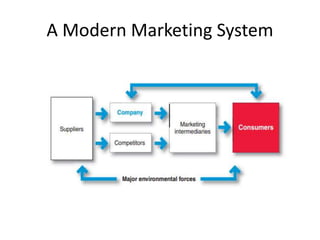
The document defines marketing according to definitions from the American Marketing Association from 1948 to 2004. It discusses that marketing involves identifying and meeting human needs profitably by creating, delivering, and communicating value. The marketing management process involves choosing target markets and growing customers through superior customer value. The document then discusses what can be marketed, who engages in marketing, demand states, the structure of exchange economies, marketing systems, customer markets, core concepts like needs and value, marketing environments, new marketing realities and capabilities, and the evolution of marketing concepts.