This document provides a musical analysis of the Oasis song "Don't Look Back in Anger" in 3 paragraphs or less:
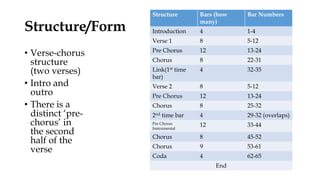
The song uses a verse-chorus structure with guitar, bass, drums, piano and backing strings. It is in the key of C major and uses a diatonic harmony with some chromatic chords. The melody is pentatonic in the verse and uses a hexachord in the chorus, with a falling contour and syncopation.
The texture is homophonic with simple chords in the accompaniment and decorated bass line. The rhythm is in common 4/4 time. The word setting is mostly syllabic with ornamentation on final words.