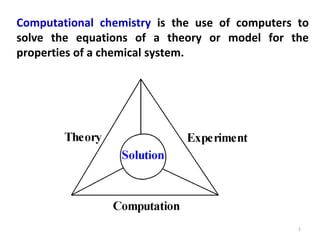
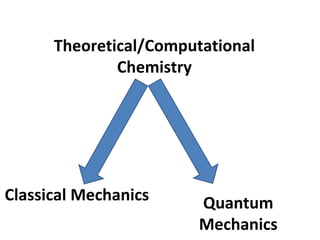
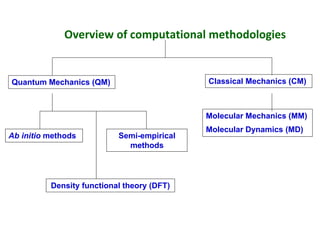
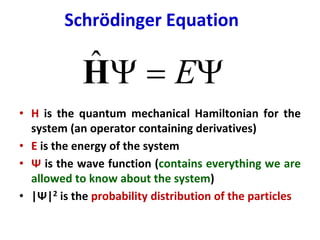
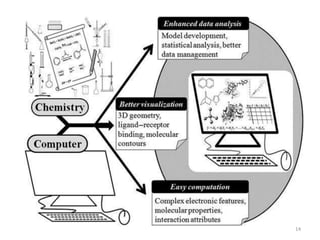
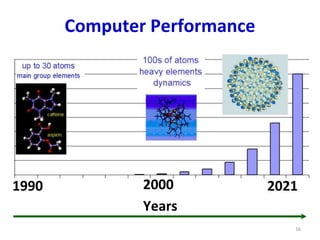
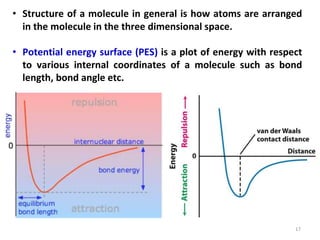
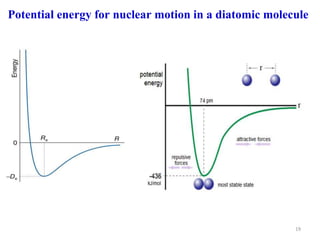
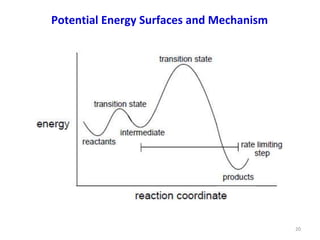
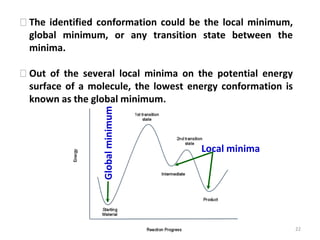
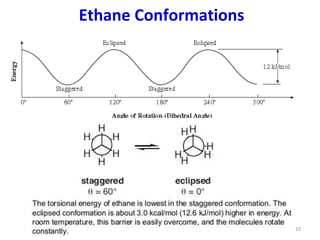
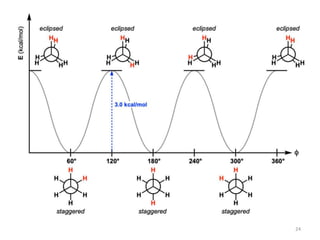
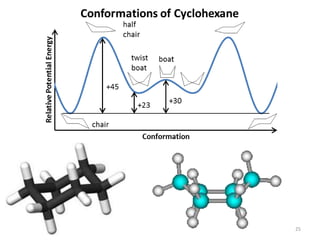
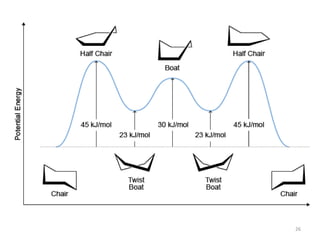
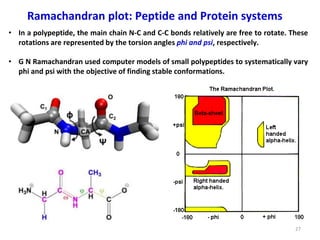
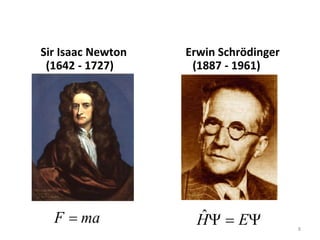Computational chemistry uses computers to simulate chemical systems and solve equations that model their properties. It is considered a third pillar of scientific investigation, along with theory and experiment. There are several computational methodologies including quantum mechanics, molecular mechanics, and molecular dynamics. Computational chemistry software can be used to optimize molecular geometries, map potential energy surfaces, perform conformational analyses, and calculate many other molecular properties and reaction kinetics. These methods have improved significantly with increasing computer power over the past few decades.