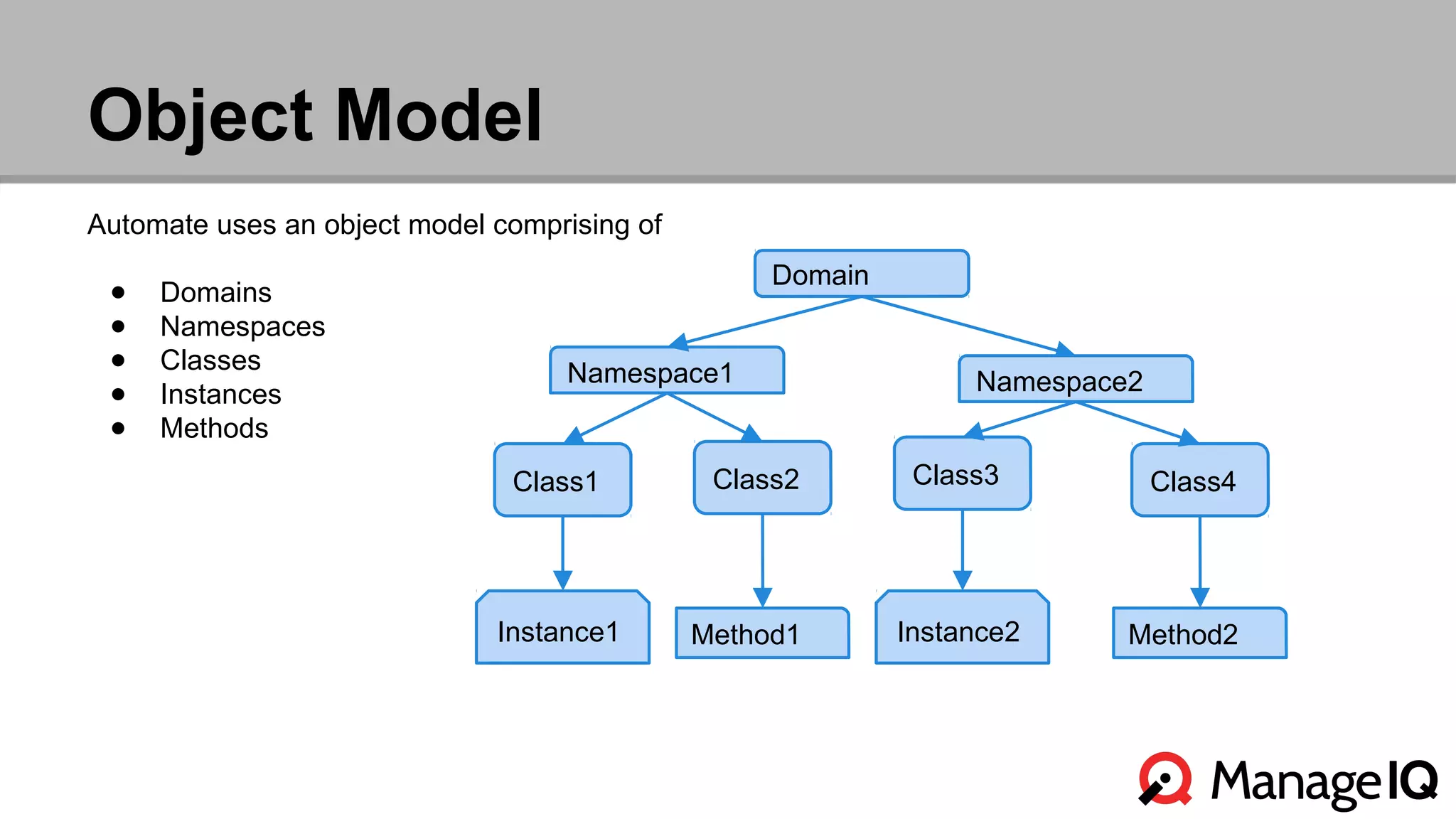
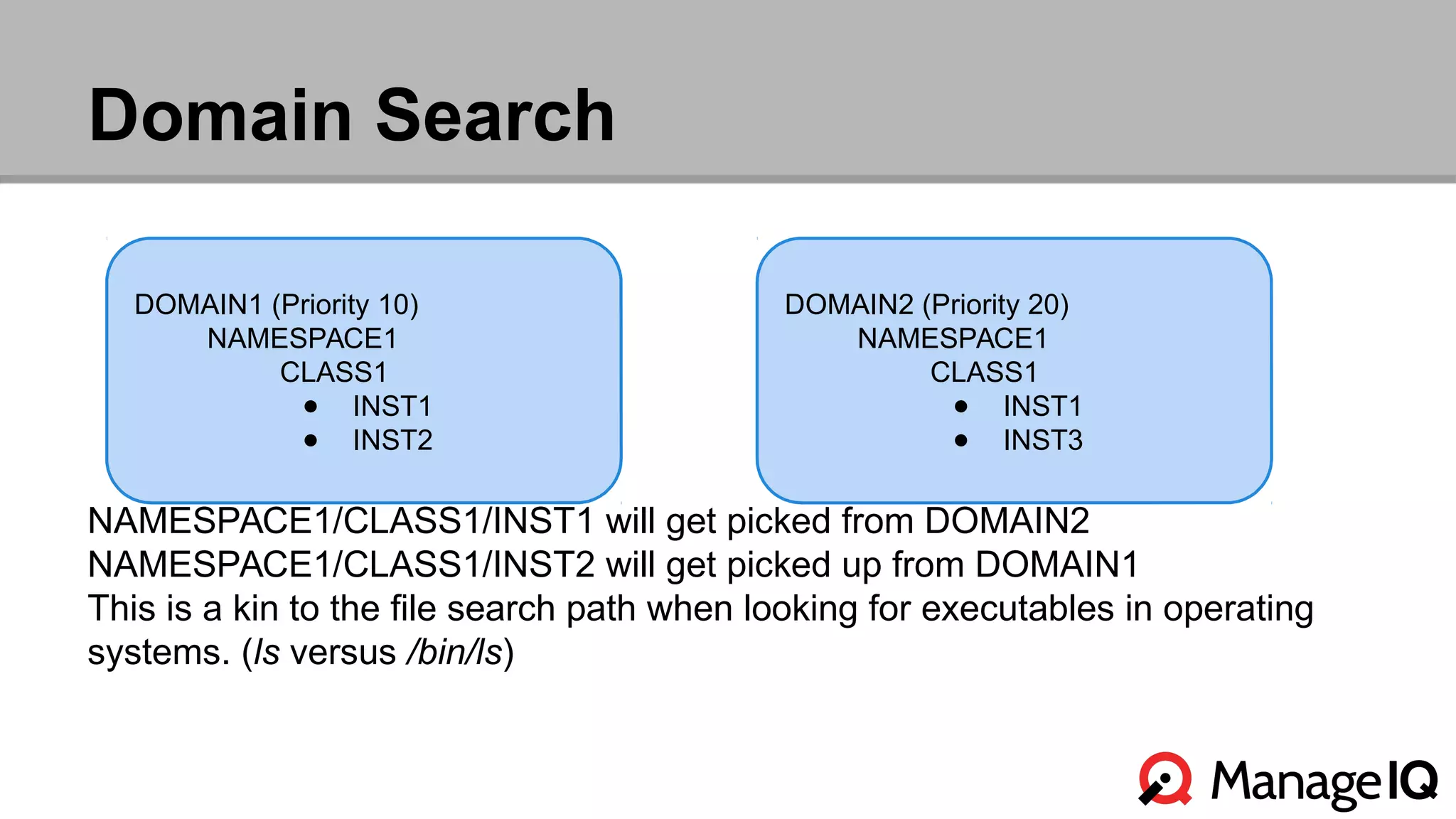
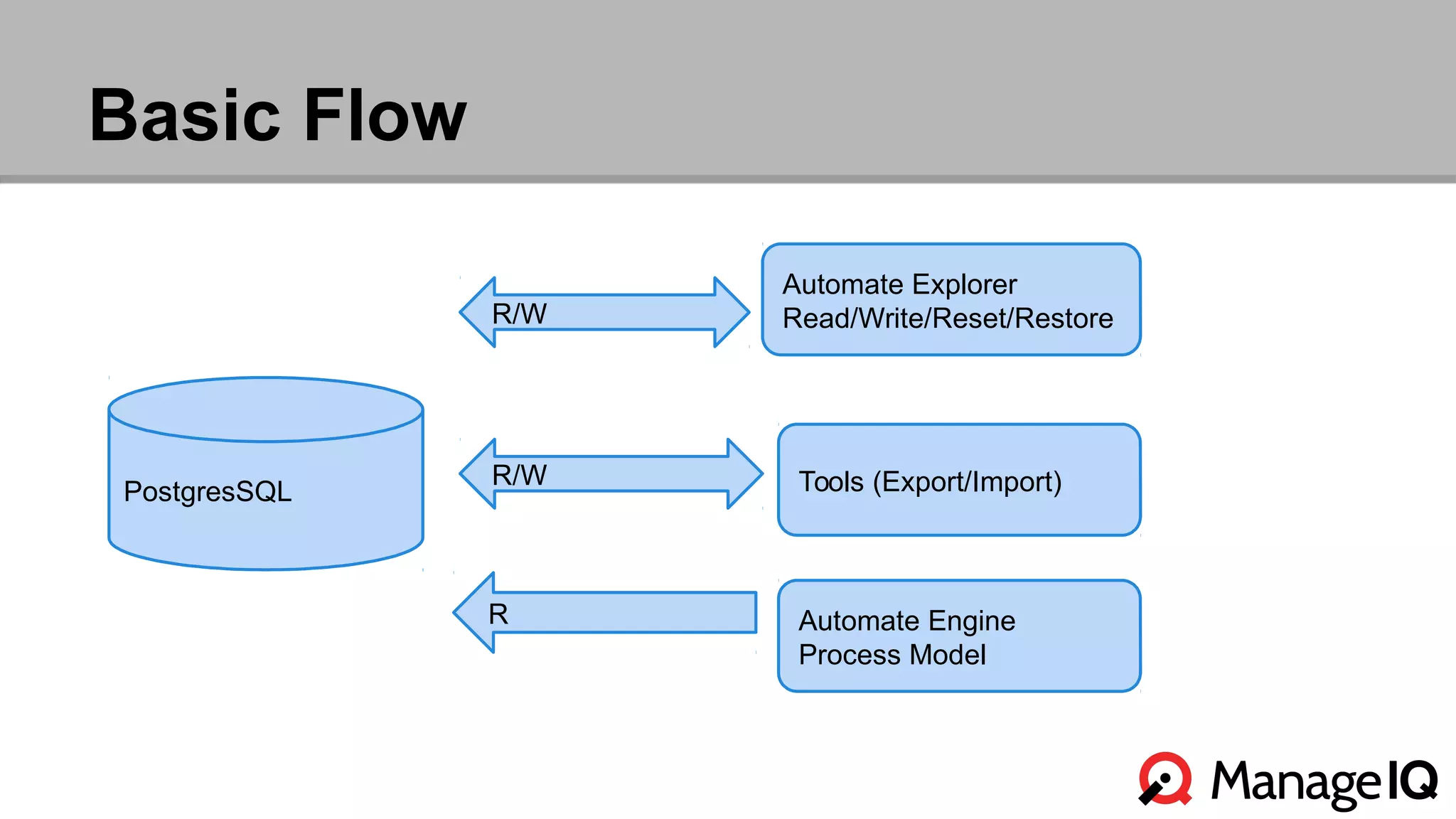
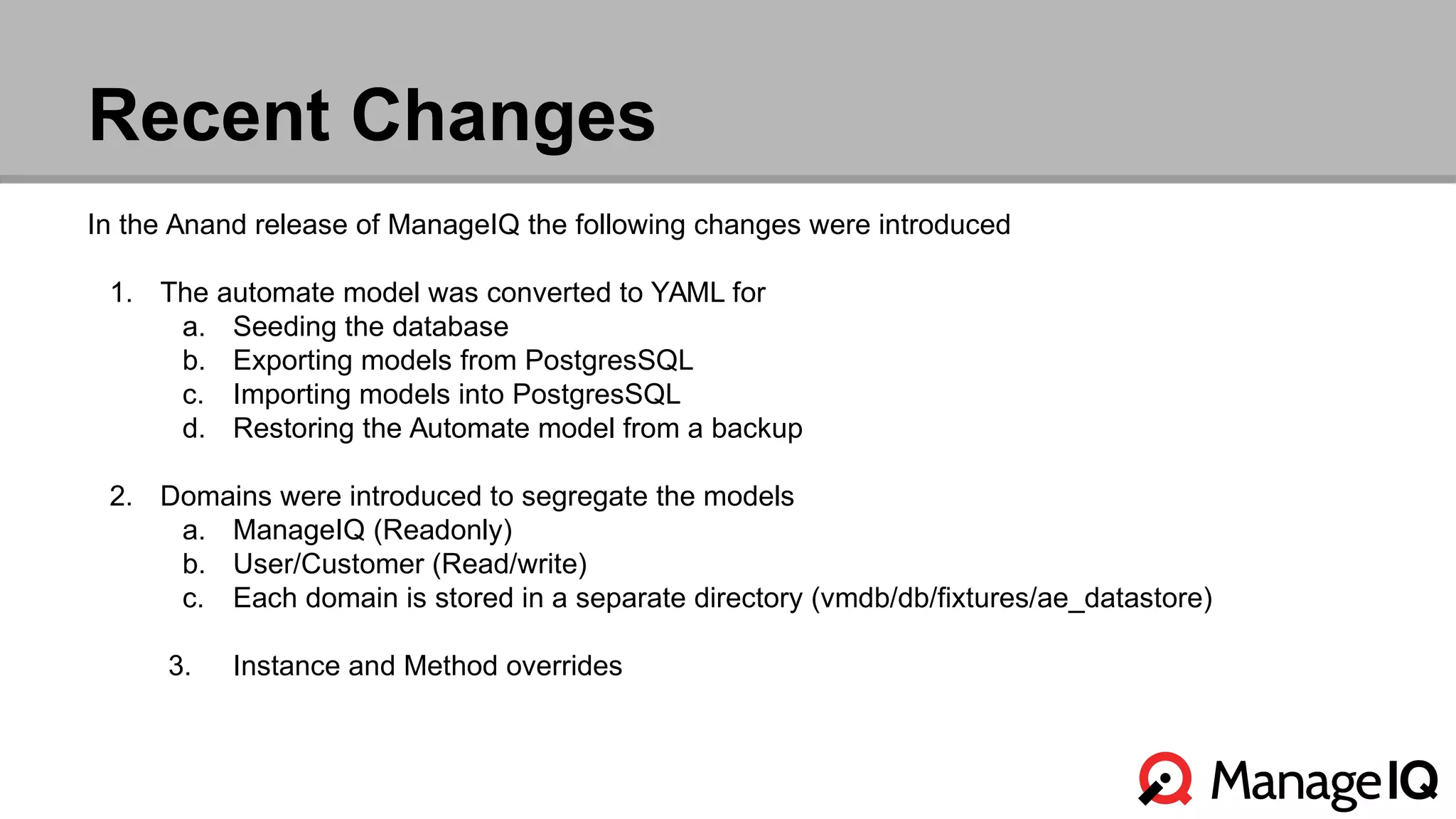
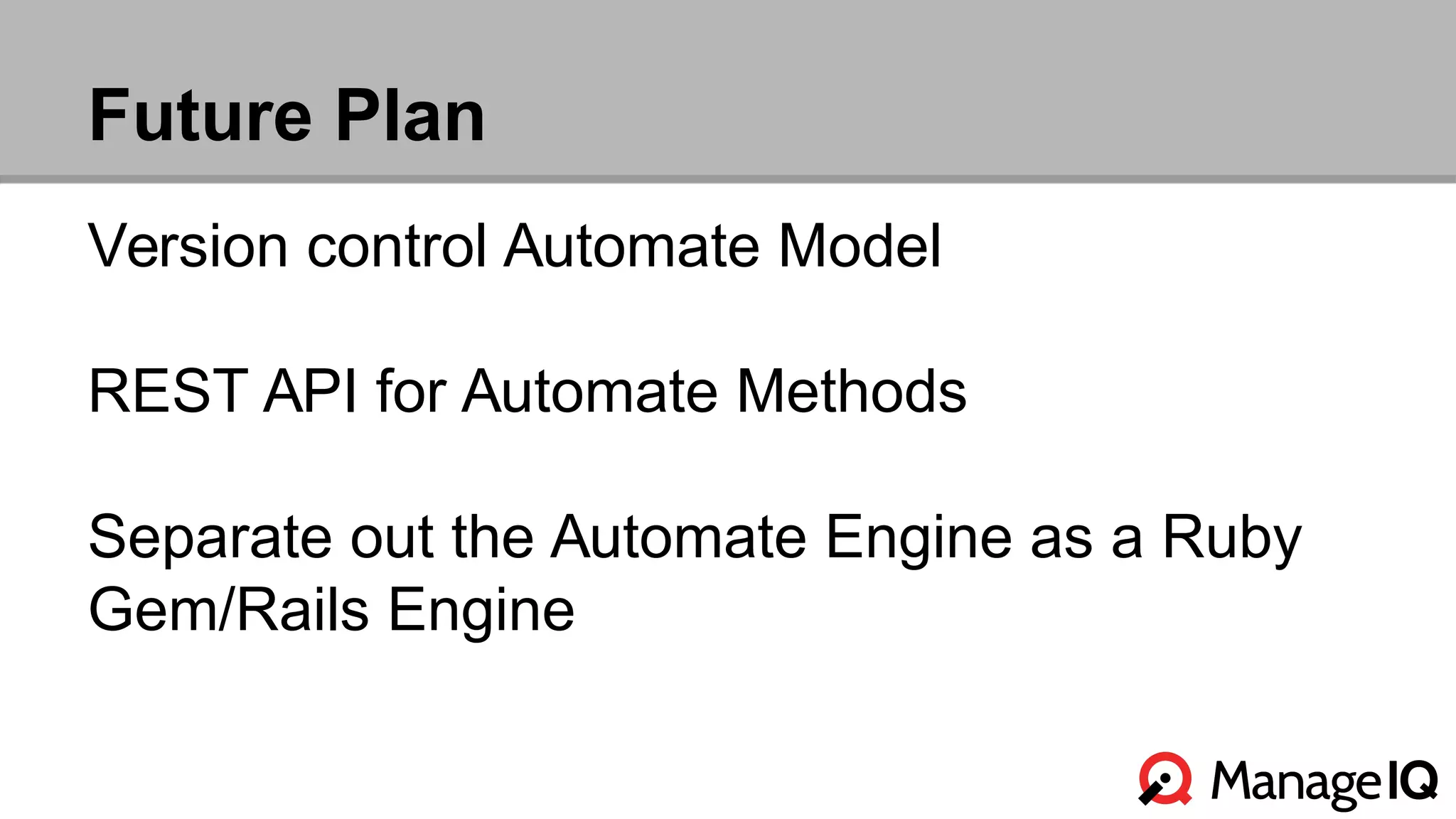
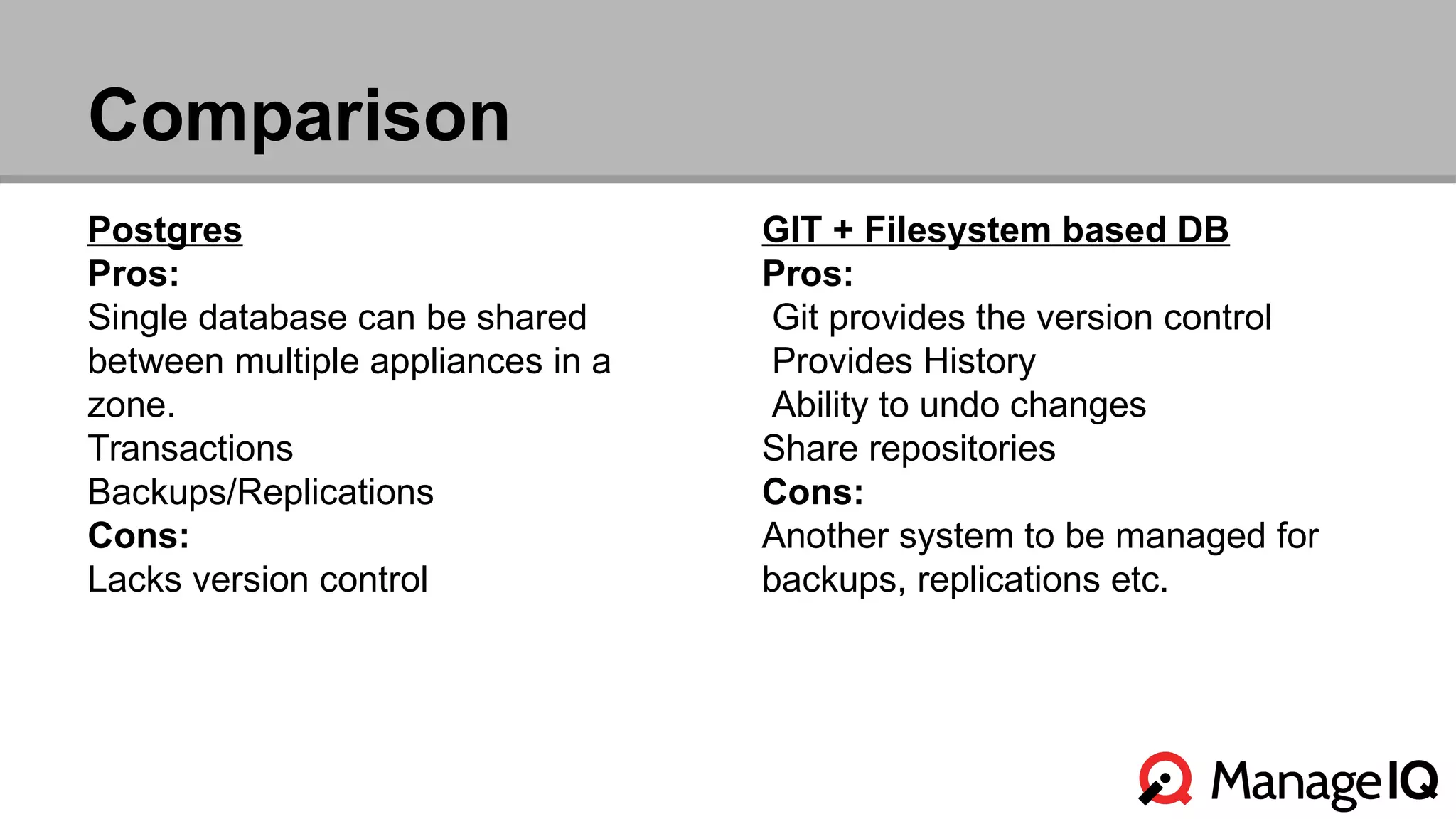
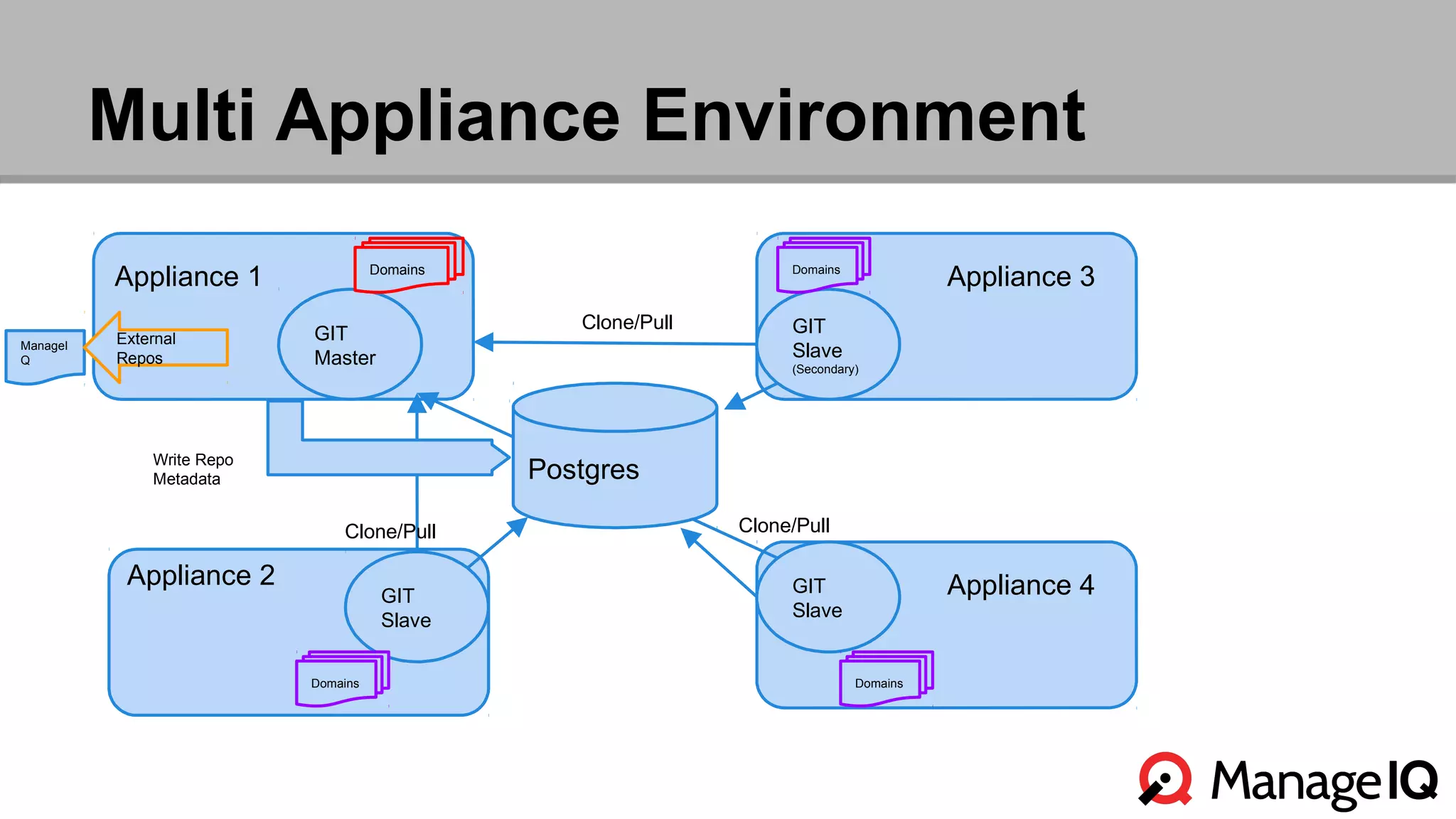
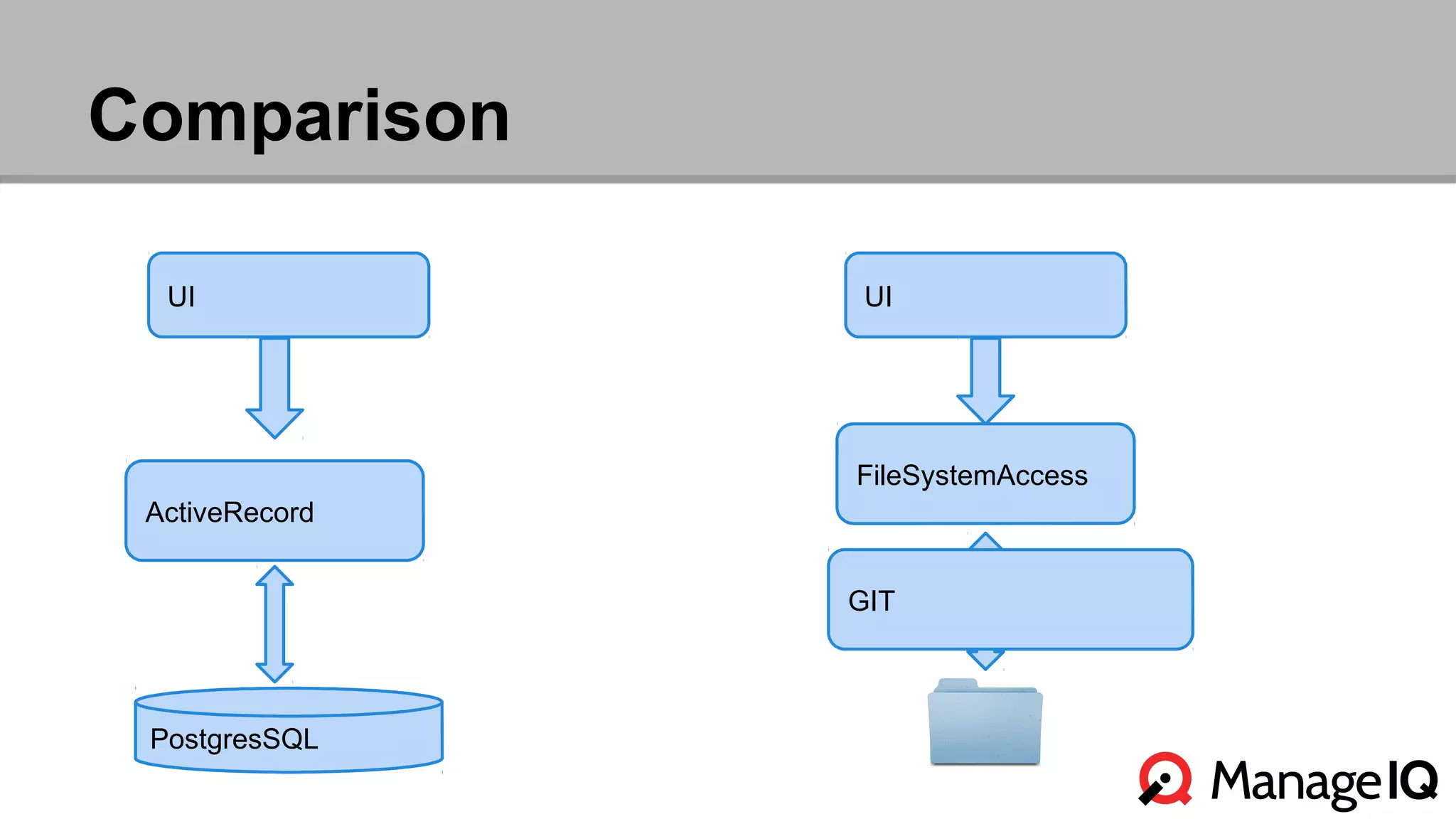
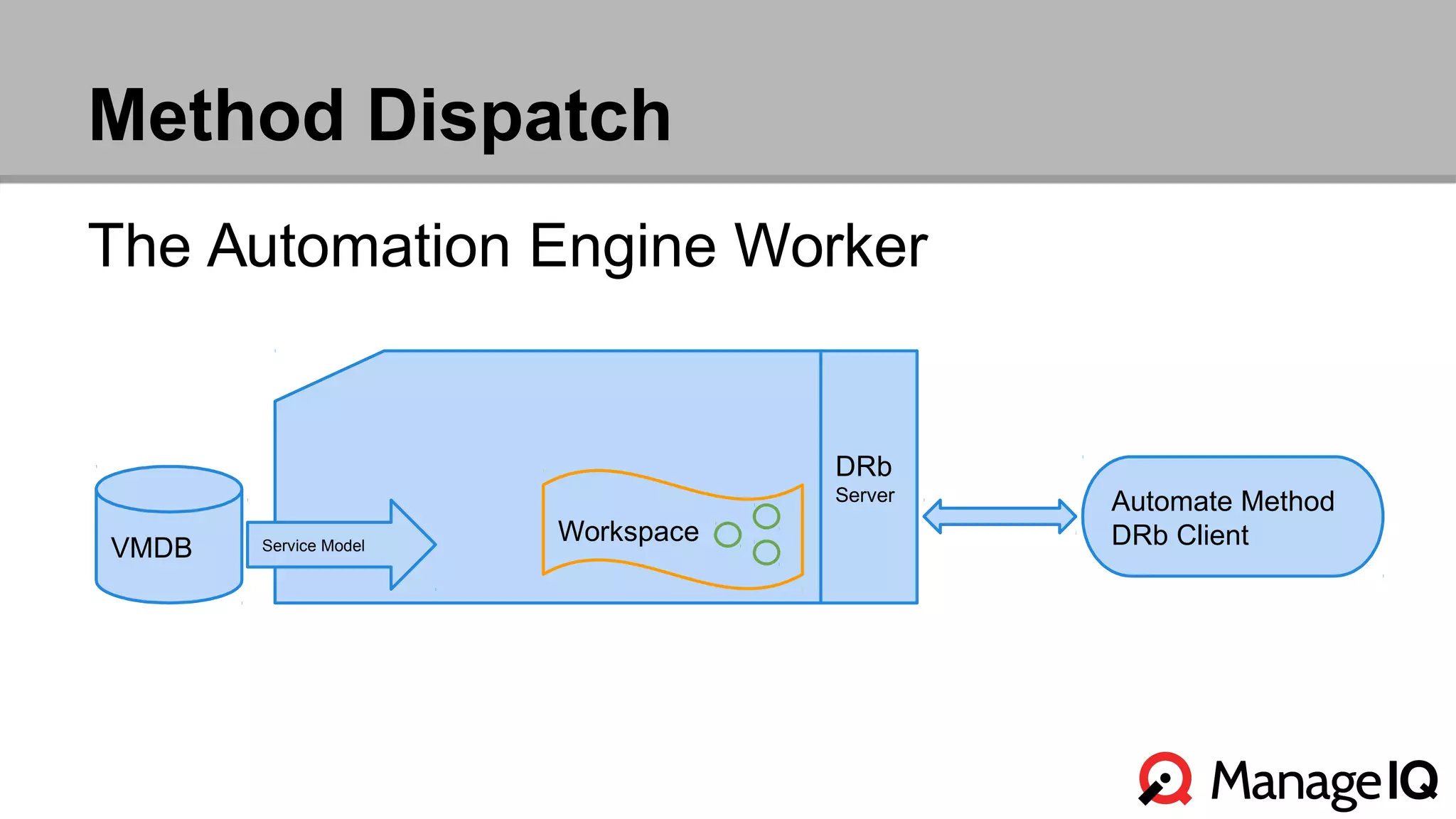
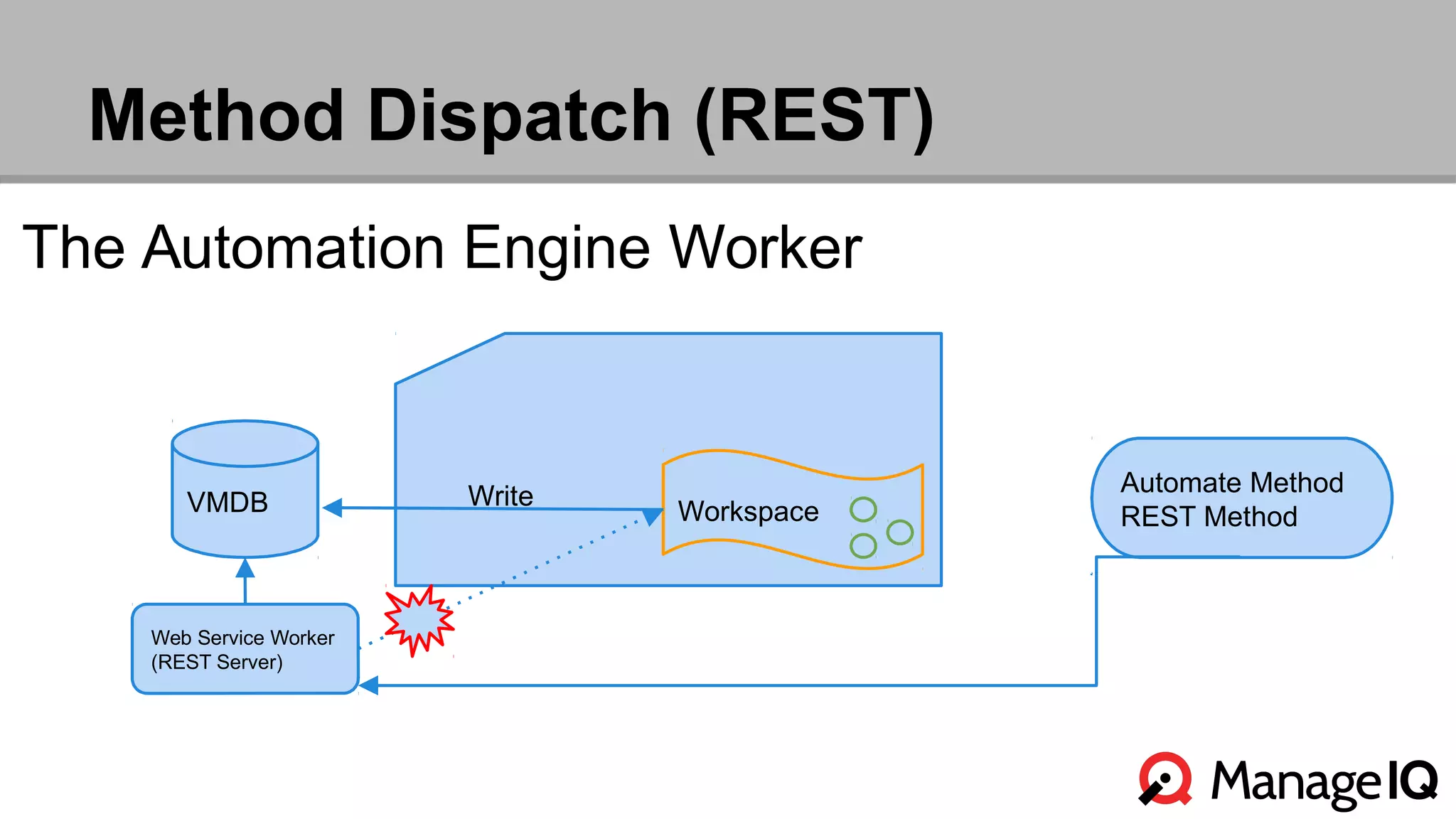
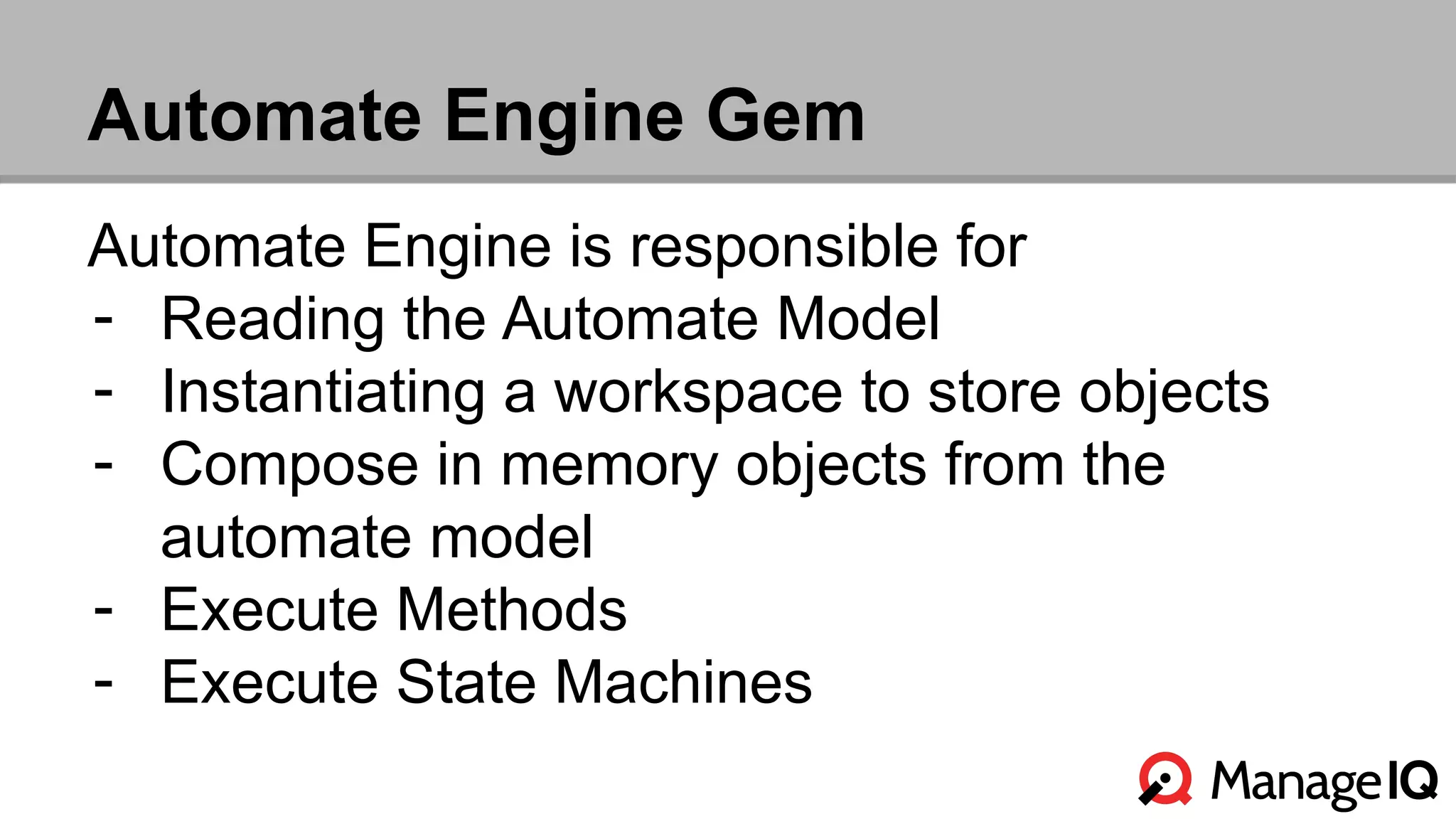
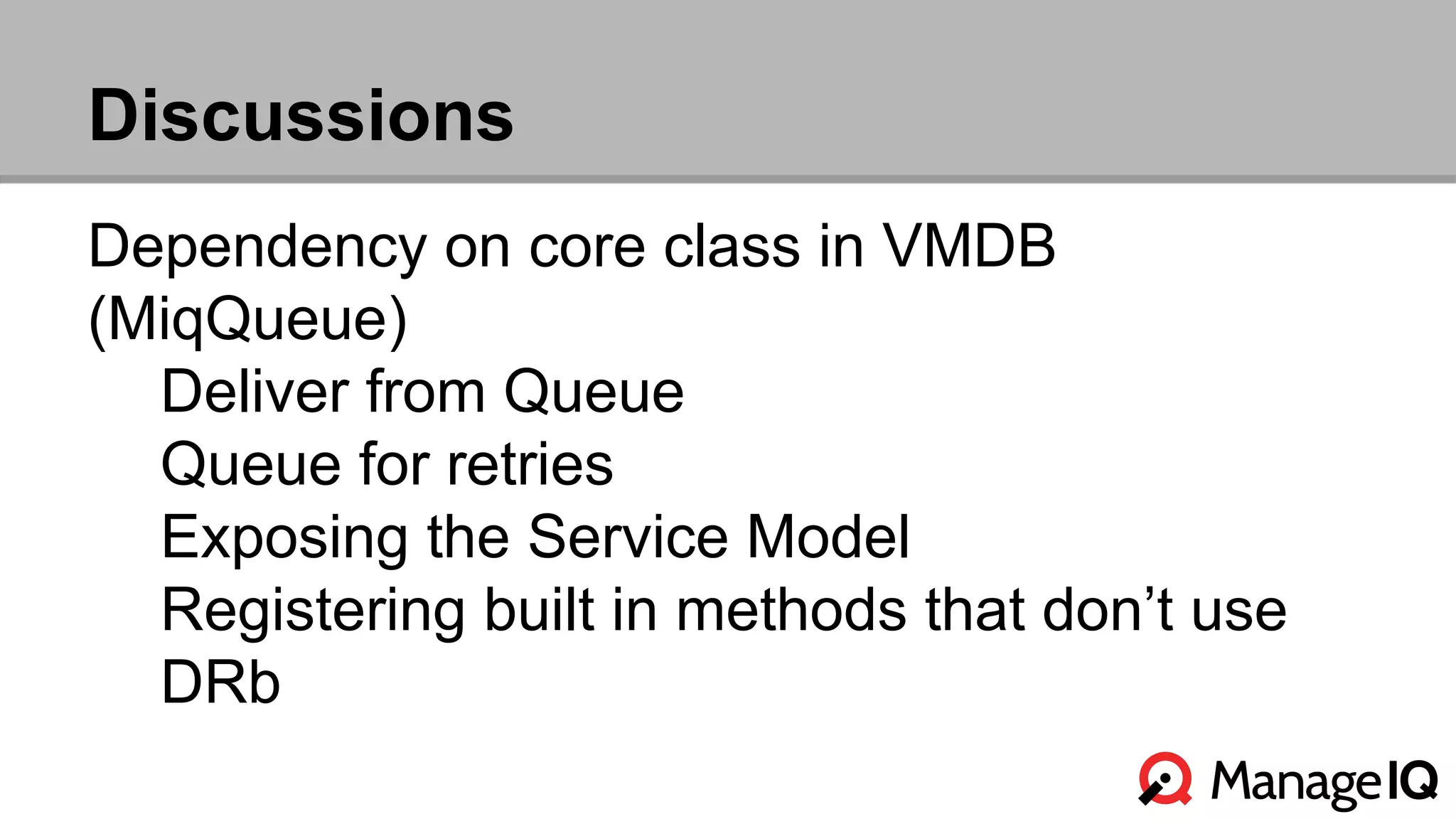
The document outlines the features and functionality of the Automate toolset in ManageIQ, detailing its object model, structure, recent changes including YAML conversion, and future plans such as version control and REST API integration. It discusses the advantages and challenges of using PostgreSQL and Git for managing models, as well as considerations for implementing an automated infrastructure. Additionally, it touches on the Automate engine's purpose, the execution of methods, and modularity benefits of a gem-based architecture.