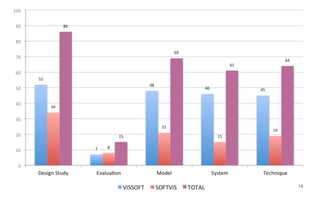
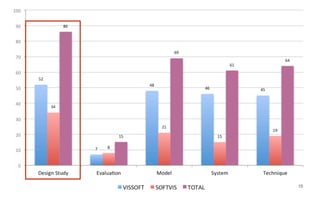
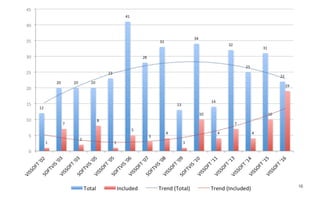
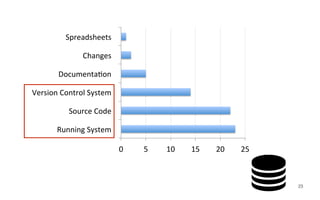
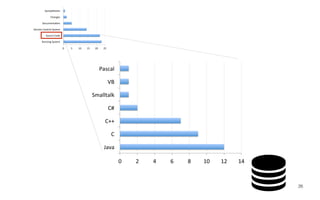
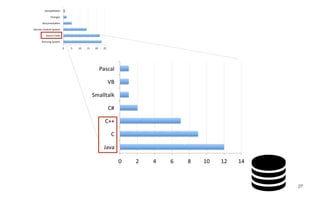
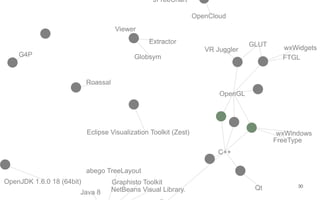
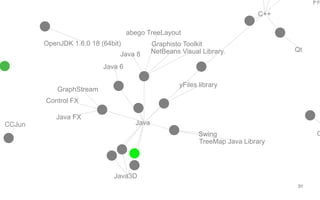
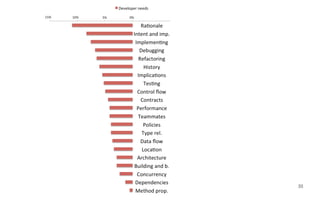
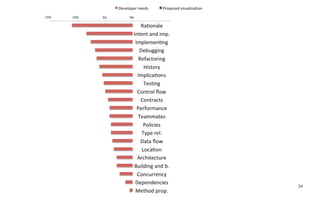
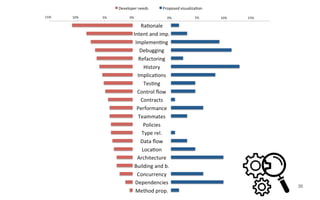
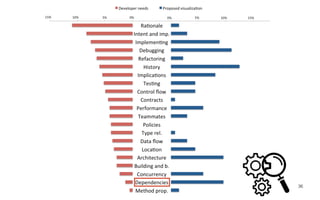
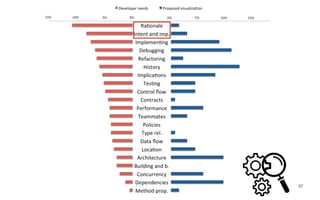
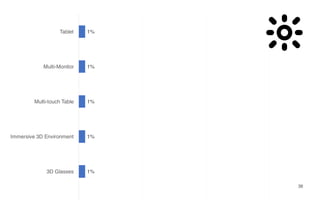
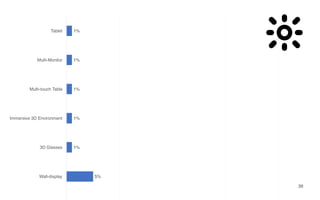
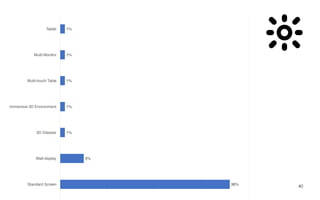
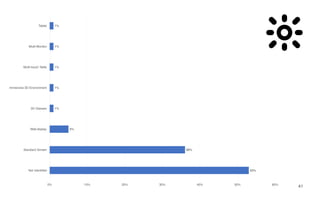
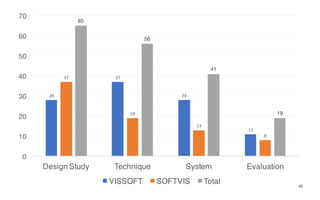
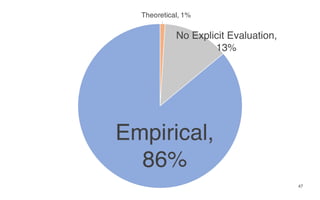
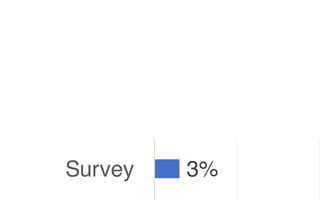
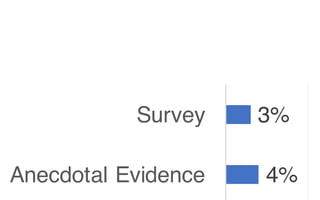
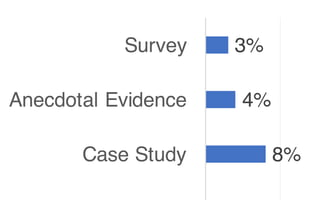
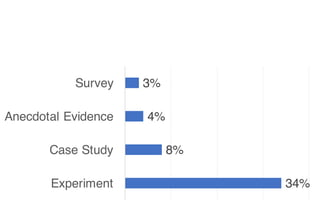
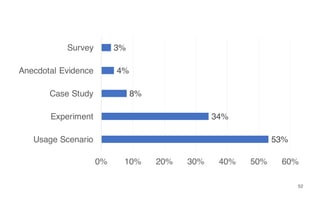
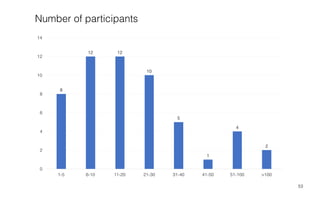
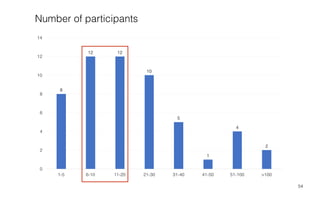
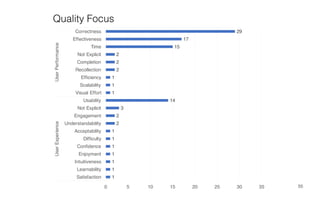
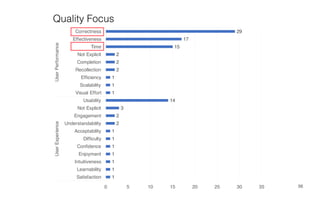
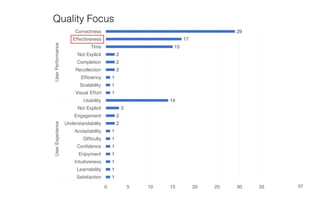
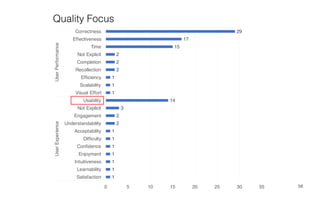
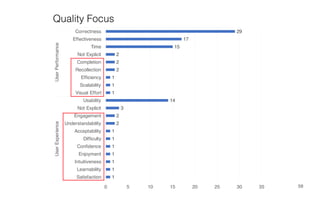
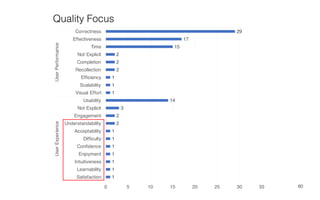
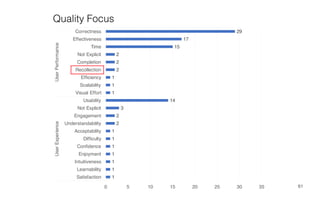
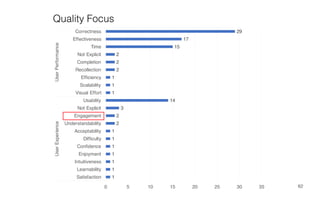
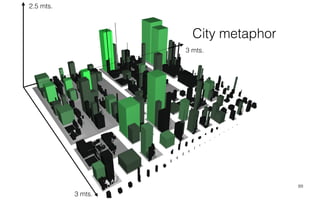
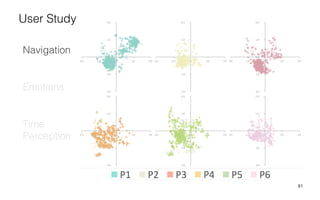
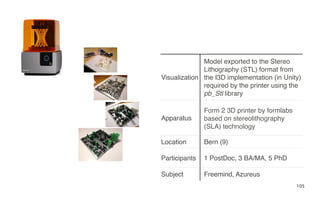
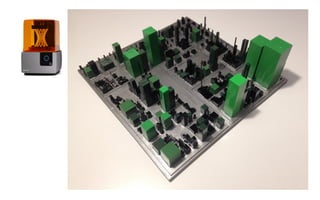
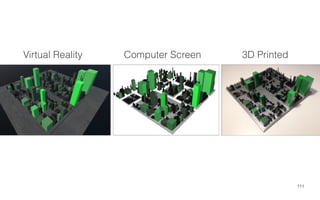
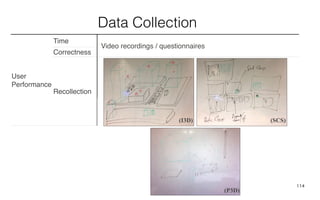
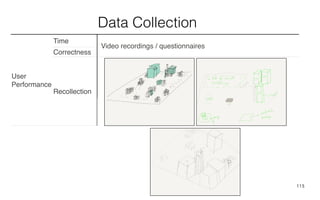
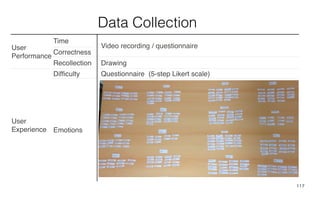
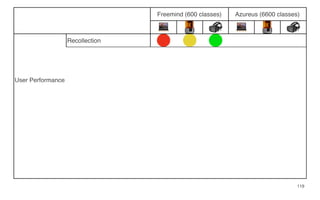
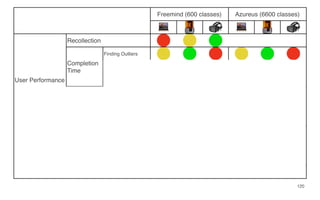
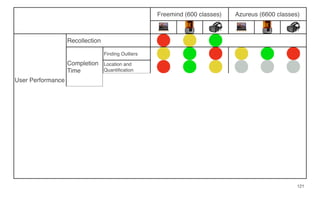
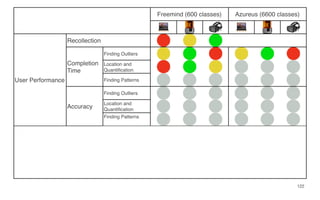
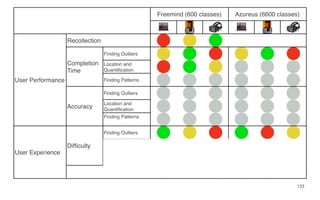
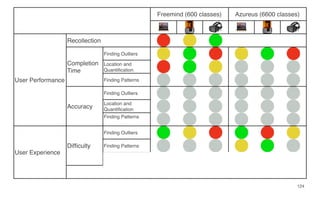
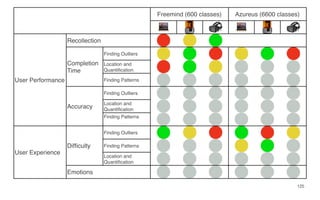
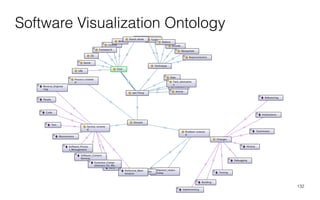
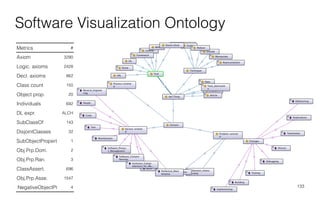
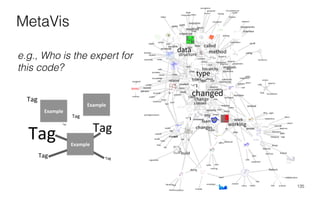
Leonel Merino is defending his PhD thesis on the medium of visualization for software comprehension. The document reviews literature on software visualization and different visualization mediums like standard screens, wall displays, virtual reality, and augmented reality. It presents results from a survey of software visualization tools showing that the majority use standard screens and the medium has not been widely considered as a factor in effectiveness. The thesis argues that the medium is an important factor and different mediums may improve effectiveness, outlining experiments comparing 3D visualizations on standard screens versus augmented reality.