Embed presentation
Downloaded 42 times

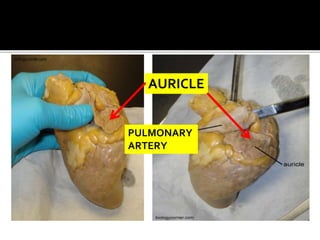
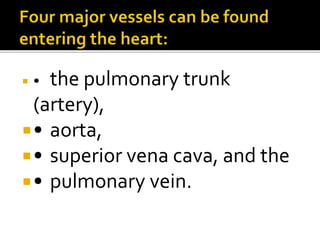
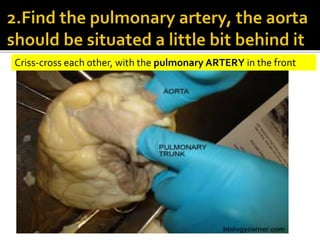
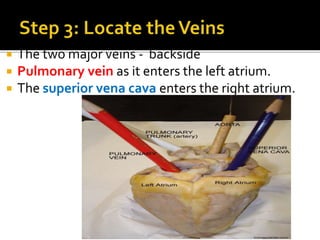
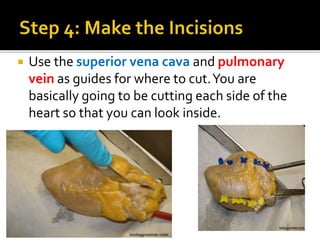

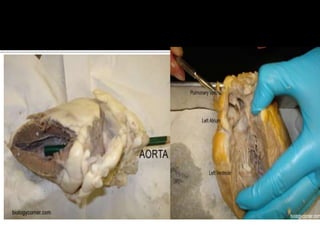

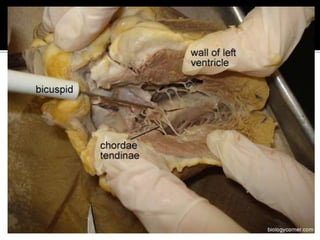
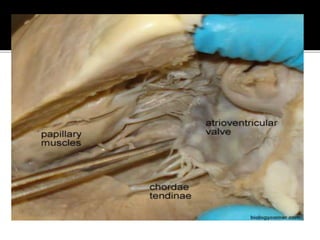

This document provides instructions for dissecting a sheep heart specimen to view its internal structures. It describes making cuts along the superior vena cava and pulmonary vein to open the heart and examine the four chambers and major blood vessels, including the left and right ventricles, aorta, and pulmonary artery. Key anatomical features discussed are the heart valves, chordae tendinae that hold the valves in place, and the thicker walls of the left ventricle compared to the right ventricle.












