summative-in-science-reviewer.pdf
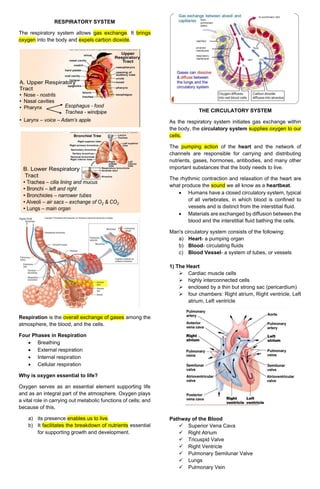
- 1. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The respiratory system allows gas exchange. It brings oxygen into the body and expels carbon dioxide. Respiration is the overall exchange of gases among the atmosphere, the blood, and the cells. Four Phases in Respiration • Breathing • External respiration • Internal respiration • Cellular respiration Why is oxygen essential to life? Oxygen serves as an essential element supporting life and as an integral part of the atmosphere. Oxygen plays a vital role in carrying out metabolic functions of cells; and because of this, a) its presence enables us to live. b) It facilitates the breakdown of nutrients essential for supporting growth and development. THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM As the respiratory system initiates gas exchange within the body, the circulatory system supplies oxygen to our cells. The pumping action of the heart and the network of channels are responsible for carrying and distributing nutrients, gases, hormones, antibodies, and many other important substances that the body needs to live. The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart are what produce the sound we all know as a heartbeat. • Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid. • Materials are exchanged by diffusion between the blood and the interstitial fluid bathing the cells. Man's circulatory system consists of the following: a) Heart- a pumping organ b) Blood- circulating fluids c) Blood Vessel- a system of tubes, or vessels 1) The Heart ➢ Cardiac muscle cells ➢ highly interconnected cells ➢ enclosed by a thin but strong sac (pericardium) ➢ four chambers: Right atrium, Right ventricle, Left atrium, Left ventricle Pathway of the Blood ✓ Superior Vena Cava ✓ Right Atrium ✓ Tricuspid Valve ✓ Right Ventricle ✓ Pulmonary Semilunar Valve ✓ Lungs ✓ Pulmonary Vein
- 2. ✓ Bicuspid Valve ✓ Left Ventricle ✓ Aortic Semilunar Valve ✓ Aorta ✓ To the body organs and cells 2) Blood Vessels ➢ The blood in the human body travels or is transported through a system of tubes called blood vessels. ➢ Transport blood from the heart ➢ Three types of blood vessels - arteries, veins, and capillaries. a) Arteries ➢ carries blood away from the heart and generally transports oxygen-rich (oxygenated/carbon dioxide-poor) blood ➢ Arteries branch into smaller branches called arterioles before further branching out to the tiniest blood vessels called capillaries b) Capillaries ➢ connect arteries and veins. ➢ This is where the gas exchange between the blood and the tissues takes place. ➢ Capillaries then merge into venules and then into larger channels called veins. c) Veins ➢ carry blood to the heart and generally transport oxygen-poor (deoxygenated), carbon dioxide-rich blood Structure of Blood Vessel 3) Blood ➢ The amount of blood in the human body is generally equivalent to 7 percent of body weight. ➢ Blood carries out all the important functions, like transporting oxygen and nutrients. ➢ The blood plays three important roles, transportation, protection, and regulation. Functions Of The Blood 1. Transport of dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones, and metabolic wastes. 2. Protection against toxins, pathogens, and blood loss injuries. 3. Stabilization of body temperature. 4. Regulation of the pH through the blood buffering system and electrolyte composition of interstitial fluids throughout the body. The Blood and Its Composition The liquid part is the plasma with 3 types of cells suspended in it: red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Blood is composed mainly of: a) Plasma - the yellowish liquid that is composed of 90% water that carries nutrients, hormones, and other important substances. b) Different blood cells: o red blood cells o white blood cells o platelets 1) The Red Blood Cells (RBC) ➢ The red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, carry oxygen to the cells. ➢ After transporting oxygen to the cells, red blood cells collect the waste gas (carbon dioxide, the by-product of cellular respiration) and transport it back to the lungs, where carbon dioxide is expelled from the body as we exhale. ➢ Red blood cells are the most abundant of the blood cells (around 5,000,000 red blood cells in a drop of blood) and their lifespan is 120 days. ➢ The red blood cells are red in color because they contain hemoglobin. ➢ Hemoglobin contains iron (Fe) making it an excellent transporter of oxygen and carbon dioxide. ➢ The long bones of your body, the spleen, and the liver continually produce new red blood cells to replace old worn-out cells. 2) The White Blood Cells (WBC) ➢ The white blood cells, also known as leukocytes, battle infection, and attack and destroy germs or foreign proteins that enter the body.
- 3. ➢ There are about 7,000 WBCs per milliliter o and this number can be used as an indicator of a disease. ➢ During infection, the body produces more white blood cells to help fight off the infection. Still, even during an increased production of white blood cells, it cannot outnumber the red blood cells. 3) Platelets ➢ also known as thrombocytes, help the blood clot, thereby preventing bleeding when an artery or vein is severed or broken ➢ The lifespan of a platelet is from five to nine days only. ➢ A normal platelet count of a healthy individual is from 150,000 to 450,000 per milliliter of blood. Plasma ➢ Blood plasma is the pale, yellow fluid where the blood cells are suspended. ➢ Plasma makes up more than half of the total blood volume, roughly 55%. ➢ It consists mainly of water and also contains dissolved constituents including proteins (such as Albumin, Fibrinogen, and globulins) glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes, and hormones. ➢ Plasma also contains carbon dioxide because it is the main medium for the elimination of waste products from our body cells. Plasma also plays a very important role in osmosis, thereby promoting the balance of electrolytes ➢ Blood serum is blood without the blood cells and the factors. The human blood groups include the ABO and Rh blood groups (+ or -). The ABO blood groups are based on the presence of antigen types A and B. ➢ When these antigens are absent in the blood, the blood type is O. ➢ When both antigens are present the blood type is AB. Types of Body Circulation 1. Pulmonary circulation transports oxygen- depleted blood from the heart to the lungs. Its main function is to oxygenate the blood. 2. Systemic circulation carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the organs and tissues. This moves blood from the heart to all of the body organs and tissues, except for the heart and lungs, and back to the heart again. QUESTION AND ANSWER 1) What is the function of the respiratory system? GAS EXCHANGE 2) Where in the lungs does a gas exchange take place? ALVEOLI 3) When the diaphragm contracts, ________ occurs. INHALATION 4) What are the two main branches from the trachea? BRONCHI 5) What is the muscle below the lung that helps with breathing? DIAPHRAGM 6) What is the small flap of tissue that covers the air- only passage when we swallow? EPIGLOTTIS 7) What is the chamber behind the nose and mouth that leads to the trachea? PHARYNX 8) What is the use of oxygen by the cells to release energy from the food? CELLULAR RESPIRATION 9) When you breathe in air, you bring oxygen into your lungs and blow out what? CARBON DIOXIDE 10) What happens when we exhale (breathe out)? THE DIAPHRAGM RELAXES AND MOVES UPWARDS 11) What type of blood vessel does the blood rich in oxygen flow through? ARTERY
- 4. 12) What is the function of valves in the human circulatory system? PREVENT THE BACKWARD FLOW OF BLOOD 13) Jake cut his hand and was bleeding. Soon his wound stopped bleeding, leaving a red lump on the wound. What component of the blood helped to stop the bleeding? PLATELETS 14) What is the TINY blood vessel that allows for exchange between blood and cells in the tissue in the body? CAPILLARY 15) How many chambers does the human heart have? 4 16) The circulatory system is composed of what? HEART, BLOOD, AND BLOOD VESSELS 17) Where does blood get oxygen from? LUNGS 18) Blood flows from the right atrium to the? RIGHT VENTRICLE 19) What is the protein in red blood cell that carries oxygen? HEMOGLOBIN 20) Through which path does blood typically flow through the circulatory system? ARTERIES-> CAPILLARIES-> VEINS Parts of the Circulatory System Heart Blood Blood Vessels pumping organ circulating fluids a system of tubes, or vessels