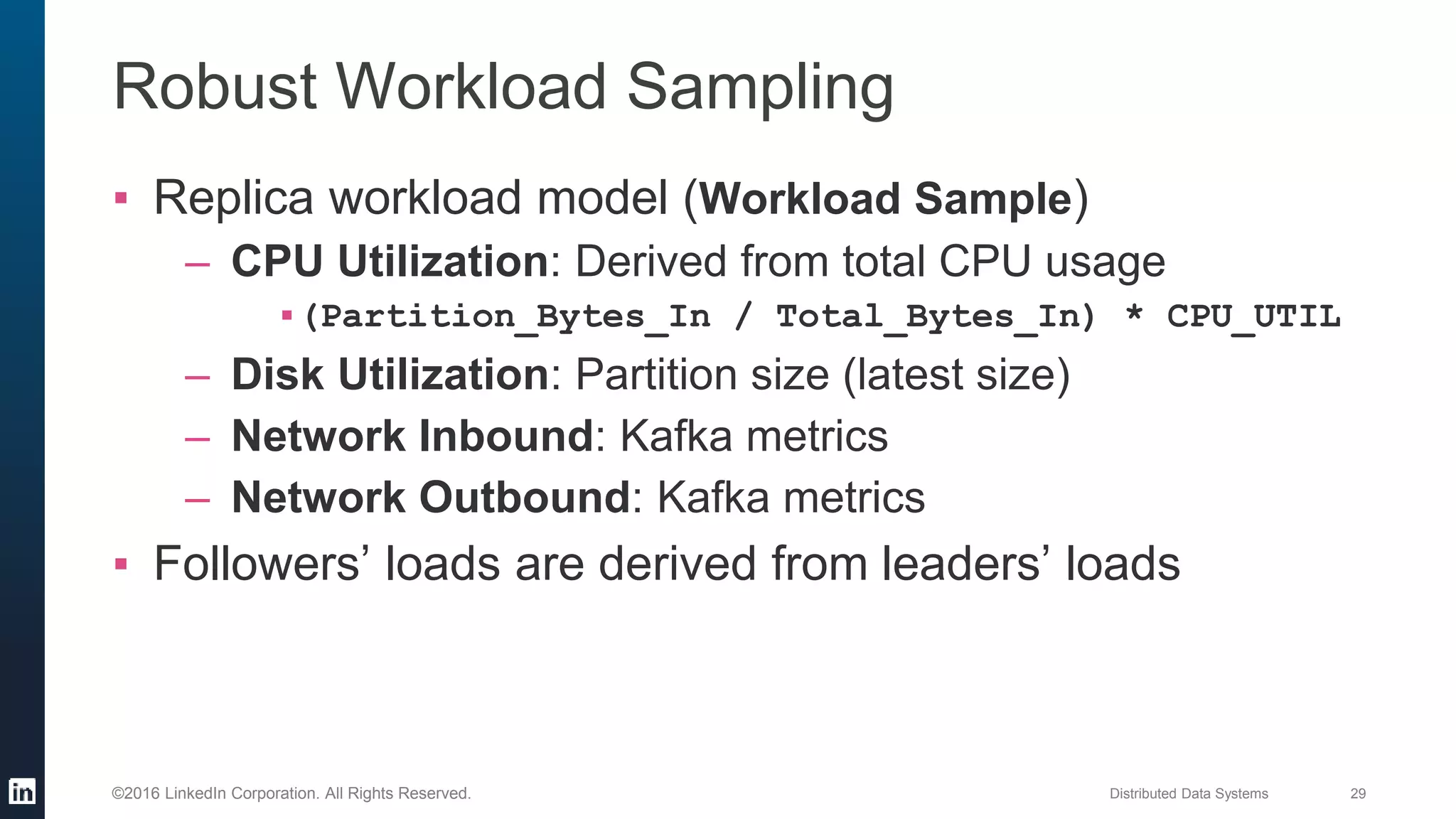
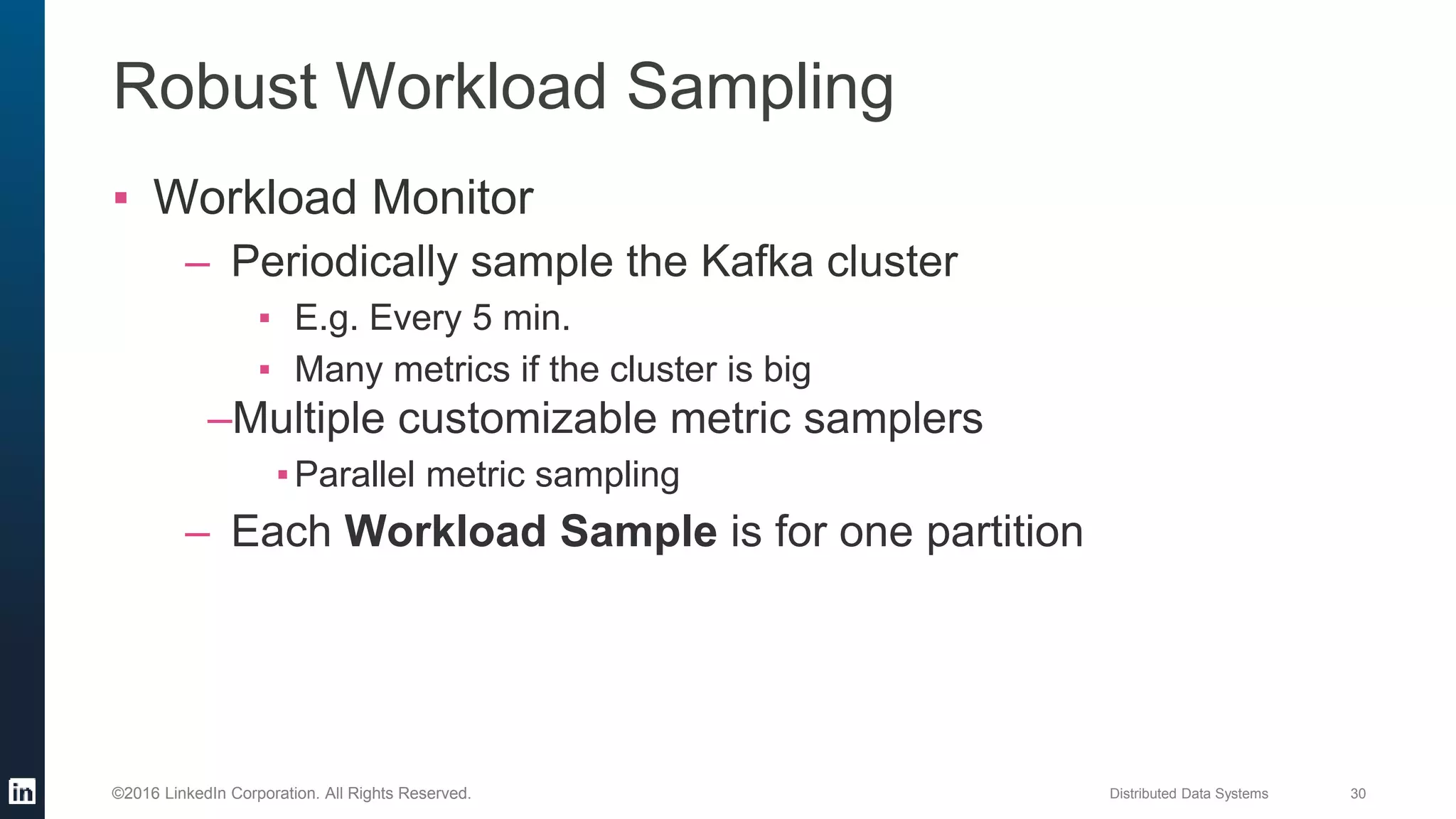
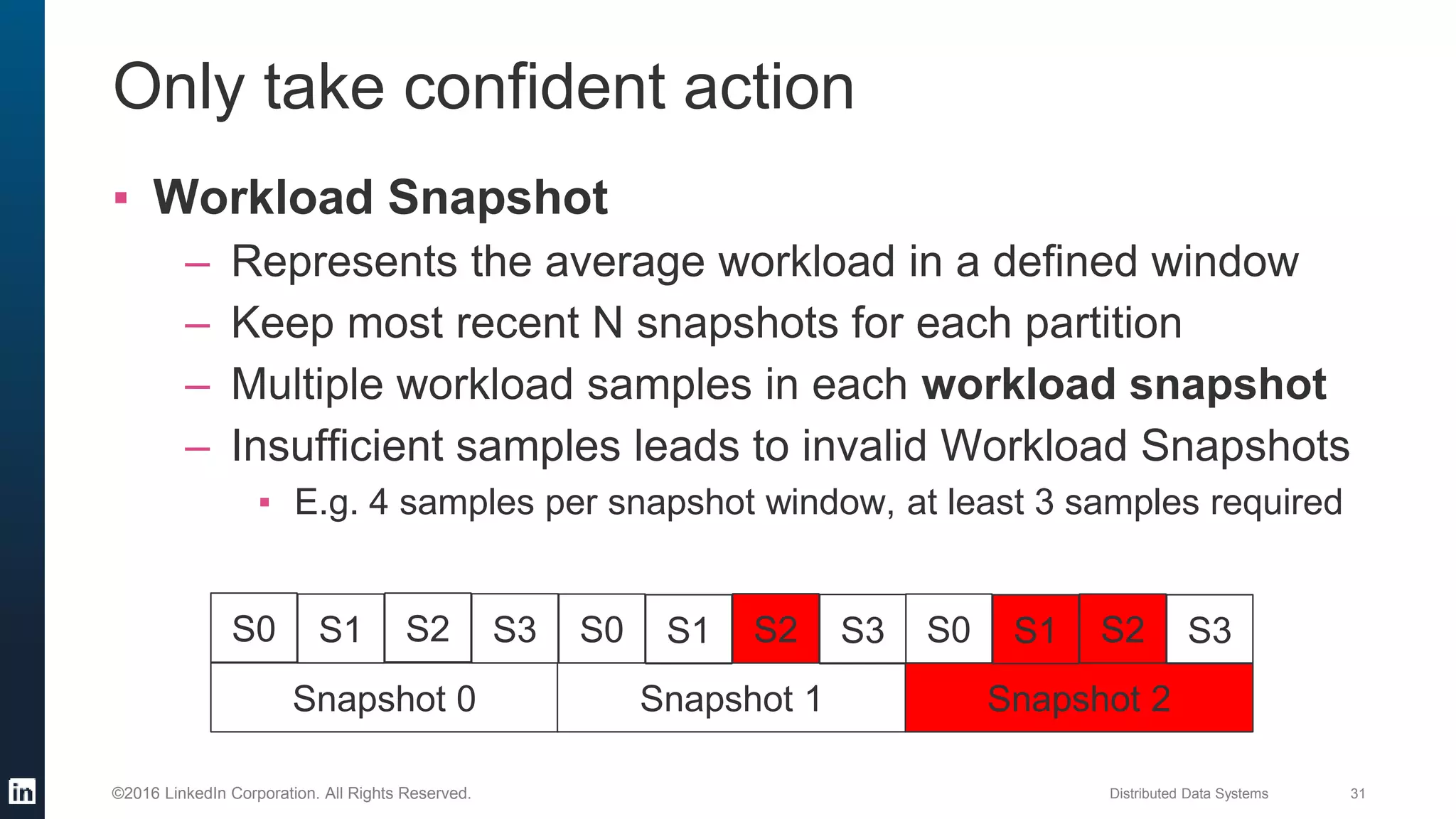
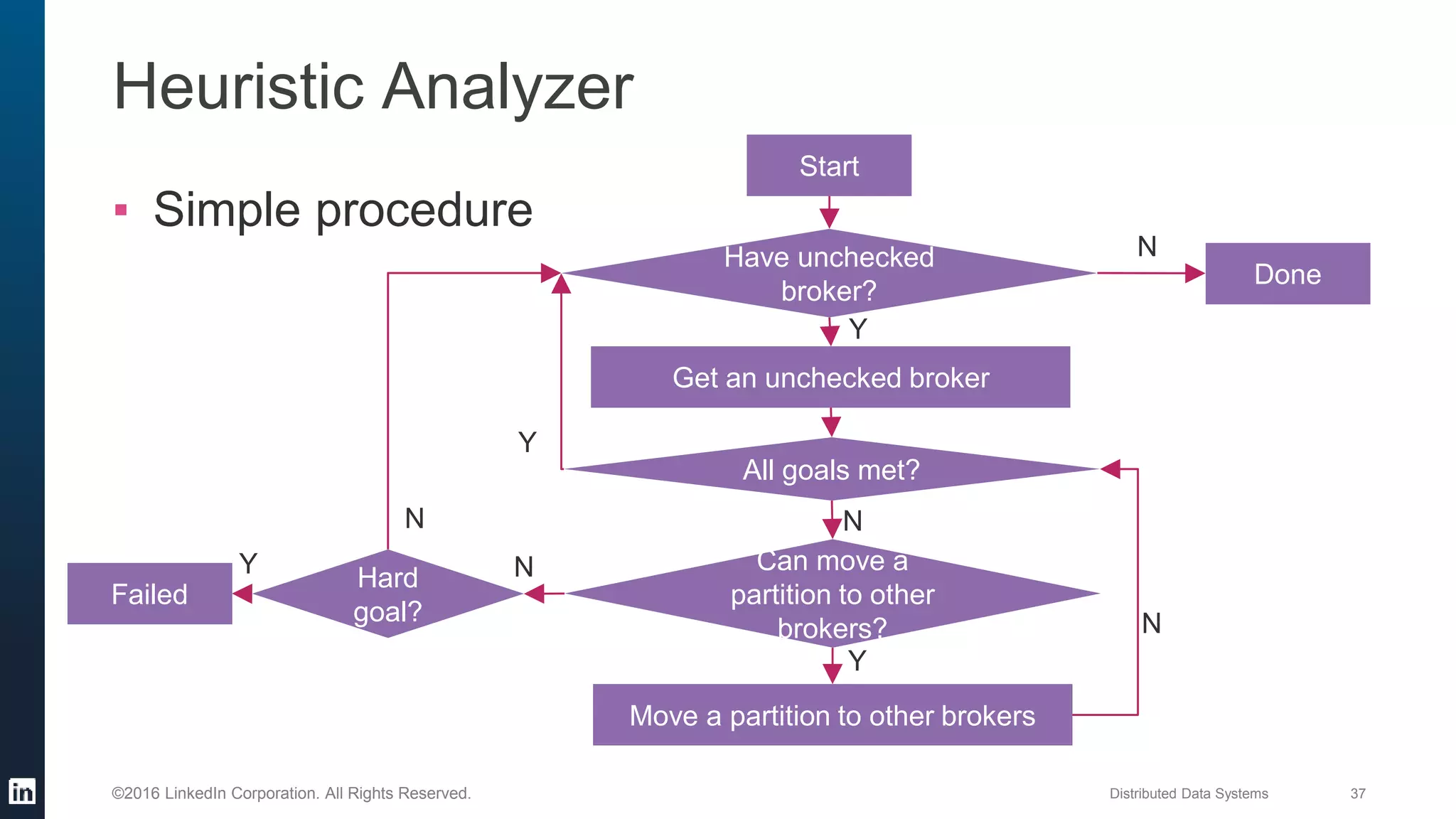
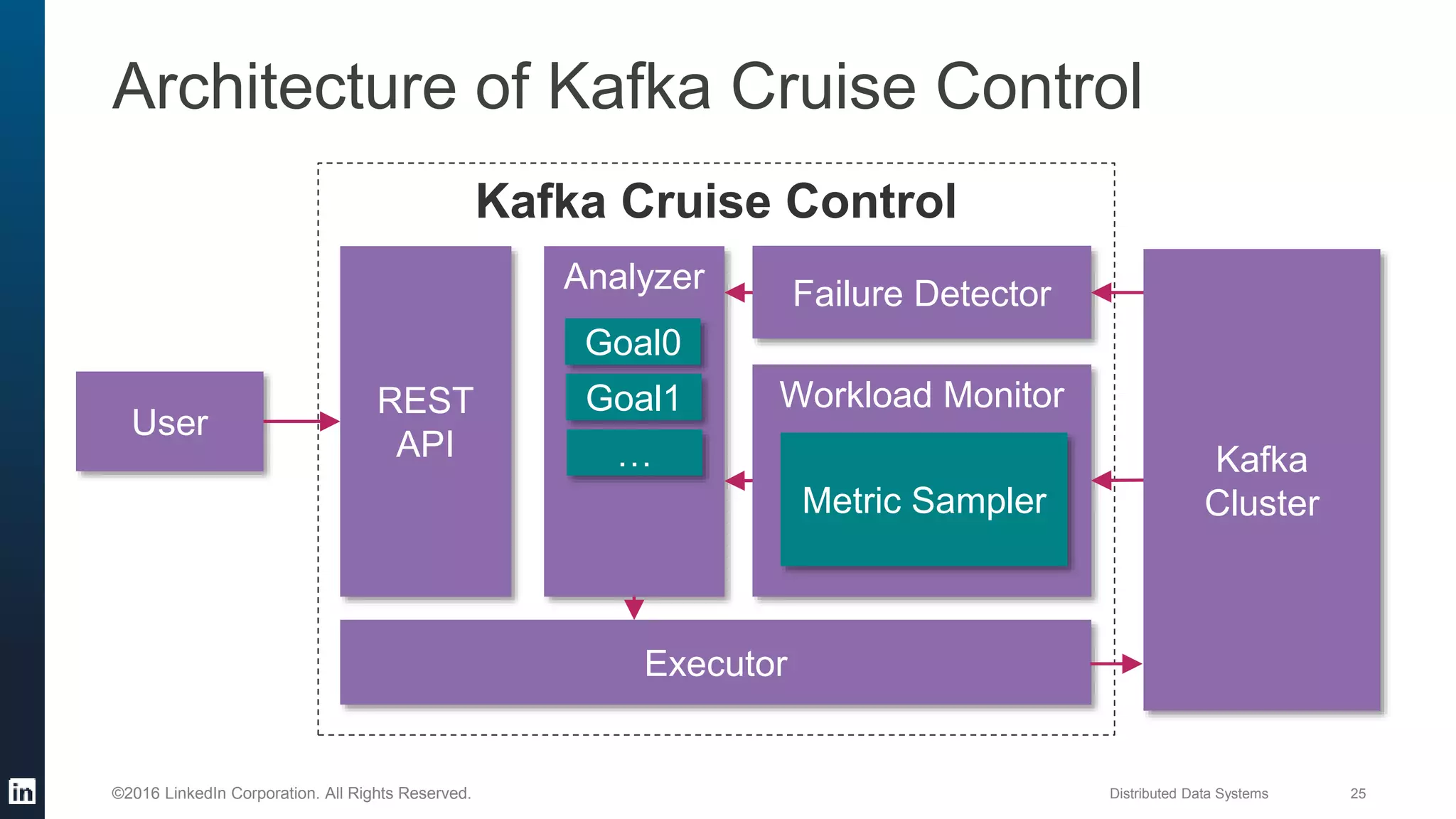
The document provides an overview of Kafka Cruise Control, which addresses operational challenges in Kafka deployments, including dynamic workload balancing and resource utilization across brokers. It outlines the complexity of balancing workloads, the goals for success in this area, and the system architecture of Kafka Cruise Control. Additionally, it discusses key challenges such as workload modeling, optimization resolution, and failure detection.
















![Distributed Data Systems 26©2016 LinkedIn Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
REST API
./rebalance_cluster [balance_percentage]
./add_brokers <broker-info>
./decommission_brokers <broker-info>
./assignment_history [option]
./restore_assignment [option]
./cancel_all
./list_assignment [option]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/35pe810r0or3khtslbje-signature-6ce679e537137b84f1dc277d23a356ff88d2b85bc01a14d311b2e4e3b4ec6955-poli-161104081506/75/Introduction-to-Kafka-Cruise-Control-26-2048.jpg)