Applications of the whole child concept
- 2. Conventional schooling traditionally reflects the view of the child as a passive receiver of information and rules, or a computer-like processor of information.
- 3. Whole Child concept is an effort towards the development of the whole human being. संपूर्ण बाल अवधारर्ा संपूर्ण मानव के ववकास के ललए एक प्रयास है।
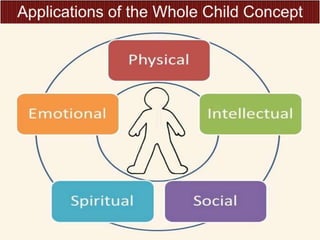
- 4. It recognizes that to become a full person, a growing child needs to develop—in addition to intellectual skills—physical, psychological, emotional, interpersonal, moral and spiritual potentials. यह मानता है कक एक पूर्ण व्यक्तत बनने के ललए, एक बढ़ते हुए बच्चे को बौद्धधक कौशल - शारीररक, मनोवैज्ञाननक, भावनात्मक, पारस्पररक, नैनतक और उत्साही क्षमताओं के अलावा ववकलसत करने की आवश्यकता है।
- 5. Education with a whole concept is concerned with the development of every person’s intellectual, emotional, social, physical, artistic, creative, and spiritual potentials. संपूर्ण अवधारर्ा के साथ शिक्षा हर व्यक्ति के बौद्धधक, भावनात्मक, सामाक्िक, भौतिक, कलात्मक, रचनात्मक और आध्याक्त्मक क्षमिा के ववकास से संबंधधि है।
- 6. In this way, the term education to whole child simply means cultivating the whole person and helping individuals live more consciously within their communities and natural ecosystems (Miller, 2005).
- 7. It engages all stakeholders—educators, families, policymakers, and community members. They recognize the need to educate the whole child—attending to cognitive, social, emotional, physical, and talent development of children and youth from widely diverse backgrounds. Parents Students
- 8. Goal of Education goal of education is to promote the highest possible levels of cognitive, social, emotional, physical, and ethical development for each child. Education must inspire children’s creativity, imagination, compassion, self-knowledge, social skills, and emotional health.
- 9. intellectually active; physically, verbally, socially, and academically competent; empathetic, kind, caring, and fair; creative and curious; disciplined, self-directed, and goal oriented; free; a critical thinker; confident; and
- 10. children and youth develop at very different rates cognitively, socially-emotionally, physically, and in language development. The developmental process for children does not occur in a step-by-step linear fashion. Rather, it zigzags, or dances, side to side and forward and backward but with a net movement forward Development is a gradual process, not an event Individual difference is not only to be expected but also valued
- 11. decisions about curriculum and adults’ interactions with children must be as individualized and as developmentally responsive as possible Children are results of both predetermined heredity and environmental influences that affect maturation. Development is viewed as the result of an interactive, transactional process between the growing, changing individual and his or her experiences in the social and physical worlds A child’s physical condition at birth may predict healthy growth, but family poverty and chronic malnutrition in early years may affect long-term outcomes and trigger a variety of developmental disabilities.
- 13. There is more discussion, questioning, experimentation, and active engagement in a holistic learning environment and a noticeable absence of grading, testing, labeling, and comparing. Learning is more meaningful and relevant to students—it matters to their lives.
- 14. Develop a sense of community and belonging and qualities of safety, respect, caring, and even love
- 15. Concern for feelings, aspirations, ideas, and questions that each student brings to the learning process Education is no longer viewed as the transmission of information; instead it is a journey inward as well as outward into the world.
- 16. It recognizes that everything in the world exists in context; that is, in relationship to inclusive communities.
- 17. Sickness Emotional stress Neurological problems Damage and Attention disorders Linguistic underdevelopment and oppositional behaviour
- 18. Inadequate housing, childcare, nutrition, food insecurity and health care Inadequate medical, dental and vision care Immigration issues Difficult process of acculturation, language barriers Frequent moves and disrupted schooling Parents negligence Separation from family These OSFs are related to a host of poverty-induced physical, sociological, and psychological problems that children often bring to school, ranging from neurological damage and attention disorders to excessive absenteeism, linguistic underdevelopment, and oppositional behavior.
- 19. Deeper understanding of the conditions that are influencing the student’s learning Can be conducted Focus groups Individual interviews Asking parents, other teachers
- 20. Screening of diseases, vaccination and prescription medication Referring students needing complex medical care Providing nutrition and wellness education to parents and help families obtain funded medical insurance. Providing mental health wellness facility to meet families in crisis and help parents realize their roles as their children’s first teachers and primary advocates.
- 21. Safety also impacts attendance and cognitive development. Students who are fearful, bullied, or distracted by fights and other disruptive behavior are unlikely to do well academically. adults in the school’s surrounding community need to be accountable for ensuring that students are safe; healthy; engaged; supported
- 22. Students who are sick, who come to school hungry, who can’t breathe because of asthma, who can’t see the blackboard because of poor vision, or who can’t concentrate because of pervasive toothaches or depression are unlikely to do well academically. Physical activity and nutrition affect learning Physical environment of home and school affects learning A school health advisory council with students, family, and community members Providing medical care to the poor and underserved families Primary care to the students at school(Common cold and other illnesses) Routine screening for immunizations and vision, hearing, dental, and orthopedic Concerns Physical education and health classes that emphasize sustaining healthy behaviors over a lifetime
- 23. Students who are bored by their classes, who don’t feel motivated to achieve, and who don’t see the connection between what they are learning in school and their real-world goals are unlikely to do well academically. They must first be motivated to learn and interested in their studies Students participate in a wide array of extracurricular activities. Schools provide opportunities for community-based internships, or projects. Teachers use active learning strategies, such as cooperative learning and project based learning.
- 24. Students who don’t have access to adult role models, advisors, mentors, counselors—or to teachers who understand their social and emotional development—are unlikely to do well academically. They must first feel supported by caring, qualified adults. Every student should have an adult advisor or mentor and that students have access to school counselors or other student support systems. Providing therapeutic counselling for students in crisis and teams up with the family caseworker to ease the stresses on
- 25. Students who spend most of their day being lectured and drilled in reading and math only, and who don’t have access to courses in the arts, music, social studies, civics, and other broadening subjects, are more likely to tune out and are less likely to do well in school. Schools should provide a well- rounded curriculum for all students. Students have access to rigorous programs in arts, foreign languages, and social studies. Schols maintain flexible graduation requirements.
- 26. The child poverty rate is perhaps the most widely used measure to identify the health and well-being of children. Conditions of poverty have been associated with crime, physical abuse, and learning and emotional problems. Fee relaxation Scholarship provision Stationery material can be provided
- 27. Two major types of abuse are typically identified— emotional physical Emotional abuse has been defined as excessive demands placed on children by parents, peers, or siblings and the failure of parents to provide an emotional support system Students who have experienced emotional abuse may exhibit a low self-esteem, suicidal thoughts, depression, antisocial behaviors, and difficulty initiating and maintaining relationships with adults and peers.
- 28. Affective development is impacted by both internal (biological predispositions, within-child abilities) and external (physical and social environment) influences. risk of academic failure, school dropout, incarceration बन्दीकरर्, suicide, and extended dependence in adulthood mood disorder; depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and substance abuse often cooccur Social Emotional learning skills (SEL skills) SEL can be defined as the process through which people learn to recognize and manage emotions, care about others, make good decisions, behave ethically and responsibly, develop positive relationships, and avoid negative behavior
- 29. Violence among children and youth contributes to disruptions in the educational process, including in-school and out-of-school suspension, school dropout, incarceration, or placement in alternative education programs. Serious violent crimes include aggravated assault, rape, robbery (stealing by force or threat of Child and adolescent violence in schools requires early assessment and positive interventions that involve collaborative and coordinated school and human service responses.
- 30. Parent education and capacity building- Workshops, seminars and discussion groups for parents about the topics of interest to them. For e. g. Strategies to help their children learn, Developing students’ leadership capacity etc.
- 31. COMPREHENSIVE CURRICULUM Integrating multiple developmental domains: academic, social-psychological, and career Including a curriculum that blends school-based and community-based approaches After school enrichment to support students’ growth in language and enriching experiences in their subjects
- 32. Families need timely information on courses, curriculum choices, grading procedures, and testing and assessments throughout elementary, middle, and high school. When students face social, academic, and personal problems, a coordinated effort is needed among families, school professionals, and community agencies to address the problems
- 33. Communication between schools and families during middle and high school years should not be one-way —from the school to the family —or only after the child has been in trouble for some time. Coordination between professionals and families can mean that clear messages are received and that adequate help is provided before the problem grows too large. Focus on strengths, capabilities, and developmental needs rather than on problems, risks, and vulnerabilities Belief that young people can make successful transitions to adulthood and gain life long
- 34. involves new relationships among people. involves sharing of resources (human or other). involves trust among people working together in peer (nonhierarchical) relationships. involves joint responsibility for outcomes. involves joint decision making and actions. is aimed at achieving specific results or change.