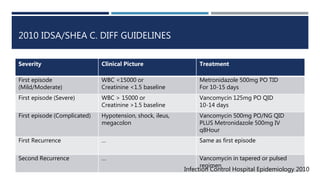
This document summarizes a randomized controlled trial comparing vancomycin to metronidazole for treating Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) in patients with varying disease severity. The study found that for mild CDAD, metronidazole and vancomycin led to similar cure rates, but for severe CDAD, vancomycin was superior to metronidazole in achieving cure. Significant risk factors for severe disease included albumin <2.5, presence of pseudomembranous colitis, and ICU stay. The 2010 IDSA/SHEA guidelines recommend metronidazole as first-line treatment for mild/moderate CDAD and vancom