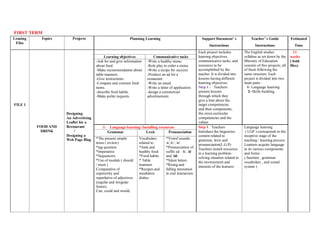
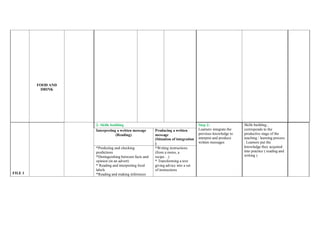
The document provides an overview of the annual English learning plan for 4th year middle school students in Tunisia. It consists of 5 projects over the school year, each lasting 5-11 weeks. Each project follows the same structure: 1) Language learning focusing on grammar, vocabulary and pronunciation, 2) Skills building where students practice reading and writing, 3) Assessment of students, and 4) Remediation as needed. The first project focuses on food and restaurants, the second on citizenship and sustainable development, and so on, covering a variety of topics to improve students' English communication skills.