Approach_to_floppy_infant__1_.pptx
- 1. BY – DR NILANJANA GHOSH
- 2. Outlines Definitions and basic physiology Differences between central and peripheral causes of hypotonia. Evaluation of hypotonia in infants. Management options
- 3. Relevant terminologies and definitions Tone: is the baseline resistance of muscle to stretch. Phasic tone: The rapid contraction in response to a high –intensity stretch, as in tendon reflex response. Postural tone: It is the prolonged contraction of antigravity muscles in response to the low- intensity stretch of gravity.
- 4. Hypotonia- reduced resistance to ta passive movements around a joint Weakness is reduction in the maximum power that can be generated Floppy infants exhibit poor control of movements, delayed motor skills, alteration in postural control, increased range of motion. Weak infants always have hypotonia but hypotonic infants may not have weakness.
- 5. How muscle tone is maintained? Cerebral cortex Cerebellum Basal ganglia Vestibular nuclei Cerebral cortex Cerebellum γ motor discharge of spinal cord Bulbo reticular facilitatory area in pons Bulbo reticular area in medulla
- 6. γ motor discharge of spinal cord Stretching of muscle spindle Activation of α motor neuron Partial contraction of muscle How muscle tone is maintained?
- 7. The maintenance of normal tone requires intact central and peripheral nervous system. Hence hypotonia is a common symptoms of neurological dysfunction and occurs in diseases of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and muscles.
- 8. The term- Floppy Infant Indicates multiple disorders with various degree of hypotonia (axial, appendicular or both). Supraspinal conditions(brain, brainstem, cervical spinal junction)- Central hypotonia Segmental conditions(anterior horn cell, peripheral nerve, neuromuscular junction, muscle)-Motor unit hypotonia/peripheral hypotonia Vast differential diagnosis-ranging from benign condition with good prognosis to life threatening condition incompatible with life.
- 9. A systematic approach to a child who has hypotonia,paying attention to the history and clinical examination, is the paramount to localizing the problem to a specific region of the nervous system.
- 10. Mainly two approaches (1) Based on neuro- anatomical localization i.e Central or Peripheral nervous system involvement. (2) To determine whether or not the hypotonia is associated with weakness.
- 11. CENTRAL HYPOTONIA PERIPHERAL HYPOTONIA Central causes account for 60% to 80% of hypotonia cases Abnormalities of other brain functions. Global developmental delay. Axial hypotonia> appendicular hypotonia. Dysmorphic features: microcephaly. Fisting of hands. Normal or brisk tendon reflex. Scissoring on vertical suspension. peripheral causes occur in 15% to 30%. Alert, normal cognition Motor delay. Hypotonia with profound limbs weakness(axial hypotonia=appendicular hypotonia) Hyporeflexia or areflexia. Reduced or absent antigravity movement. Fasciculation. Muscle atrophy or pseudohypertrophy. Respiratory and feeding impairment.
- 12. Causes of Central hypotonia Brain malformations : Chromosomal disorders- Down syndrome, Praderwilli syndrome. Genetic disorders- Familial dysautonomia, Lowe syndrome. Endocrine disorders- hypothyroidism Metabolic- rickets, renal tubular acidosis
- 13. IEM- aminoaciduria, organic aciduria, mucopolysaccharidoses, glycogen storage disorder, fatty acid oxidation defect etc Cerebral insult- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, intracranial hemorrhage, Hypoglycemia. Cerebellar disorder- Joubert syndrome, Ponto- cerebellar hypoplasia. Paroxysmal disorder- neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, Zellweger syndrome.
- 14. Causes of peripheral hypotonia Anterior horn cell disorders- Spinal muscular atrophy. Congenital neuropathy- Hereditary motor- sensory neuropathy, congenital hypo myelinating neuropathy, Charcot Marie tooth disease. Neuromuscular junction disorders- Transient neonatal myasthenia, congenital myasthenic syndrome, infantile botulism, magnesium toxicity, aminoglycoside toxicity Myopathies- Congenital myopathy, Nemaline myopathy, central core disease, myotubular myopathy, Muscular dystrophies- Walker- Warburg, Fukuyama, muscles- eye-brain disease,merosin positive CMD, early infantile facioscapulohumeral dystrophy.
- 15. APPROACH Presenting complaints: Age of presentation Onset(sudden or gradual) Course(progressive, static or fluctuating) Muscles weakness distribution(proximal –myopathy or distal –neuropathy)
- 16. Antenatal history Decreased fetal movement Polyhydramnios Drug exposure Breech presentation Prolonged labour
- 17. Postnatal history Birth asphyxia Weak cry Respiratory distress, prolonged ventilatory support Feeding difficulties Convulsion Honey consumption Joint dislocation
- 18. History of consanguinity Family history Developmental history(isolated motor or motor and cognitive) Anthropometry: head circumference, weight
- 19. Salient points in history Any significant family history-affected parents or siblings,consanguinity,stillbirths,childhood deaths Maternal disease- myotonic dystrophy Pregnancy and delivery history- drug or teratogen exposure, decreased fetal movements, abnormal presentations, polyhydramnios/oligohydramnios, Apgar score, resuscitation requirements. History since delivery Respiratory effort Ability to feed Level of alertness Level of spontaneous activity Character of cry
- 20. EXAMINATION Dysmorphic features Anterior fontanel Eyes: cataract(Lowe syndrome) Eye lid drop Tongue fasciculation Genitalia hypogonadism Limbs examination
- 21. Neurologic examination Detailed neurologic assessment- tone, strength and reflexes Assessment of tone- begin by examining posture and movement. A floppy infant often lies with limbs abducted and extended.
- 22. Evaluation of hypotonia Observation of position at rest, Palpation of muscles, Passive movements Further evaluation of hypotonia by Amiel Tison method and 18o degree flip merhod.
- 23. Amiel-Tison method Age (months) Adductor angle Popliteal angle Dorsiflexion angle Scarf sign 0-3 40˚-80˚ 80˚-100˚ 60˚-70˚ Elbow does not cross midline 4-6 70˚-110˚ 90˚-120˚ 60˚-70˚ Elbow crosses midline 7-9 110˚-140˚ 110˚-160˚ 60˚-70˚ Elbow goes beyond axillary line 10-12 140˚-180˚ 150˚-170˚ 60˚-70˚ -----
- 24. 180 degree flip method A supine infant is pulled to sit, held vertical, held in ventral suspension and finally put in prone position, completing 180 degree flip. Supine- assess any preferred position, like external rotation of lower limb indicating weakness of floppiness on that side. Floppy baby may have frog like posture.
- 25. Traction response The presence of more than minimal head lag and failure to counter traction by flexion of the limbs in the term newborn is abnormal and indicate hypotonia.
- 26. Sitting- assess sitting ability(with or without support),rounded or straight back etc.
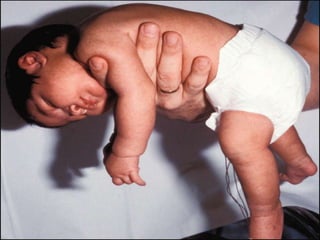
- 27. Vertical suspension The examiner places both the hands in the infant’s axillae and without grasping the thorax, lifts up. Normal response- Head erect in the mid line with flexion at the knee.hip and ankle joints. Hypotonic infant- suspends vertically, head falls forward, legs dangle and the infant may slip through examiner’s hand.
- 28. Horizontal suspension Baby suspended in the prone position with the examiner’s palm underneath the chest Normal infant- keeps the head erect, maintains the back straight and flexes the elbow,hip,knee and ankle joints. Hypotonia- infants drape over the examiner’s hand legs hanging limply
- 29. Prone- place the child prone in bed and look for any arching.
- 30. Deep tendon reflexes(DTRs) DTRs often normal/hyperactive in central conditions. DTRs- normal/decreased/absent in peripheral disorders.
- 31. Other pertinent findings Decreased resistance to flexion and extension of the extremities. Exaggerated hip abduction and ankle dorsiflection Oral-motor dysfunction Poor respiratory efforts Gastro esophageal reflux Note the distribution of weakness. Ex. Face is spared versus the trunk and extremities.
- 32. Variable Central injury Central developm ental Anterior horn cell Periphera l nerve NM junction Muscle Strength Normal or slight weakness Normal or slight weakness weakness weakness weakness weakness DTRs Normal/increase d normal decreased decreased Normal/decreas ed Decreased to absent Babinski’s sign +/- +/- absent absent Infantile reflex persistent Persistent/absen t absent absent absent absent Muscle fasciculation absent absent prominent absent absent absent Muscle mass Normal/disuse atrophy Normal/disuse atrophy Prominent atrophy(proxima l) Distal atrophy Normal/decreas ed Proximal atrophy: increased or decreased pseudo hypertrophy Sensation normal normal normal Increased /decreased normal normal Localization of disorder producing hypotonia
- 33. Anterior horn cell disease versus NM junction disorder Usually spares extra ocular muscles, while diseases of the neuromuscular junction may be characterized by ptosis and extra ocular muscles weakness.
- 34. Clues to central hypotonia Dysmorphic features : Trisomy-21,Prader-willi syndrome, DiGeorge syndrome. Depressed level of consciousness or lethargy Abnormal eye movement or inability to track visually Early onset seizure. Apnea Exaggerated irregular breathing patterns .. Joubert syndrome Predominant axial weakness Normal strength with hypotonia Scissoring on vertical suspension- Cerebral palsy Fisting of the hands Hyperactive or normal reflexes Malformation of other organs
- 35. Characteristics of peripheral causes of hypotonia Alert infant and appropriate response to surroundings Normal sleep-wake patterns Associated with profound weakness Hypotonia and hyporeflexia/ areflexia Other features- muscle atrophy, presence of respiratory and feeding impairment.
- 36. Clues to anterior horn cell disorders(Infantile form of spinal muscular atrophy) Hypotonia Generalized weakness Absent reflexes Feeding difficulties Fasciculation of tongue Alert face Profound distal weakness
- 37. Clues to specific diagnosis Hepatosplenomegaly-storage disorder, congenital infections. Hepatomegaly,retinitis pigmentosa-neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Renal cyst, high forehead, wide fontanel's- Zellweger’s syndrome. Congenital cataracts,glucoma-oculocerebrorenal syndrome. Abnormal odor- metabolic disorder. Hyperpigmentation,undescended testis- Prader willi
- 38. Peripheral causes Diagnosis mainly by history and clinical examination Molecular genetics-CTG repeats, deletions in SMN gene Nerve conduction studies and muscle biopsy(Depending on clinical situation, may be delayed until around 6 months of age as neonatal results are difficult to interpret) Creatine kinase-elevated in muscular dystrophy but not in spinal muscular atrophy or many other myopathies Specific DNA testing-for myotonic dystrophy and for spinal muscular atrophy(SMN gene) Electrophysiological studies- shows abnormalities in nerves , myopathies and disorders of NM junction.