ASPIRIN BRIEF intro
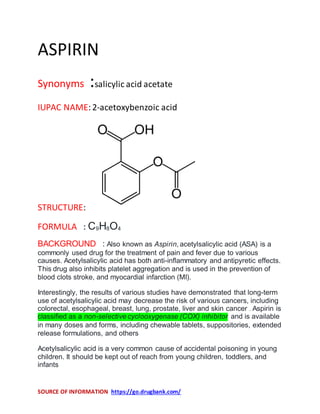
- 1. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ ASPIRIN Synonyms :salicylic acid acetate IUPAC NAME:2-acetoxybenzoic acid STRUCTURE: FORMULA : C9H8O4 BACKGROUND : Also known as Aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) is a commonly used drug for the treatment of pain and fever due to various causes. Acetylsalicylic acid has both anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. This drug also inhibits platelet aggregation and is used in the prevention of blood clots stroke, and myocardial infarction (MI). Interestingly, the results of various studies have demonstrated that long-term use of acetylsalicylic acid may decrease the risk of various cancers, including colorectal, esophageal, breast, lung, prostate, liver and skin cancer . Aspirin is classified as a non-selective cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor and is available in many doses and forms, including chewable tablets, suppositories, extended release formulations, and others Acetylsalicylic acid is a very common cause of accidental poisoning in young children. It should be kept out of reach from young children, toddlers, and infants
- 2. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ PHYSIOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES . melting point 130-140 0 C Boiling point 140 0 C Water solubility 10 mg/mL PKa 3.5 . PHARMACOLOGY : Indication Pain, fever, and inflammation Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), in the regular tablet form (immediate- release), is indicated to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation associated with many conditions, including the flu, the common cold, neck and back pain, dysmenorrhea, headache, tooth pain, sprains, fractures, myositis, neuralgia, synovitis, arthritis, bursitis, burns, and various injuries. It is also used for symptomatic pain relief after surgical and dental procedures . The extra strength formulation of acetylsalicylic acid is also indicated for the management migraine pain with photophobia (sensitivity to light) and phonophobia (sensitivity to sound) Other indications ASA is also indicated for various other purposes, due to its ability to inhibit platelet aggregation. These include: Reducing the risk of cardiovascular death in suspected cases of myocardial infarction (MI) . Reducing the risk of a first non-fatal myocardial infarction in patients, and for reducing the risk of morbidity and mortality in cases of unstable angina and in those who have had a prior myocardial infarction For reducing the risk of transient ischemic attacks (TIA) and to prevent atherothrombotic cerebral infarction (in conjunction with other treatments)
- 3. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ For the prevention of thromboembolism after hip replacement surgery For decreasing platelet to platelet adhesion following carotid endarterectomy, aiding in the prevention of transient ischemic attacks (TIA) Used for patients undergoing hemodialysis with a silicone rubber arteriovenous cannula inserted to prevent thrombosis at the insertion site Important note regarding use of the extended-release formulation In the setting of acute myocardial infarction, or before percutaneous interventions, the extended-release form of acetylsalicylic acid should not be used. Use immediate-release formulations in scenarios requiring rapid onset of action The extended-release form is taken to decrease the incidence of mortality and myocardial infarction (MI) for individuals diagnosed with chronic coronary artery disease (CAD), including patients with previous myocardial infarction (MI) or unstable angina or with chronic stable angina. Additionally, the extended-release form is used to decrease the risk of death and recurrent episodes of stroke in patients with a history of stroke or TIA CONTRAINDICATION: Aspirin is contraindicated in patients with known allergy to NSAIDs and in patients with asthma, rhinitis, and nasal polyps. It may cause anaphylaxis, laryngeal edema, severe urticaria, angioedema, or bronchospasm (asthma) Pharmacodynamics Effects on pain and fever Acetylsalicylic acid disrupts the production of prostaglandins throughout the body by targeting cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2
- 4. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ (COX-2) . Prostaglandins are potent, irritating substances that have been shown to cause headaches and pain upon injection into humans. Prostaglandins increase the sensitivity of pain receptors and substances such as histamine and bradykinin. Through the disruption of the production and prevention of release of prostaglandins in inflammation, this drug may stop their action at pain receptors, preventing symptoms of pain. Acetylsalicylic acid is considered an antipyretic agent because of its ability to interfere with the production of brain prostaglandin E1. Prostaglandin E1 is known to be an extremely powerful fever-inducing agent Effects on platelet aggregation The inhibition of platelet aggregation by ASA occurs because of its interference with thromboxane A2 in platelets, caused by COX-1 inhibition. Thromboxane A2 is an important lipid responsible for platelet aggregation, which can lead to clot formation and future risk of heart attack or stroke A note on cancer prevention ASA has been studied in recent years to determine its effect on the prevention of various malignancies . In general, acetylsalicylic acid is involved in the interference of various cancer signaling pathways, sometimes inducing or upregulating tumor suppressor genes Results of various studies suggest that there are beneficial effects of long-term ASA use in the prevention of several types of cancer, including stomach, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers . Research is ongoing. Mechanism of action Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) blocks prostaglandin synthesis. It is non- selective for COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes Inhibition of COX-1 results in the inhibition of platelet aggregation for about 7-10 days (average platelet lifespan). The acetyl group of acetylsalicylic acid binds with a serine residue of the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) enzyme, leading to
- 5. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ irreversible inhibition. This prevents the production of pain-causing prostaglandins. This process also stops the conversion of arachidonic acid to thromboxane A2 (TXA2), which is a potent inducer of platelet aggregation . Platelet aggregation can result in clots and harmful venous and arterial thromboembolism, leading to conditions such as pulmonary embolism and stroke. It is important to note that there is 60% homology between the protein structures of COX-1 and COX-2. ASA binds to serine 516 residue on the active site of COX-2 in the same fashion as its binding to the serine 530 residue located on the active site of COX-1. The active site of COX- 2 is, however, slightly larger than the active site of COX-1, so that arachidonic acid (which later becomes prostaglandins) manages to bypass the aspirin molecule inactivating COX-2 . ASA, therefore, exerts more action on the COX-1 receptor rather than on the COX-2 receptor A higher dose of acetylsalicylic acid is required for COX-2 inhibition Absorption Absorption is generally rapid and complete following oral administration but absorption may be variable depending on the route, dosage form, and other factors including but not limited to the rate of tablet dissolution, gastric contents, gastric emptying time, and gastric pH Detailed absorption information When ingested orally, acetylsalicylic acid is rapidly absorbed in both the stomach and proximal small intestine. The non-ionized acetylsalicylic acid passes through the stomach lining by passive diffusion. Ideal absorption of salicylate in the stomach occurs in the pH range of 2.15 - 4.10. Intestinal absorption of acetylsalicylic acid occurs at a much faster rate. At least half of the ingested dose is hydrolyzed to salicylic acid in the first-hour post-ingestion by esterases found in the gastrointestinal
- 6. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ tract. Peak plasma salicylate concentrations occur between 1-2 hours post-administration Volume of distribution This drug is distributed to body tissues shortly after administration. It is known to cross the placenta. The plasma contains high levels of salicylate, as well as tissues such as spinal, peritoneal and synovial fluids, saliva and milk. The kidney, liver, heart, and lungs are also found to be rich in salicylate concentration after dosing. Low concentrations of salicylate are usually low, and minimal concentrations are found in feces, bile, and sweat Protein binding 50% to 90% of a normal therapeutic concentration salicylate (a main metabolite of acetylsalicylic acid ) binds plasma proteins, particularly albumin, while acetylsalicylic acid itself binds negligibly . Acetylsalicylic acid has the ability to bind to and acetylate many proteins, hormones, DNA, platelets, and hemoglobin . Metabolism Acetylsalicylic acid is hydrolyzed in the plasma to salicylic acid. Plasma concentrations of aspirin following after administration of the extended- release form are mostly undetectable 4-8 hours after ingestion of a single dose. Salicylic acid was measured at 24 hours following a single dose of extended-release acetylsalicylic acid . Salicylate is mainly metabolized in the liver, although other tissues may also be involved in this process . The major metabolites of acetylsalicylic acid are salicylic acid, salicyluric acid, the ether or phenolic glucuronide and the ester or acyl glucuronide. A small portion is converted to gentisic acid and other hydroxybenzoic acids Half-life The half-life of ASA in the circulation ranges from 13 - 19 minutes. Blood concentrations drop rapidly after complete absorption. The half- life of the salicylate ranges between 3.5 and 4.5 hours ADVERSE EFFECT rash
- 7. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ gastrointestinal ulcerations, abdominal pain, upset stomach, heartburn, drowsiness, headache, cramping Toxicity Lethal doses Acute oral LD50 values have been reported as over 1.0 g/kg in humans, cats, and dogs, 0.92 g/kg - 1.48 g/kg in albino rats, 1.19 g/kg in guinea pigs, 1.1 g/kg in mice, and 1.8 g/kg in rabbit models Acute toxicity Salicylate toxicity is a problem that may develop with both acute and chronic salicylate exposure 7. Multiple organ systems may be affected by salicylate toxicity, including the central nervous system, the pulmonary system, and the gastrointestinal system. Severe bleeding may occur. In the majority of cases, patients suffering from salicylate toxicity are volume-depleted at the time of presentation for medical attention. Fluid resuscitation should occur immediately and volume status should be monitored closely. Disruptions in acid-base balance are frequent in ASA toxicity 7. The acute toxicity of acetylsalicylic in animals has been widely studied. The signs of poisoning in rats from lethal doses are mild to severe gastroenteritis, hepatitis, nephritis, pulmonary edema, encephalopathy, shock and some toxic effects on other organs and tissues. Mortality has been observed following convulsions or cardiovascular shock. An important differentiating property between various animal species is the ability to vomit toxic doses. Humans, cats and dogs have this ability, but rodents or rabbits do not Chronic toxicity and carcinogenesis Chronic ASA toxicity is frequently accompanied by atypical clinical presentations that may be similar to diabetic ketoacidosis, delirium, cerebrovascular accident (CVA), myocardial infarction (MI) or cardiac failure. Plasma salicylate concentrations should be measured if salicylate intoxication is suspected, even if there no documentation available to suggest ASA was ingested. In older age, nephrotoxicity from salicylates increases, and the risk of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage is increased, with higher rates of mortality . It is also
- 8. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ important to note that ASA toxicity may occur even with close to normal serum concentrations. Prevention of chronic ASA includes the administration of smallest possible doses, avoidance of concurrent use of salicylate drugs, and therapeutic drug monitoring. Renal function should be regularly monitored and screening for gastrointestinal bleeding should be done at regular intervals Chronic toxicity studies were performed in rodents. ASA was administered at doses measured to be 2 to 20 times the maximum tolerated clinical dose to mice for up to one year. Negative dose- related effects were seen. These include decreased mean survival time, decreased number of births and progeny reaching an appropriate age for weaning. No evidence of carcinogenesis was found in 1-year studies At daily doses of 0.24 g/kg/day given for 100 days to albino rats, ASA led to signs to excessive thirst, aciduria, diuresis, drowsiness, hyperreflexia, piloerection, changes in respiration, tachycardia, followed by soft stools, epistaxis, sialorrhea, dacryorrhea and mortality during hypothermic coma in the second study month Use in pregnancy and lactation While teratogenic effects were observed in animals nearly lethal doses, no evidence suggests that this drug is teratogenic in humans . It is advisable, however, to avoid ASA use the first and second trimester of pregnancy, unless it is clearly required. If acetylsalicylic acid containing drugs are ingested by a patient attempting to conceive, or during the first and second trimester of pregnancy, the lowest possible dose at the shortest possible duration should be taken This drug is contraindicated in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy DRUG-DRUG INTERACTIONS if you are taking aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke, avoid also taking ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin). Ibuprofen can make aspirin less effective in protecting your heart and blood vessels. If you must use both medications, ask your doctor how far apart your doses should be. Food Interactions
- 9. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ Avoid alcohol. Alcohol increases the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Avoid herbs and supplements with anticoagulant/antiplatelet activity. Examples include garlic, ginger, bilberry, danshen, piracetam, and ginkgo biloba. Take after a meal. This reduces irritating gastrointestinal effects. Take with a full glass of water. ASPIRIN Aspirin is prepared by chemical synthesis from salicylic acid, through acetylationwith acetic anhydride.The molecular weight of aspirin is 180.16g/mol. THERAPEUTIC APPLICATION Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) Anxiety Arthritis Atherothrombotic cerebral infarction Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Cardiovascular Events Cardiovascular Mortality Colorectal Adenomas Colorectal Cancers Common Cold Coronary artery reocclusion Death Dyspeptic signs and symptoms Fever Flu Like Symptom Flu caused by Influenza Headache Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia Inflammation Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) Kawasaki Syndrome
- 10. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/ Major Adverse Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCE) Migraine Morbidity Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome Muscle Contraction Myocardial Infarction Myocardial Infarction (MI), first occurrence Neuralgia Pain Pain caused by Common Cold Pain, Menstrual Pericarditis Polycythemia Vera (PV) Preeclampsia Rheumatic Pain Rheumatism Rheumatoid Arthritis Rhinosinusitis Severe Pain Soreness, Muscle Spondyloarthropathies Stroke Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Tension Headache Thromboembolism Toothache Transient Ischemic Attack Venous Thromboembolism Acute Inflammation Atherothrombotic events Death by myocardial infarction Moderate Pain Thrombotic events Associated Therapies Antiplatelet Therapy Hemodialysis Treatment Secondary Prevention.
- 11. SOURCE OF INFORMATION https://go.drugbank.com/