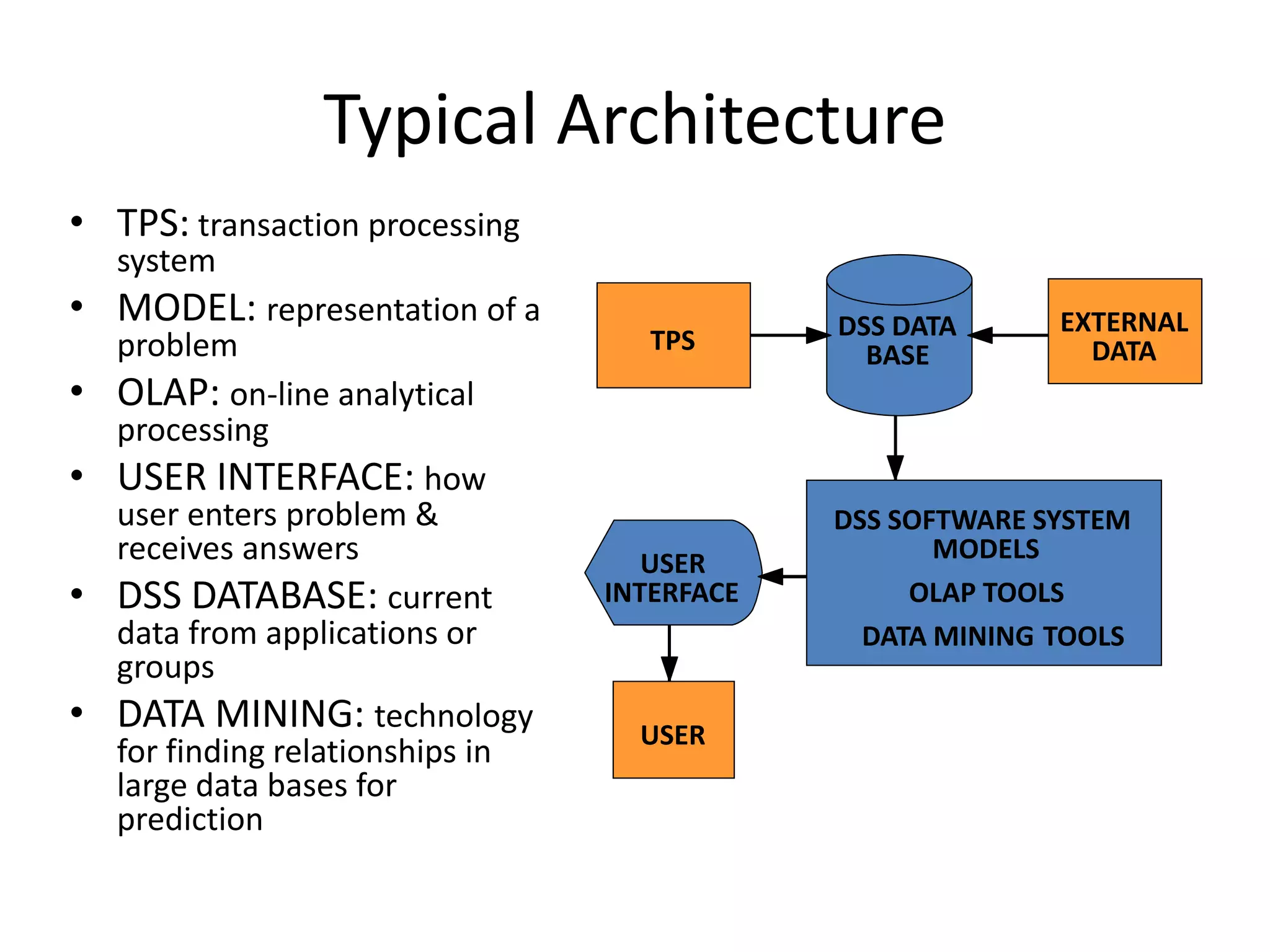
Decision support systems (DSS) are computer-based systems that analyze data and help decision-makers solve semi-structured or unstructured problems. DSS provide access to internal and external data, models, and documents to help identify problems and solutions. There are different types of DSS including data-driven, model-driven, communication-driven, document-driven, and knowledge-driven systems. DSS have benefits like improved efficiency, faster decision-making, and competitive advantages. They are used in various applications including clinical decision support, banking, and analyzing business performance.