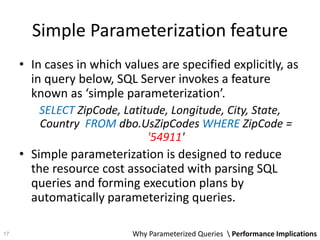
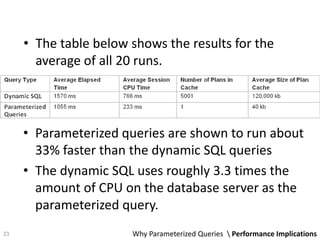
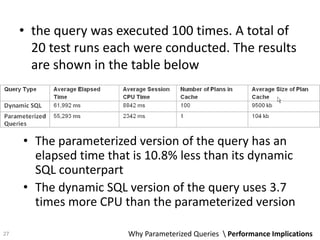
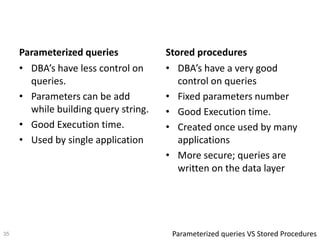
The document discusses the concept and advantages of parameterized queries in SQL, highlighting their role in preventing SQL injection attacks and improving performance over dynamic SQL. It compares parameterized queries to stored procedures, mentioning their pros and cons, including issues with code duplication and control over queries. Additionally, experimental results show that parameterized queries can lead to faster execution and lower CPU usage compared to dynamic SQL.











![• [Firstname] will be compared with the value:
“Ali';Truncate Table dbo.Customer;--”
13 Why Parameterized Queries Protection against SQL Injection Attack](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sqlparametrizedqueries-170421054903/85/Sql-parametrized-queries-13-320.jpg)