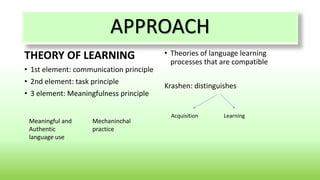
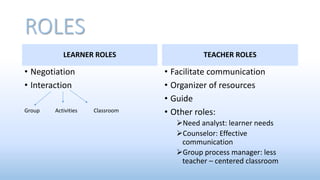
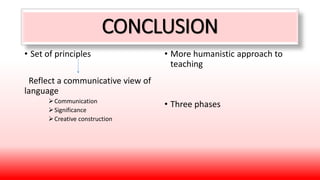
Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) emerged in the late 1960s based on theories that language is fundamentally for communication. CLT focuses on real-world language use and teaches grammatical, sociolinguistic, discourse and strategic competence. Lessons incorporate tasks, social interaction activities, and group work to encourage student negotiation, interaction and creative language use. The teacher facilitates communication rather than merely transmitting information. Materials include texts, tasks, and realia to support developing communicative skills.