The document discusses several theories about how audiences interact with and make meaning from media texts:
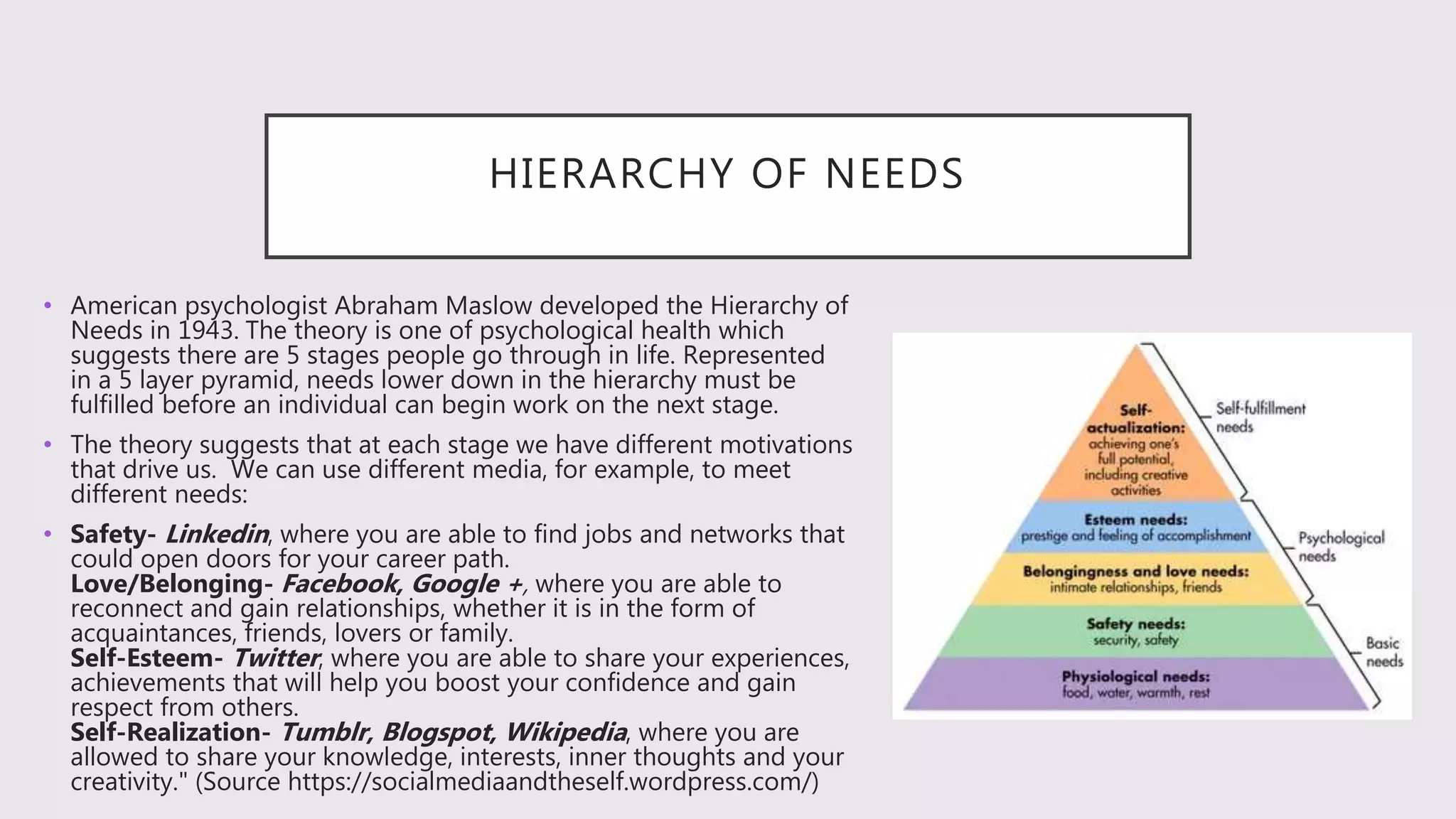
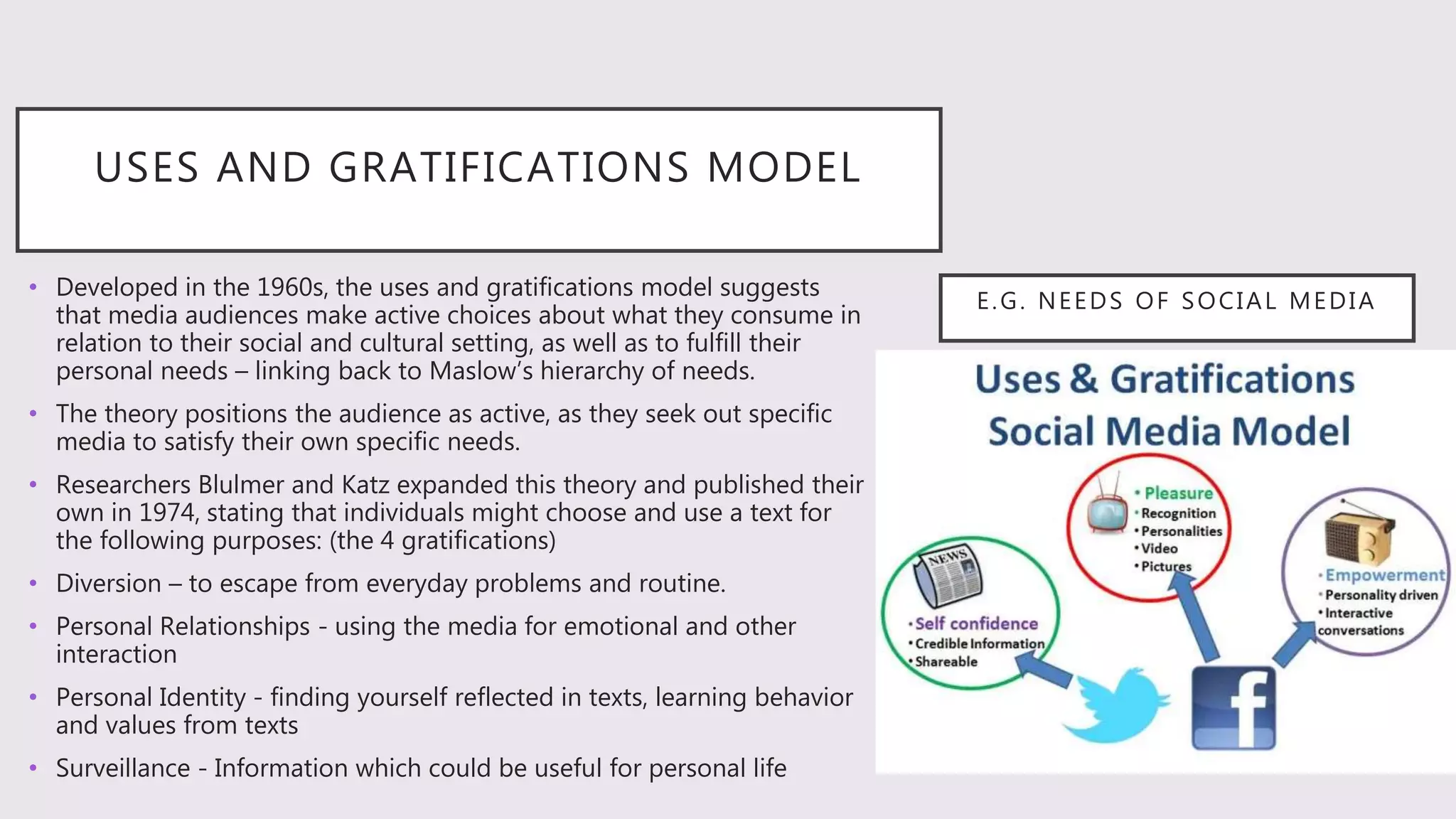
- The uses and gratifications model sees audiences as active in choosing media to fulfill personal needs like relationships, identity, and information.
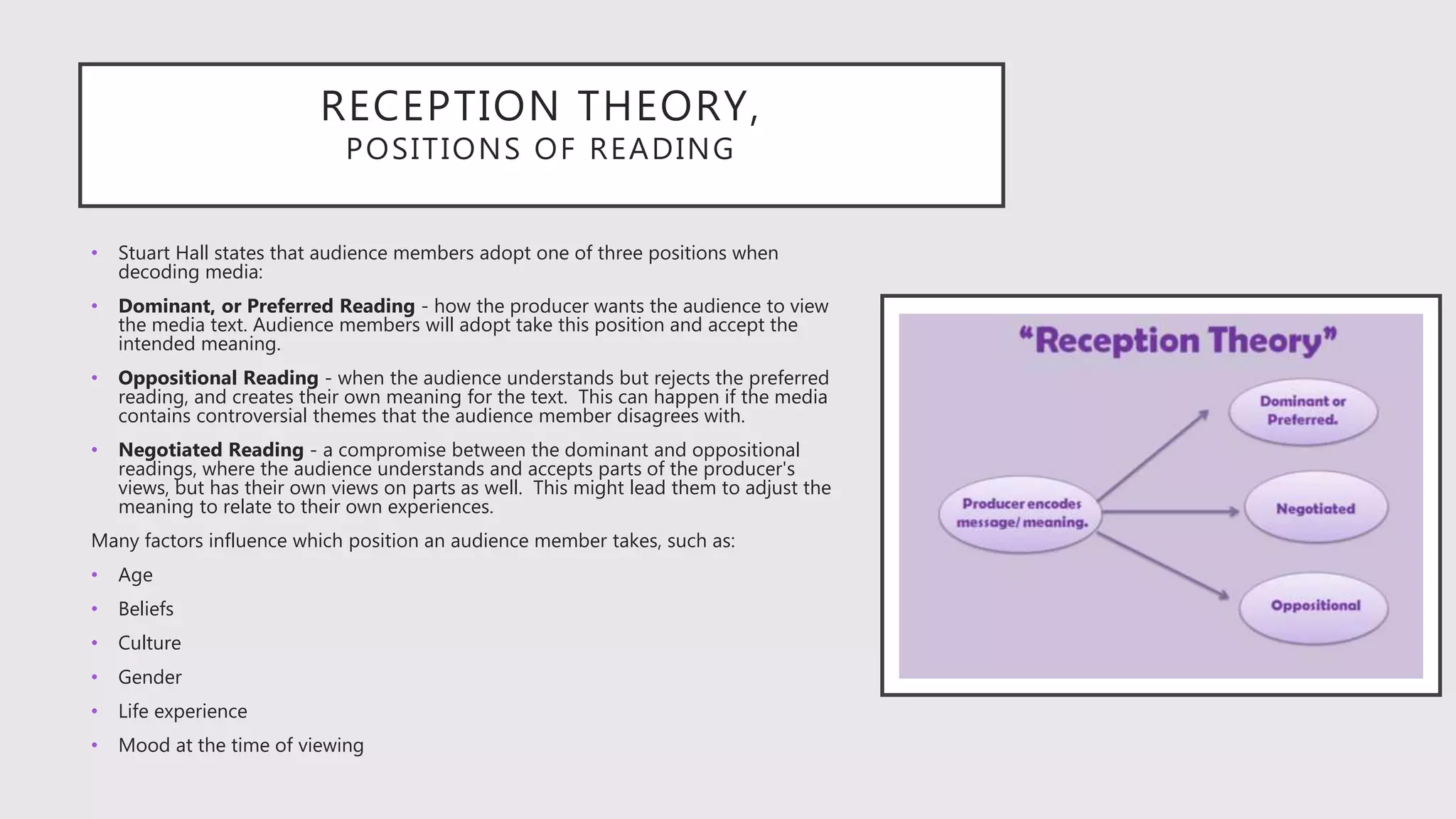
- Reception theory argues audiences actively interpret media based on their own experiences and backgrounds, adopting dominant, oppositional, or negotiated readings.
- More recent theories recognize interactive audiences who both consume and produce media as prosumers through social media platforms.