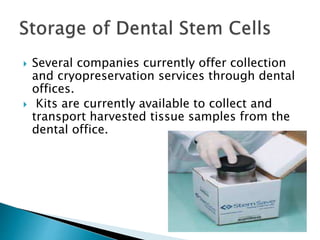
Denise Resen will give an informative speech on dental stem cells. She will discuss what dental stem cells are, the benefits they provide, how they are harvested and stored, and when this new technology will be available. Dental stem cells are unspecified cells harvested from extracted teeth that can be stored for future use in treating diseases and regenerating tissues. They are an accessible stem cell source and pose fewer ethical issues than other sources. Current technology allows for their storage in dental offices using collection kits.