Managing Acoustic Neuromas: Surgery and Radiotherapy Options
- 1. ROLL NO. :25
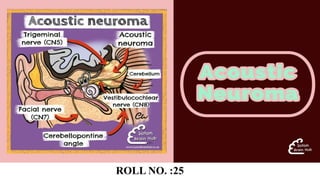
- 3. ACOUSTIC NEUROMA Tumor of VIIIth cranial nerve Acoustic Neuroma also known as VESTIBULAR SCHWANNOMA, NEURILEMMOMA Or VIIIth NERVE TUMOUR Incidence: It constitutes of around 80% of cerebellopontine angle tumours and 20% of all brain.
- 5. PATHOLOGY Gross: Benign, encapsulated, slow growing tumour of the VIIIth cranial nerve. Microscopy: Elongated spindle cells. Rod shaped nuclei lying in rows or palisades
- 6. ORIGIN AND GROWTH Origin: • The tumour almost always arises from the schwann cells of the vestibular. • Rarely from the cochlea division of VIIIth nerve within the external auditory canal. Growth: • Causes widening and erosion of the canal and then appears in cerebellopontine angle.
- 7. CEREBELLOPONTINE ANGLE Triangular space in the posterior cranial fossa. ANATOMY Bounded by: Tentorium- Superiorly Brainstem- Posteromedially Petrous part of temporal bone- Posteriorly laterally It is important landmark anatomically and clinically as it is occupied by CPA cistern, which houses the C.N. Vth , VIth , VIIth , VIIIth
- 8. • It grows: Antero-superiorly - to involve Vth nerve Inferiorly – to involve IXth , XIth nerve • In later stages it causes displacement of the brain stem pressure on cerebellum and raised intracranial lesion.
- 9. CLASSIFICATION ACOUSTIC NEUROMA Intracanalicular (confined to internal auditory canal) Small size (up to 1.5cm) Medium size (1.5-4cm) Large size (over 4cm)
- 10. CLINICAL FEATURES • Age and sex : - Mostly seen in age group of 40 to 60 years. - Both sexes are equally affected. • COCHLEOVESTIBULAR SYMPTOMS: -Earliest symptoms when tumour is still intracanalicular. -Caused by pressure on cochlear or vestibular nerve fibres or on the internal auditory artery. -Progressive unilateral sensorineural hearing loss - Tinnitus
- 11. Mark difficulty in understanding speech: • Imbalance / unsteadiness- Vestibular symptoms • Vertigo • Sudden hearing loss • Fullness in the ear
- 12. CRANIAL NERVE INVOLVEMENT 1. 5th Nerve: Earliest nerve to be involved. Reduced corneal sensitivity Numbness or paraesthesia of face. Involvement indicates – Tumour size = 2.5 cm and occupies the cerebellopontine angle 2. 9th and 10th nerve – Dysphagia and Hoarseness-Due to palatal, pharyngeal and laryngeal paralysis 3. Other cranial nerves : XIth , XIIth, IIIth IVth and VIth are affected when tumours are very large
- 13. 4. Facial nerve • Sensory fibres are affected early. • Hitzelberger’s sign: Hypoaesthesia of posterior meatal wall. • Loss of taste (Tested by- Electrogustometry) • Schirmer test: Reduced lacrimation. • Motor fibres: Affected late • Delayed blink reflex
- 14. BRAINSTEM INVOLVEMENT • Ataxia • Weakness & Numbness of arms and legs • Exaggerated tendons reflexes RAISED INTRA-CRANIAL TENSION • Headache • Nausea • Vomiting • Diplopia (VIth) • Papillo-edema with blurring of vision.
- 15. CEREBELLAR INVOLVEMENT • Pressure symptoms on cerebellum are seen in large tumors. Revealed by: Finger nose test Knee-heel test Dysdiadochokinesia (Inability to perform rapid alternative muscles movement) Ataxic gait Inability to walk along a straight line (tendency to fall on the affected side)
- 17. AUDIOLOGICAL TESTS A) PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY : PTA with AC and BC will show sensorineural hearing loss, more marked in high frequencies. B) SPEECH AUDIOMETRY It shows poor speech discrimination and this is proportionate to pure tone hearing loss. Roll-over phenomenon : Reduction of discrimination score when loudness is increased beyond a particular limit is most commonly observed.
- 18. NOTE : SISI and Threshold Tone Decay are not sensitive or specific and have been abandoned in favour of imaging techniques.
- 19. VESTIBULAR TEST A) CALORIC TEST : • Diminshed or absent response in 96% of patients. • May be normal, when tumour is small.
- 20. BERA • BRAINSTEM-EVOKED RESPONSE AUDIOMETRY • Useful in the diagnosis of retrocochlear lesions. • In the presence of the VIIIth nerve tumour, a delay of >0.2 ms in wave V between two ears is significant.
- 22. IMAGING STUDIES 1) MRI with Gadolinium contrast : GOLD STANDARD More sensitive and specific. Non-invasive and free of radiation hazards to the patient. Can detect even intracanalicular tumours of few millimetres.
- 24. 2) Computed Topography (CT) Scan : Can show any erosion of the temporal bone. 3) Plain X-rays : Different views : • Transorbital • Stenver’s • Towne’s • Submentovertical
- 25. 4) Vertebral angiography : Helps to differentiate acoustic neuroma from other tumours of cerebellopontine angle.
- 26. CSF EXAMINATION Protein level is raised. Lumbar puncture is usually avoided.
- 27. IMPORTANT TESTS FOR AN WORK-UP • PTA • Speech discrimination curve • Roll-over curve • Evoked response audiometry • Imaging studies
- 28. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS • Acoustic Neuroma • Meningioma • Epidermoid (cholesteatoma) • Arachnoid cyst • Schwannoma of other cranial nerves • Aneurysm • Glomus tumour • Metastasis
- 29. Management Of Acoustic Neuroma Chinmay Sharma 19027
- 31. Surgery: • Treatment of choice • Various approaches are: 1) Middle cranial fossa approach 2) Translabyrinthine approach 3) Suboccipital (retrosigmoid) approach 4) Combined translabyrinthine-suboccipital approach
- 32. 1)Middle cranial fossa approach: • Ultimate goal of this approach is to expose the Internal Auditory Canal (IAC) from the roof of the petrous temporal bone. • Smaller tumours are removed that are typically confined to internal auditory canal. • Only procedure that fully exposes the lateral third of the internal auditory canal without sacrificing hearing. • Adequately exposes the facial and superior vestibular nerves within the IAC. • Hearing is preserved.
- 33. Middle cranial fossa approach
- 34. Translabyrinthine approach: • Indicated in: Tumours >2.5 cm Poor preoperative hearing • Provides the best view of the lateral brain stem and CPA facing the acoustic tumor. • Hearing sacrifice is complete and unavoidable. • Allows early identification of facial nerve and its preservation • A C-shaped incision is planned behind the ear as needed to expose the mastoid tip, sigmoid sinus and transverse-sigmoid junction.
- 35. • In this approach (1) Tumour size is not a limiting factor; (2) It allows early identification of facial nerve in the IAM and its preservation; (3) Cerebellar retraction is not required. Incision in Translabyrinthine approach
- 37. Suboccipital (retrosigmoid) approach • Posterolateral neurosurgical technique to access various posterior fossa structures and even extends into the middle fossa • A surgical approach to the cerebellopontine angle through the occipital bone posterior to the sigmoid sinus. • Least extensive soft tissue dissection and bony removal. • Hearing-sparing technique • Can be applied to all acoustic tumors • Destruction of the labyrinth is not required
- 38. • May require cerebellar retraction or resection. provides opportunities for CSF leak and postoperative edema, hematoma, infarction, and bleeding. • skin incisions: 1)Linear, 2)Lazy S-shaped, 3)C-shaped, and 4)Curvilinear inverted U-shaped incisions
- 40. Combined translabyrinthine-suboccipital approach • In translabyrinthine approach, separation of tumours adherent to brain stem and exposure of vital arteries and cranial nerves may be compromised; total removal may not be possible • In suboccipital approach, it is often difficult to preserve facial nerve and remove the portion of tumour in the petrous bone. • In combined approach: Translabyrinthine approach- Facial nerve preservation Retrosigmoid approach- tumour removal.
- 41. Comparision
- 42. Approach will depend on: •Size •Location •Quality of preoperative hearing •Hearing preservation
- 43. Size • Opportunities for hearing conservation decrease as tumors become larger. • It is much more difficult to conserve when tumors are >2.5cm in diameter. • Surgeons limit hearing conservation surgery to smaller tumors • Prefer translabyrinthine approach to maximize the chance of facial nerve conservation for larger tumors.
- 44. Location •Lies within the lateral portions of the internal auditory canal- Middle cranial fossa approach •Significant volume medial to the plane of the Internal acoustic meatus- Retrosigmoid approach
- 45. Quality of preoperative hearing •If the patient has no useful hearing, either the translabyrinthine or the retrosigmoid approach is selected.
- 46. Hearing preservation • Hearing completely preserved: Middle cranial fossa approach • Hearing preservation depends on size of tumour: Retrosigmoid approach • Hearing loss unavoidable: Translabyrinthine approach
- 47. Radiotherapy •X-knife or Gamma knife surgery •Cyber knife
- 48. X-knife surgery • Form of stereotactic radiotherapy • Radiation energy converged on the tumour • Minimal effect on the surrounding normal tissue • Cause arrest of growth and reduction in size • Indication:1)Patient who refuse surgery 2) Surgery is contraindicated 3) Residual tumour left after surgery
- 49. Cyber knife •Improved form of X-knife surgery •Without skull frame for stereotactic localization •More accurate •Uses real-time image guidance technology.