Respiration
- 1. Respiration
- 2. Why do living organisms respire? • Living organisms needs: Energy to move Excrete Grow Reproduce • In all living cells, including plants and animals, food molecules are broken down by a reaction called oxidation • Respiration is the oxidation of food substances with the release of energy in living cells
- 3. Respiration • There are two kinds of Respiration: Aerobic respiration It is the oxidation of food substances in the presence of oxygen with the release of a large amount of energy Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy C6H12O6 + O2 → H2O + CO2 + ATP Anaerobic respiration It is the breakdown of food substances in the absence of oxygen • The energy that is released by respiration packed as another molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) • Anaerobic respiration release less energy than aerobic respiration
- 4. Some examples of energy consuming process in organisms: • The synthesis of protein from amino acid • Building up cells • Cell division • Muscular contraction • respiratory movement • Active transport • Transmission of nerve impulses
- 5. Anaerobic Respiration • Anaerobic respiration releases less energy than aerobic respiration • Yeast needs a little amount of energy to survive Yeast release ethanol and carbon dioxide as waste products anaerobic respiration in yeast is called alcoholic fermentation Glucose→ ethanol + carbon dioxide + small amount of energy C6H12O6 → C2H5OH + CO2 + ATP
- 6. Energy conversion in muscle cells • Muscle respire aerobically • When less oxygen is available, muscles will respire anaerobically for short time • During intensive exercise, aerobic respiration is unable to produce enough energy to meet the demands The muscles produce extra energy by anaerobic respiration Lactic acid is produced in this process
- 7. Energy conversion in muscle cells The equation of anaerobic respiration in your muscles is: Glucose → 2 Lactic acid + small amount of energy C6H12O6 → 2 C3H6O3 + ATP When there is insufficient oxygen to meet the demands of the vigorous muscular contractions, the muscles are said to incur an oxygen debt During the period of rest, the breathing rate continues to be the fast for some time. This is to provide sufficient oxygen to repay the oxygen debt • Lactic acid builds up in the muscles and cause fatigue and muscular pains Lactic acid is transported to the liver and converted back into glucose Oxygen debt is the amount of oxygen required to oxidize the lactic acid produced in the muscles during anaerobic respiration
- 9. Gas exchange system in humans Nose • Air usually enters your body through the two external nares (nostrils). The wall of the nostril has a fringe of hairs • The nostrils leads into two nasal passages Which lined with a moist mucous membrane • Breathing though the nose has the following advantage: Dust, bacteria and foreign particles trapped by: 1. hairs in the nostrils 2. Mucous in the mucus membrane Air is warmed up before entering the lung Harmful substances may be detected by small sensory cells in mucus membrane
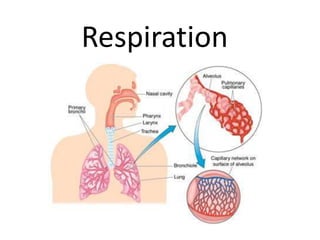
- 10. • The air in the nasal passages enters the pharynx then larynx and then into the trachea through an opening known as glottis. • Trachea is supported by C-ring shaped cartilage to keep it open • Trachea divides into two tubes, the bronchi, one to each lung • Each bronchus divides into very fine bronchioles • Each bronchiole ends in a cluster of air sacs
- 11. The Respiratory Epithelium of the Nasal Cavity and Conducting System Figure 23.6a, b • The thinner wall of the trachea and bronchi are lined by cilia • Gland cells secrete mucus to trap dust and bacteria • The cilia sweep these particles up into the pharynx • From the pharynx, they are swallowed into the esophagus or removed by coughing
- 12. The Lung • Each lung lies inside pleural cavity The pleural cavity is lined by two transparent elastic membranes called pleural membranes The pleural cavity contains lubricating fluid to reduce friction during breathing • Thousands of alveoli (air sacs) are found inside the lung Alveoli provide a very large surface area for gaseous exchange
- 13. How are the lungs adapted for efficient gaseous exchange? 1. The numerous alveoli provide a large surface area 2. The alveoli are richly supplied with blood capillaries 3. The wall of the alveolus and capillary is only one cell thick (diffusion of gases is easy) 4. The wall of alveolus is covered with thin moist film. This allows oxygen to dissolve in it
- 15. The Chest Cavity • Chest wall is supported by ribs. • Your ribs are attached dorsally to the backbone • And attached ventrally to the chest bone or sternum 10 pairs only are attached to the sternum 2 pairs are free • External and internal coastal muscles are found between ribs These muscles are antagonistic ( one contract other relax) • The thorax is separated from the abdomen by elastic muscle sheet called diaphragm Diaphragm move down ward and upward during breathing
- 17. Inspiration or Inhalation Inspiration means breath in. 1. Diaphragm contract and push down 2. External coastal muscles contract 3. Internal coastal muscle relax 4. Ribs move upward and forward 5. Volume of the thoracic cavity increase 6. Pressure in the lungs decrease 7. Air moves into the lung
- 18. Expiration and exhalation Inhalation means breath out 1. Diaphragm relax and push up 2. External coastal muscles relax 3. Internal coastal muscle contract 4. Ribs move downward and inward 5. Volume of the thoracic cavity decrease 6. Pressure in the lungs increase 7. Air moves out of the lung
- 19. Gaseous exchange in alveolus • Gaseous exchange in the lungs takes place by diffusion • The alveolus has: High concentration of oxygen Low concentration of carbon dioxide • Blood entering the lung has: Low concentration of oxygen High concentration of carbon dioxide
- 22. How is Carbon dioxide removed from your body? In the tissues: • Carbon dioxide diffuses to the blood and enter red blood cells • Carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid in the red blood cells • This reaction in the presence of enzyme carbonic anhydrase • The carbonic acid then converted to hydrogencarbonate ions • Hydrogencarbonate diffuse out of the red blood cell and carried by plasma to the lungs In the lungs: • Hydrogencarbonate ions diffuse back into red blood cells and converted into carbonic acid • Then carbonic acid converted to water and carbon dioxide • The carbon dioxide then diffuses into the alveoli Also a small amount of CO2 is carried and dissolved in the blood