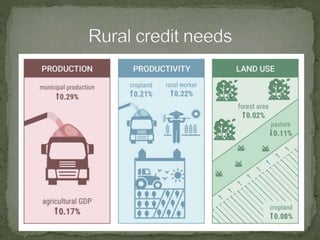
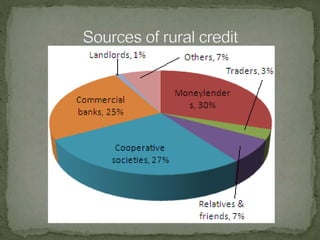
Rural development aims to improve living conditions in rural areas through agriculture development and other initiatives. It targets improvements in human resources, land reforms, infrastructure, poverty alleviation, and local resources. Rural development includes short, medium, and long-term credit from various sources for productive and unproductive purposes. It also involves agriculture marketing through assembly, storage, processing, transport, and distribution of commodities. Government interventions include market regulation, infrastructure, cooperatives, minimum prices, grading, and information dissemination to support rural development.