GSM5421 Investment Analysis MBA Quick Notes
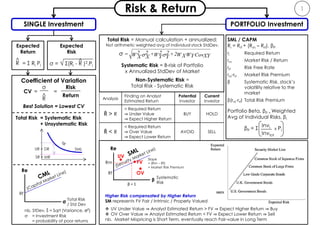
- 1. 1Risk & Return PORTFOLIO Investment Expected Return = Σ Ri Pi ^ R σ = √ Σ(Ri - R )2.Pi Expected Risk ^ SINGLE Investment Analysis Finding on Analyst Estimated Return Potential Investor Current Investor Ȓ > R > Required Return ⇒ Under Value ⇒ Expect Higher Return BUY HOLD Ȓ < R < Required Return ⇒ Over Value ⇒ Expect Lower Return AVOID SELL CV = = σ ^ R Risk Return Coefficient of Variation Best Solution = Lowest CV Invi Invtot βP = Σ x Pi SML / CAPM Ri = Rrf + (Rm – Rrf). βP ri Required Return rm Market Risk / Return rrf Risk Free Rate rm-rrf Market Risk Premium β Systematic Risk, stock’s volatility relative to the market β(rm-rrf) Total Risk Premium Portfolio Beta, βP = Weighted Avg of Individual Risks, βi UR = DR SR = MR SML Higher Risk compensated by Higher Return SM represents FV Fair / Intrinsic / Properly Valued UV Under Value ⇒ Analyst Estimated Return > FV ⇒ Expect Higher Return ⇒ Buy OV Over Value ⇒ Analyst Estimated Return < FV ⇒ Expect Lower Return ⇒ Sell nb. Market Mispricing is Short Term, eventually reach Fair-value in Long Term Rf σ Re Total Risk / Std Dev nb. StDev, ŝ = Sqrt (Variance, σ2) σ = Investment Risk = probability of poor returns Rm Rf β Re β = 1 UV OV FV Systematic Risk Slope = (Rm – Rf) = Market Risk Premium Total Risk = Systematic Risk + Unsystematic Risk Total Risk = Manual calculation + annualized; Not arithmetic weighted avg of individual stock StdDev. Systematic Risk = Β-risk of Portfolio x Annualized StdDev of Market Non-Systematic Risk = Total Risk - Systematic Risk
- 2. Interest Rate Risk Purchasing Power Risk Business / Liquidity Risk Financial / Credit Risk Operational Risk Systematic Risk (Macro) ▌ @ Non-diversifiable Risk, Undiversifiable Risk, Market Risk, Economic Risk, Volatility, Beta Risk ▌ Inherent and associated to entire market, not just a particular stock or industry ▌ Underlies all other investment risks ▌ Impossible to mitigate by Portfolio Diversification ▌ Reduce exposure through hedging ▌ Higher Undiversifiable Risk rewarded by Higher Return ▌ Beta = volatility compared to overall market > 1 means more systematic risk than the market < 1 means less systematic risk than the market = 1 means the same systematic risk as the market Unsystematic Risk (Micro) 2 ▌ @ Non-systematic Risk, Unsystematic Risk, Diversifiable Risk, Company Specific Risk, Portfolio Risk, Residual Risk ▌ Very broad group or individual securities, as stocks of particular jurisdiction tend to move together ▌ Mitigation through Diversification – mix / different companies, industries, uncorrelated assets, securities, time frame, required rate of return and risk tolerance Total Risk Absolute Relative Directional Non Directional Volatility Exchange Rate GDP Industrial Growth Price Reinvestme nt Rate Political Governme nt Policies Scams War Like Situation Monsoon Natural Calamities Internation al Events Demand Inflation Cost Inflation Internal External Cash Flow Default Portfolio Exposure Rate Recovery Rate Credit Event Sovereign Settlement Borrowings Model People LegalRecession New Competitor Product Recall Policy Political Political Market Risk
- 3. 3 Non-Fixed Income: Stocks rs = rrf + (rm – rrf). β rs Required Rate of Return rrf Risk Free Rate β Beta Risk rm Mkt Risk rm – rrf Mkt Risk Premium β(rm – rrf) Risk Premium Dn Dividend in Yr n g Growth Rate Dividend Yield = Dn+1/Pn Price, Pn+1 = Pn (1+gn) Dividend, Dn+1 = Dn (1+gn) Multiple / Supernormal Growth Dividend & Capital Gains Yld not constant. Capital Gains Yld ≠ g. 1. Tabulate FCF = NOPAT – Net Capital Investment 2. TV = Stock Price when dividend growth constant 3. NPV = ΣPV(Future Div + FCFs - Debts - PrefShrs) - InitOutlay 4. Market Value (MV) = NPV / NOSH (common stock) Relative Valuation • Price to Earning (P/E) • Price to Sales (P/S) • Price to Cash Flow (P/CF) • Price to Book Value (P/BV) • Enterprise Val to EBITDA (EV/EBITDA) • Enterprise Val to Revenue (EV/Revenue) Discounted Cash Flow / Present Value Best Method – Represent Expected Cashflows & Arbitrages. Problem: Intrinsic value subject to quality of forecast. Value of Returns = PV of future benefits = PV of Dividends + Free Cash Flow (e.g. Capital Gains) Intrinsic Value = Fair / Expected Value FA Indicator IV > MP Under-Priced IV = MP Fairly Valued IV < MP Over-Priced Asset Based / Book Value Useful when firm has high tangible assets + liabilities, or low proportion intangible assets, or deteriorating business (worst-case). 1.Statement of Comp Income / Balance Sheet 2.Book Value of assets and liabilities 3.Value of additive parts 4.MV(Equity) = MV(Assets+Liabilities–PrefShares) 5.Divide by NOSH Problem: 1. Difficult to determine MV of Asset (PPE) 2. Intangibles not on balance sheet, e.g. IP, synergies, reputation 3. If intangibles significant, use floor value or fwd CF 4. Difficult to estimate in hyper-inflation environment = (1 + ) Dividend Discount Model (DDM) Present Value of all future dividends generated = (1 + ) Corporate Value Model or Free Cash Flow (FCF) or Operating Cash Flow Subject to growth rate. Constant Growth g constant forever rs > g = − = (1 + ) − Zero Growth Dividend is Perpetual, g=0 = Multiplier: Estimate based on multiples of share price or enterprise value to certain comparable value or fundamental value, e.g. earnings, EBITDA, book value, sales, cashflow. EV = Total Market Capitalization plus Liabilities plus Preferential Shares less Cash and equivalents. • Fwd basis, e.g. EPS forecast for next year • Trailing basis, e.g. EPS for past year • Must be consistent across companies Favorite price multiples include: • Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E) most frequently cited, or to EBITDA • Price-to-Book ratio (P/B) • Price-to-Sales ratio (P/S) • Price-to-Cashflow ratio (P/CF), i.e. free cashflow (FCF), operating cash flow (OCF) Price multiples is then analyzed using DCF method, e.g. Gordon growth model. Comparable: Based on relative values of price multiples, which is the most widely used approach by analysts; both cross-sectional (versus the market or another comparable) and in time series. Approach easy to calculate and beneficial for particular industry / sector, which need to identify the best performing stocks within sector. Large firms operate different lines of business, scale and scope. Problem: Choice of comparable. Price and enterprise ratios do not consider the future. CF1 CF2 CF3 CF4 Growth g1 g2 G3 gt Dividend D1 D2 = D1(1+g) D3 = D1(1+g) D4 = D3 Price , = − NPV (1 + ) (1 + ) (1 + ) + (1 + ) Yr1 Yr2 Yr3 Yr4 to forever Terminal Value
- 4. Intrinsic Value = Fair / Expected Value FA Indicator IV > MP Under-Valued IV = MP Fairly Valued IV < MP Over-Valued Terminal Value Super Normal Growth Dividend & Cap Gains Yld not constant. Cap Gains Yld ≠ g. 1. Company Strategic Analysis 2. Establish Key Assumptions / Strategy 3. Tabulate FCF = NOPAT – Net Capital Investment 4. TV = Stock Price when dividend growth constant 5. NPV = ΣPV(FutDiv + FCFs - Debts - PrefShrs) - InitOutlay 6. Market Value (MV) = NPV / NOSH (common stock) Yr1 Yr2 Yr3 Yr4 to forever 4 Non-Fixed Income: Stocks rs = rrf + (rm – rrf). Β Growth, g Price, Pn+1 = Pn (1+gn) Div Yield = Dn+1/Pn Div, Dn+1 = Dn (1+gn) 4. Precedent Transactions 1. Define M&A transaction same profile • Business activity, geo-location, transaction / buyer, scale, growth, recent time period 2. Find Past Transactions • Price paid • Consideration (cash / shares) • Takeover premium (implied or explicit) • Synergies (if available) • Other terms / conditions 3. Build Table & Ratios at transaction time 4. Calc Avg Multiples (Median if outliers) 5. Work backward towards EV • Earning, EBITDA, EBIT, Sales, CF, CE, BV 2. Discounted Cash Flow / Present Value Best Method = Represent Expected Cashflows & Arbitrages. Problem: Intrinsic value subject to quality of forecast. Value of Returns = PV of future benefits = PV of Dividends + Free Cash Flow (e.g. Capital Gains) 1. Book Value / Asset-Based Useful when firm has high tangible assets + liabilities, or low proportion intangible assets, or deteriorating business (worst-case). 1.Statement of Comprehensive Income or Balance Sheet 2.Book Value of assets & liabilities 3.Value of additive parts 4.Equity = Assets – Liabilities – PrefShares; or Equity = Share Capital – Treasury Shares + Retained Earnings + Other Stockholder Equity 5.Divide by NOSH Problem: 1. Difficult to determine MV of Asset (PPE) 2. Intangibles not on balance sheet, e.g. IP, synergies, reputation 3. If intangibles significant, use floor value or fwd CF 4. Difficult to estimate in hyper-inflation environment = (1 + ) Dividend Discount Model (DDM) Present Value of all future dividends generated = (1 + ) Corporate Value Model or Free Cash Flow (FCF) or Operating Cash Flow Subject to growth rate. Constant Growth g constant forever, rs > g = − = (1 + ) − Zero Growth Dividend is Perpetual, g=0 = CF1 CF2 CF3 CF4 Growth g1 g2 G3 gt Div D1 D2 = D1(1+g) D3 = D1(1+g) D4 = D3 Price , = − NPV (1 + ) (1 + ) (1 + ) + (1 + ) 3. Comparable / Relative Value 1. Select COMPS Universe / Peers same profile • Industry, activity, geo-location, scale, growth, profitability, acc’ policies, capital structure 2. Download Historical / Trailing Data • Revenue, GrossProfit, EBITDA, EBIT, NPAT • NOSH, SharePrices, Cash, Debt, Minority interest 3. Download Forecast Metrics • Revenue, Gross profit, EBTIDA, EBIT, net income 4. Build Forward Table • MarketCap, EV, Ratios, Growth, Margins, etc 5. Calc Average Multiples (Median if outliers) Enterprise Value Ratio (Before Interest Paid) – EV to EBITDA (Common for DCF analysis = core revenue) – EV to EBIT – EV to Revenue = EV/EBIT x EBIT/Sales – EV to CE = EV/(BVDebt+Equity) Equity Value Ratio (After Interest Paid) – Price to Earning (P/E) = MC/NetEarnings – Price to Book Value = MC/BookValue – Price to Cash Flow 6. Work backward towards Market Cap or EV • Earning, EBITDA, EBIT, Sales, CF, CE, BV Multiple Characteristics Stage EV /Sales • No cash or profit • Pattern of sales clear • Ignores operating economics • Ignores capital structure • Early sign growth • Rapid growth EV/EBITDA • Operating cash flow positive • Incorporates profitability • Ignores capital structure • Ignores tax differences • Rapid growth • Slowing growth EV/EBIT • Operating profit • Ignores capital structure • Ignores tax differences • Slowing growth • Maturity P/E • Stable operating economics • Stable capital structure • Profit & cash flow similar • Early maturity • Late maturity Gross Profit = Revenue - Variable Cost EBITDA = Gross Profit - Fixed Cost EBIT = Oper Profit = EBITDA - NonCash EBT = EBIT - Cost of Debt NOPAT = EBT (1-Tax) OCF = NOPAT + NonCash ± ∆WorkgCap FCF = OCF (PreInvest CF) + CAPEX EV = MarketCap + NetDebt Net Debt = Interest Bearing Debt – Cash Eqv
- 5. Valuation Metrics Lions Gate Trading Precedents Warner** EV/EBITDA* 13.7x / 11.4x 7.4x – 18.1x 8.3x – 27.6x 10.1x EV/Sales* 1.8x / 1.7x 1.8x – 3.6x 1.2x – 5.3x 2.7x P/E* 27.1x / 18.9x 13.3x – 40.9x 21.2x 17.1x EBITDA Margin 9.5% 23% – 30% 3% – 55% 23.2% Net Income Margin 8.5% 8% – 15% 26% 12.7% 5Sample Valuation Summary Broker Estimates (M/D/Y) Results Period Revenues ($mm) EBITDA($mm) EBITDA Margin (%) EV/EBITDA P/E RBC (11/18/2013) Target Price $38.00 2014E 2,791 359 12.9% NA NA EV ($mm) NA 2015E 2,887 407 14.1% NA 26.1x J.P. Morgan (05/31/2013) Target Price $32.00 2014E 2,651 345 13.0% 13.9x 24.7x EV ($mm) $4,795 2015E 2,851 408 14.3% 11.8x 18.2x Evercore (11/10/2013) Target Price $42.00 2014E 2,877 375 13.0% 13.2x 30.7x EV ($mm) $4,945 2015E 3,049 471 15.4% 10.5x 20.2x 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 $0 $5 $10 $15 $20 $25 $30 $35 $40 LGF Current: $31.64 52wk High: $15.26 52wk Low: $37.81 *P/E and EV/EBITDA are based on FY14 and FY15 to reflect imminent growth; **based on FY14 GUY appears to be valued fairly relative to peer group but peer group valuation has come down recently Current Price low relative to Two-Year Trading Range due to recent drop in sector and overall market index One-year Analyst forecasts are optimistic due to: – Expected de-risking of asset priced into target – Expected resource update (Q1 2012) There may be benefit to further de-risking as current valuation may not be optimal time to sell Stock has outperformed based on strong cashflows from Twilight and Hunger Games in 2012 Current multiples are high but compress in FY14 / FY15 as growth is realized Industry multiples support share price but only if Hunger Games meets its forecast Further upside could be possible if another hit is produced but downside risk is more significant Lions Gate produced limited or no free CF in 2007-2011 despite big successes Football Field Analysis Factors to Stock Price Performance
- 6. Proposition Weak form EMH Semi-strong form EMH Strong form EMH Market is Efficient Efficiently priced wrt historical info ⸫ Exploit public info using FA Efficiently priced wrt historical & public info ⸫ Exploit private / insider info Efficiently priced wrt to historical, public & insider info ⸫ Cannot consistently beat mkt Market is NOT Efficient Inefficiently priced wrt historical info Exploit by BF Inefficiently priced wrt historical info Exploit by BF Inefficiently priced wrt historical info Exploit by BF 6Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) Fama (1969) States that mkt tend to be correctly & efficiently priced. Most mkts including Malaysia, US, China, Singapore are in the Semi-Strong Form. Under developed countries exist in the Weak Form. No country in Strong Form. Fundamental Analysis (FA) = Fair Value or Intrinsic Value Indicator Technical Analysis (TA) = Buy / Hold / Sell or Entry / Exit Signal Behavioral Finance (BF) = Market Sentiments / Speculation Speculators and traders still make money from small + short term mispricing opportunities, due to: Different method for stock valuation (DCF, comparable, dividend) Different source of information Different frequency Market delays / response However, FA & TA & BF is an art & not science Paralysis of Analysis = Complicated Decision Historical Analysis Scenario Analysis Return RA = (SR)/n = AVERAGE RG = [P(Return Relatives)]1/n – 1 = GR E(R) = S Pi Ri Risk s2 = [S(Rt-RA)2]/n-1 s = √{[S(Rt-RA)2]/n-1} = STDEV s2 = SPi[Ri-E(R)]2 s= √ {SPi[Ri-E(R)]2} CV CV = s/RA CV = s/E(R) Pot Return Rpot= w1 R1 + w2 R2 E(Rpot) = w1 R1 + w2 R2 Pot Risk σpot 2 = w1 2σ1 2 + w2 2σ2 2 + 2W1W2 Cov(r1r2) σpot 2 = w1 2σ1 2 + w2 2σ2 2 + 2W1W2 Correl(1,2)*σ1σ2-VARp σpot = √σpot 2 (STDEVp) σpot 2 = w1 2σ1 2 + w2 2σ2 2 + 2W1W2 Cov(r1r2) σpot = √σpot 2 Arithmetic Mean = Simple avg of series of returns. Calculated by summing all of returns in the series and dividing by the number of values. Geometric Mean = Return that if earned in each of n years of an investment’s life, gives same total dollar result as the actual investment.
- 7. Fixed Income: Bonds 7 N = Maturity Period / Duration @ Years to Maturity x Compounding (M) i.e. 1 yearly, 2 semi annual, 4 quarterly I/YR = YTM = Interest on Bond @ FV RM1000 to PV at I/YR PV = Present Value @ Price of Bond Sold / Purchased Inc. Floatation Cost at PVf = PV0 (1-FC) PMT = Coupon Payment or Cashflow at ROR or Promised Yield @ Coupon Rate x RM1000 FV = Par / Face Value Principal @ Redeem at Maturity i.e. RM1K CY = Current Yield = Annual PMT / (PV or Current Price) CGY = Capital Gains Yield = P1/P0 - 1 = Total Yield – Current Yield Expected Total Return = Expected CY + Expected CGY 1. Fixed Term & Coupon Rate 2. Floating Rate periodically review 3. Zero coupon 4. Inflation Linked 5. Callable 6. Convertible Factors affecting Bond, R = Rfr + Rinf + Rprem • Macro Economic Factors: Real Growth, Expected Inflation, Capital Market Liquidity, Supply / Demand Loans • Bond Characteristics: Bond Rating / Credit Quality, Terms to Maturity, Indenture Provision, Foreign Bond Risk • Coupon Rate: inverse var to sensitivity • Effective Maturity: Maturity & Duration: direct var to sensitivity YTC PMT & FV = same PV1 = PV0 + (Penalty RM or %) n = Reduced by lapsed Years YTC = I/YR x M Realized Rate of Return PMT & PV = same FV1 = FV0 + (Penalty RM or %) n = Lapsed Years YTC = I/YR x M MY > CR | PV < FV >> Bond Price at Premium MY = CR | PV = FV >> Bond Price at Par Value MY < CR | PV > FV >> Bond Price at Discount Call Provision • Non-Callable | Callable = Penalty • Most bonds have a deferred call & declining call premium • Refund bond if rates decline (helps issuer, but hurts investor) Bond Price Market Yield Bond Price Premium if CR > MY Par if CR = MY Discount if CR < MY P V Price Volatility V ∝ Duration Interest Bond Strategy • Portfolio Duration vs Interest • Passive: Buy + Hold | Indexing • Immunization (Interest Rate Risk): Price Risk vs Reinvestment Risk • Active: Forecast, Valuation Analysis & Credit Analysis (Altman Z-Score) Macaulay Duration • Modified Duration, Dmod = • Ym Nominal YTM M # payments per year 1 + Duration ΔPrice Price0 X 100% = - Dmod X ΔYield ,Yield Change in basis pts divided by 100 • Creditor • No voting rights / decision making
- 8. 8Hedging / Derivative Contracts FORWARD Contract Agreement between parties Specific amount + price + date Zero Sum Game = symmetric gains + loss Not Liquid. Credit Risk / Default Risk Realize Value at Expiration More popular in Currency Exchange Process: Negotiate Amount + Price + Date Engage Over-the-Counter Exchange Asset at Forward Rate FUTURES Contract Agreement between parties at Trading Floor of Exchange e.g. Chicago Mercantile Exchange Standardized Reverse position to offset future obligation More liquid. Less Risk / Default Risk Initial margin required (good faith) Others: Marking to Market, Maintenance Margin, Margin Calls Must be settled at Delivery Date Process: Order Contract via Broker Trade at Exchange Matched order sent to ClearingHouse Pay initial Margin (10% of total cost) Delivery of currencies at ClearingHouse OPTION Contract Standardized offered on Trading Floor of Exchange through brokers and Over Counter CALL Option Grants right to BUY specific stock at Exercise Price within specific time period Process: Buy Call Option = Rights to buy stock at fixed price Spot price ↑ ⇒ Payable Hedged Spot price ↓ ⇒ Let contract expire • In the Money: Future Price > EP+Prem • On the Money: Future Price = EP+Prem • Out the Money: Future Price < EP+Prem PUT Option Grants right to SELL specific stock at Exercise Price within specific time period Process: Buy Put Option = Rights to sell stock at fixed price Spot price ↓ ⇒ Receivable Hedged Spot price ↑ ⇒ Let contract expire • In the Money: Future Price < EP-Prem • On the Money: Future Price = EP-Prem • Out the Money: Future Price > EP-Prem Factors affecting Option Call | Put 1. Stock Price + - 2. Exercise Price - + 3. Time to Maturity + + 4. Stock Volatility + + 5. Interest Rate + - Secure Price against Forward & Futures Options Options Benefits Rising Stock Price Buy Long Position Take Delivery Call Risk Shifting / Insurance Price Formation / forgo profits Investment Cost ReductionDeclining Stock Price Sell Short Position Make Delivery Put Key D I F F E R E N C E 1.Contract Obligation / Regulation • Forward: Obligated / Self • Futures: Obligated by Commission / Association • Option: Optional / Clearinghouse 2.Currencies • Forward: Almost all stocks • Futures / Option: Commonly traded stocks 3.Size of Contract • Forward: Tailored to individual needs • Futures: Standardized, useless if excess • Option: Matching Concept 4.Delivery Date (popular with Forward) • Forward: Tailored to needs • Futures: Standardized • Option: Tailored to needs 5.Market Place / Clearing Operations • Forward: Major Banks & Brokers • Futures: Matching @ Central Exchange Floor • Option: Central Exchange Floor 6.Others • Forward: Not regulated • Futures: More complex but least expensive • Option: Premium charges • Futures & Option: Opportunity for Speculators PayoffDiagram CallOption PayoffDiagram PutOption
- 9. ▐ Definition: Pool of investment sourced from a number of individual investors ▐ Portfolio Performance = Stock Portfolio subject to Fund Manager’s ability to: derive above market / average return diversify portfolio completely to eliminate systematic risk ▐ Total Risk, = Std Dev of Portfolio Returns ▐ Systematic Risk = Undiversifiable Risk = Beta Risk Hi Risk rewarded by Hi Return ▐ Unsystematic Risk mitigated by Diversification Degree of Diversification = Correlation Coefficient, R2 (Portfolio Return vs Market Return) Market totally diversified when R2 = 1 If perfectly diversified, Sharpe & Treynor ranking identical ▐ Advantage: Diversification Liquidity Managed Professionally Flexible Choice, Market Returns (DLM.FM) ▐ Net Asset Value, NAV = [Market Value of Assets – Liabilities] [#Units of Outstanding] ▐ Mutual Fund Return = [(Income Dist.) + (Capital Gains Dist.) + (∆NAV)] [Beginning NAV] Jensen = Superior | Inferior Pot performance 9Mutual Funds Sharpe Ratio Reward to Variability Treynor Ratio Reward to Volatility Jensen Alpha, α Differential Return Asset Pricing Model CML CAPM / SML CAPM / SML Portfolio Measure SRpot = (Rpot - Rf) pot TIpot = (Rpot - Rf) βpot αpot = Rpot - Rf - βj.(Rmkt-Rf) Market Benchmark SRmkt = (Rmkt - Rf) mkt TImkt = (Rmkt - Rf) n/a Superior Portfolio SR > Mkt Benchmark ⇒ High SR = High Rank TR > Mkt Benchmark ⇒ High TR = High Rank α > 0 Average Portfolio SR = Mkt Benchmark TR = Mkt Benchmark α = 0 Inferior Portfolio SR < Mkt Benchmark TR < Mkt Benchmark α < 0