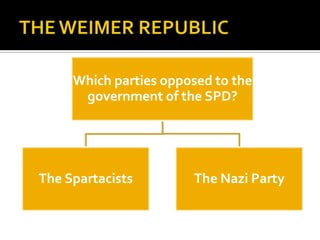
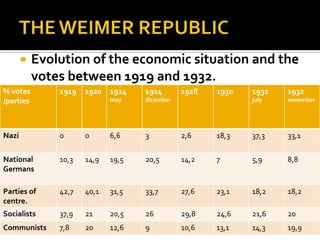
The document discusses the political situation and parties in Germany during the Weimar Republic after World War 1. It analyzes the Social Democratic Party (SPD) that governed and the opposition parties like the Spartacists and Nazi Party. It shows the Nazi Party receiving increasing votes from 1920-1932 elections. In 1932, the Nazi Party obtained the most votes and Hitler was appointed Chancellor by the President. When in power, Hitler purged the Nazi Party during the Night of the Long Knives in 1934 and consolidated his control over Germany.