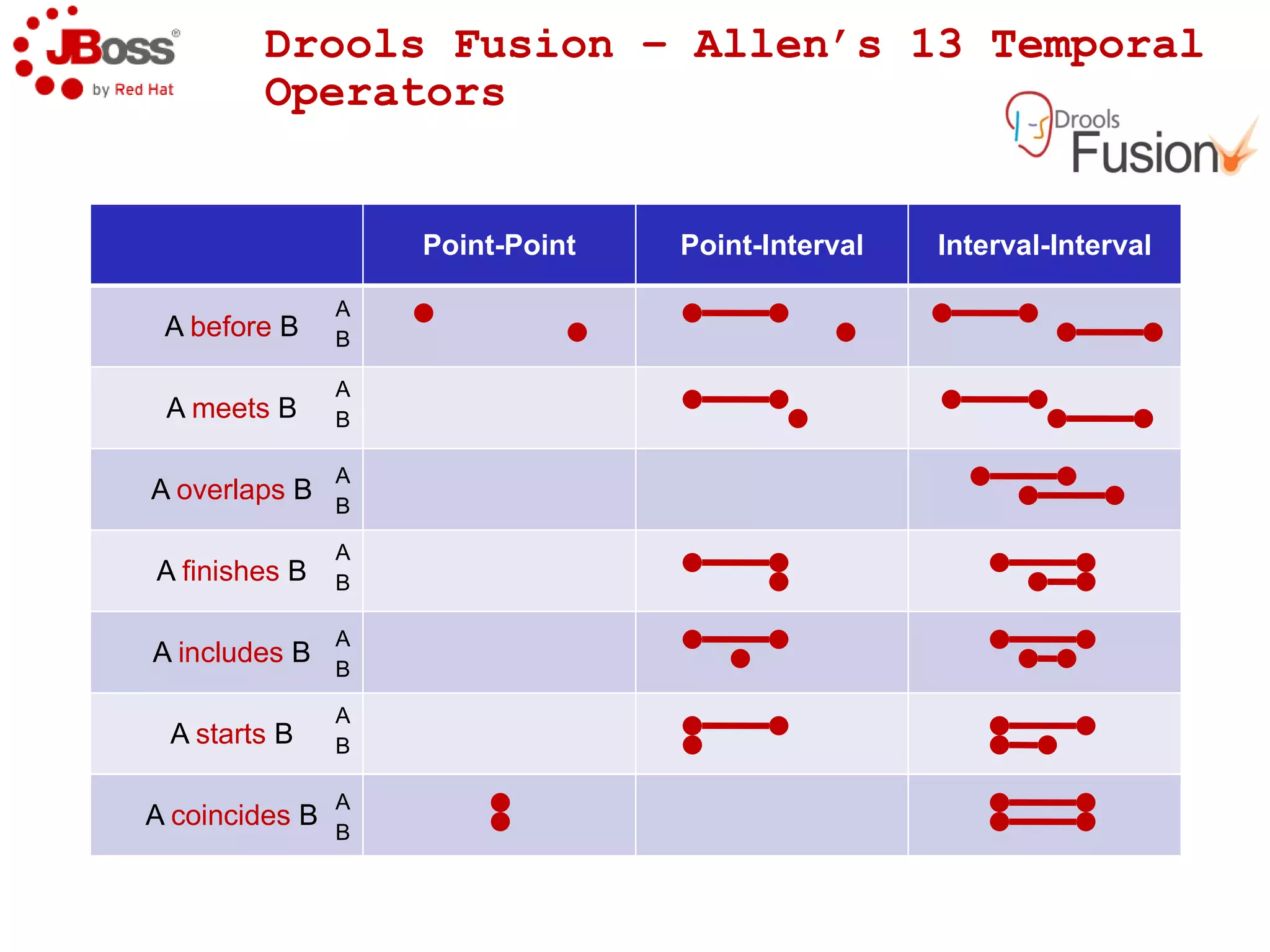
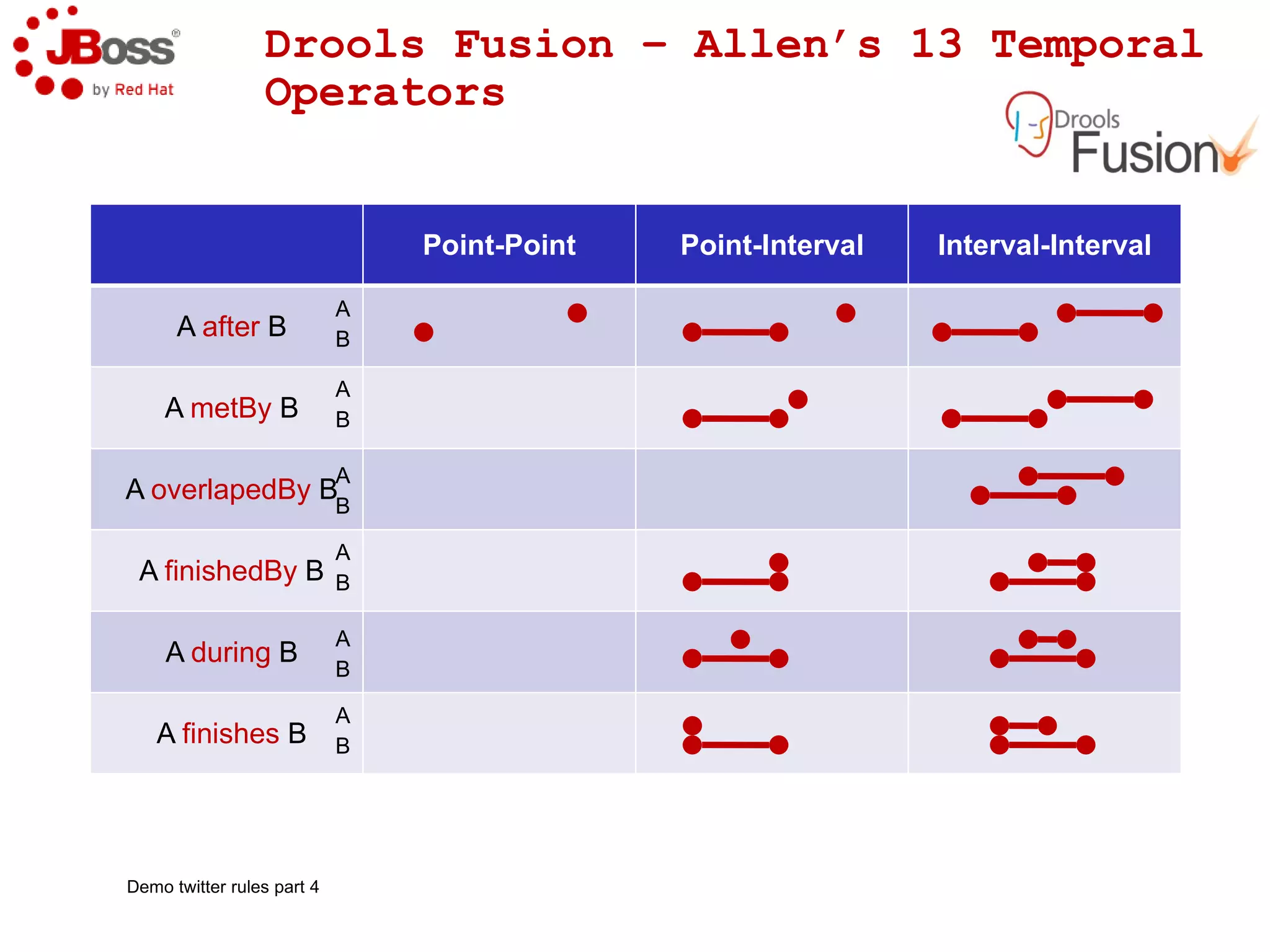
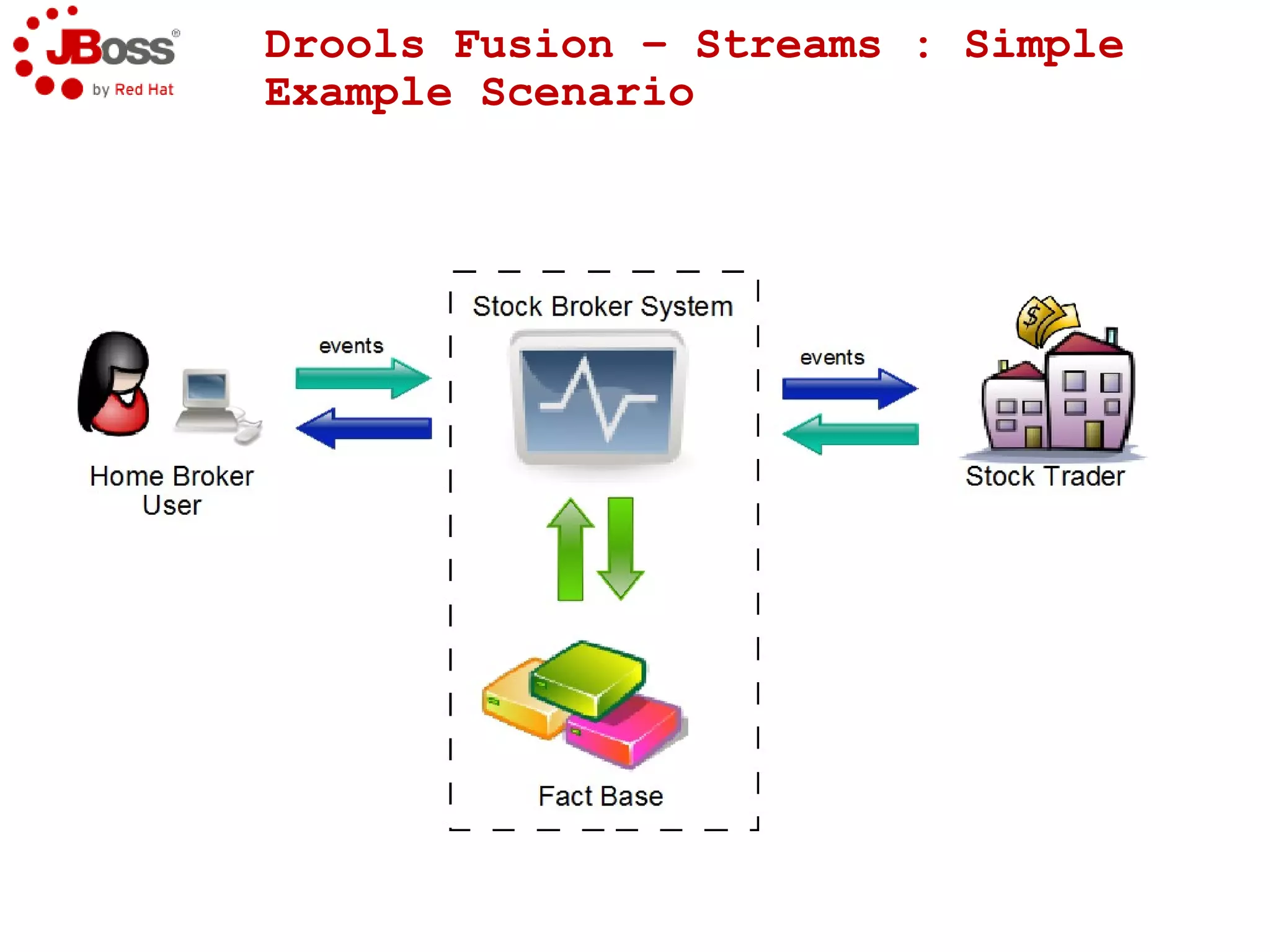
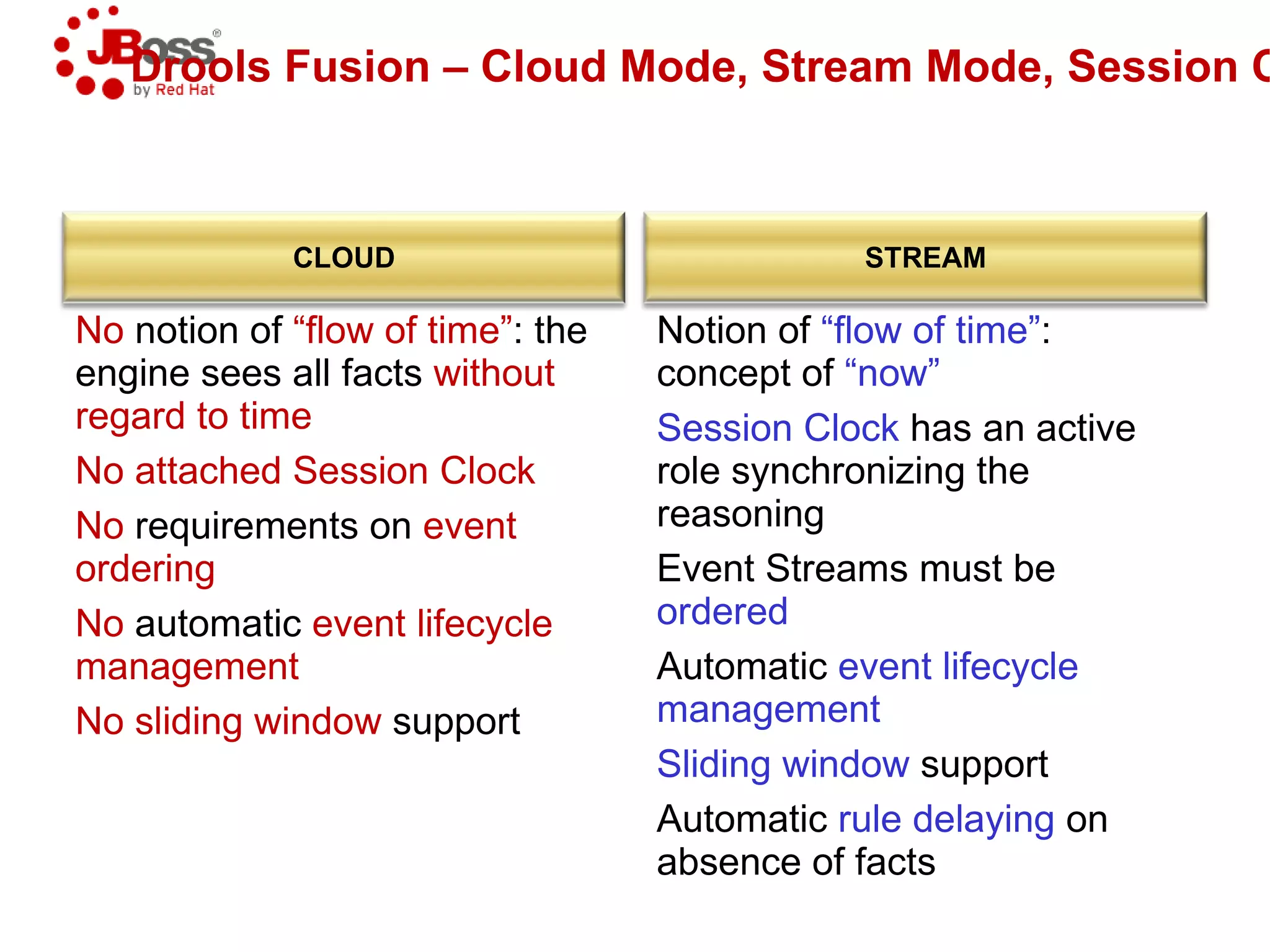
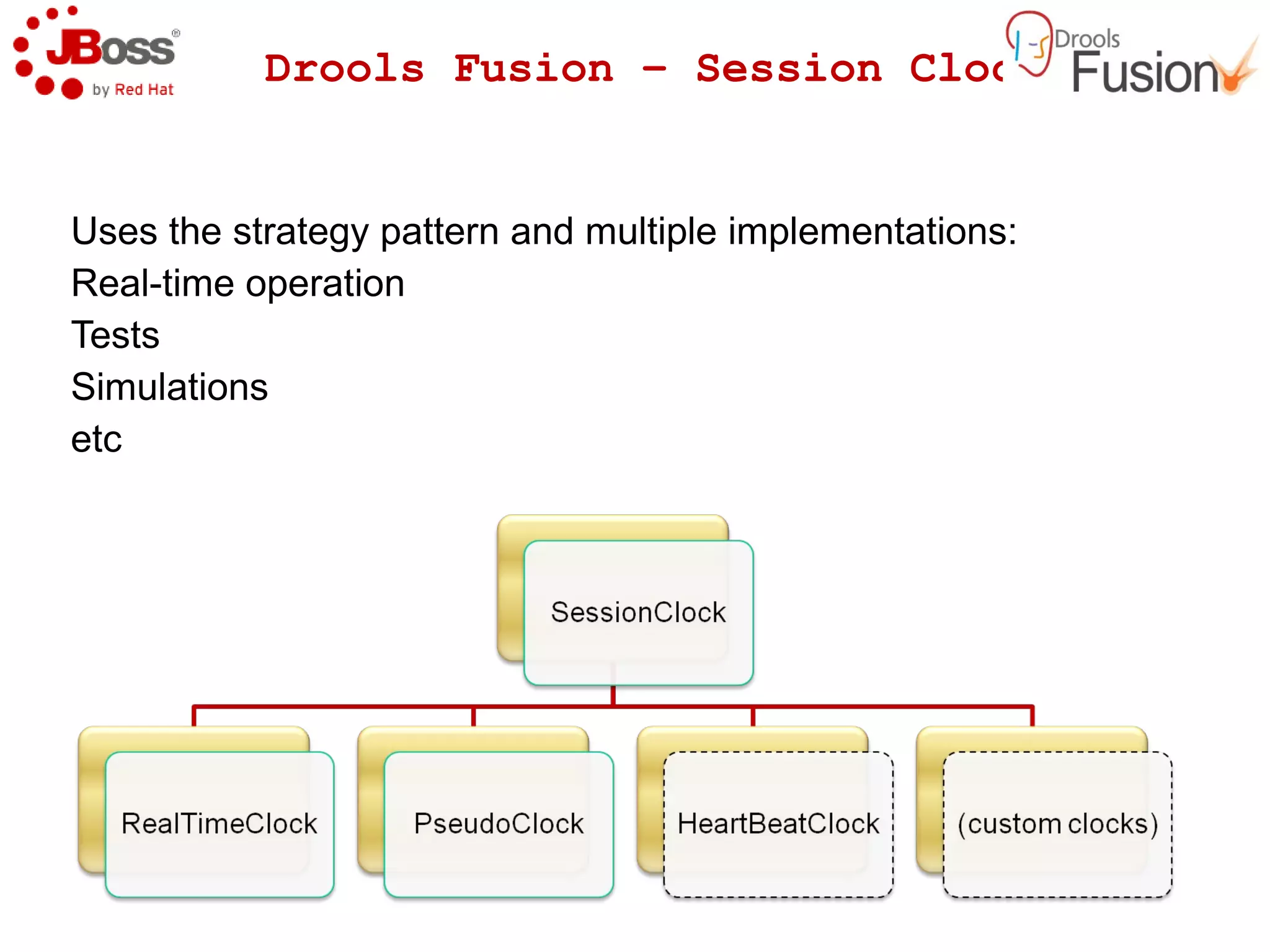
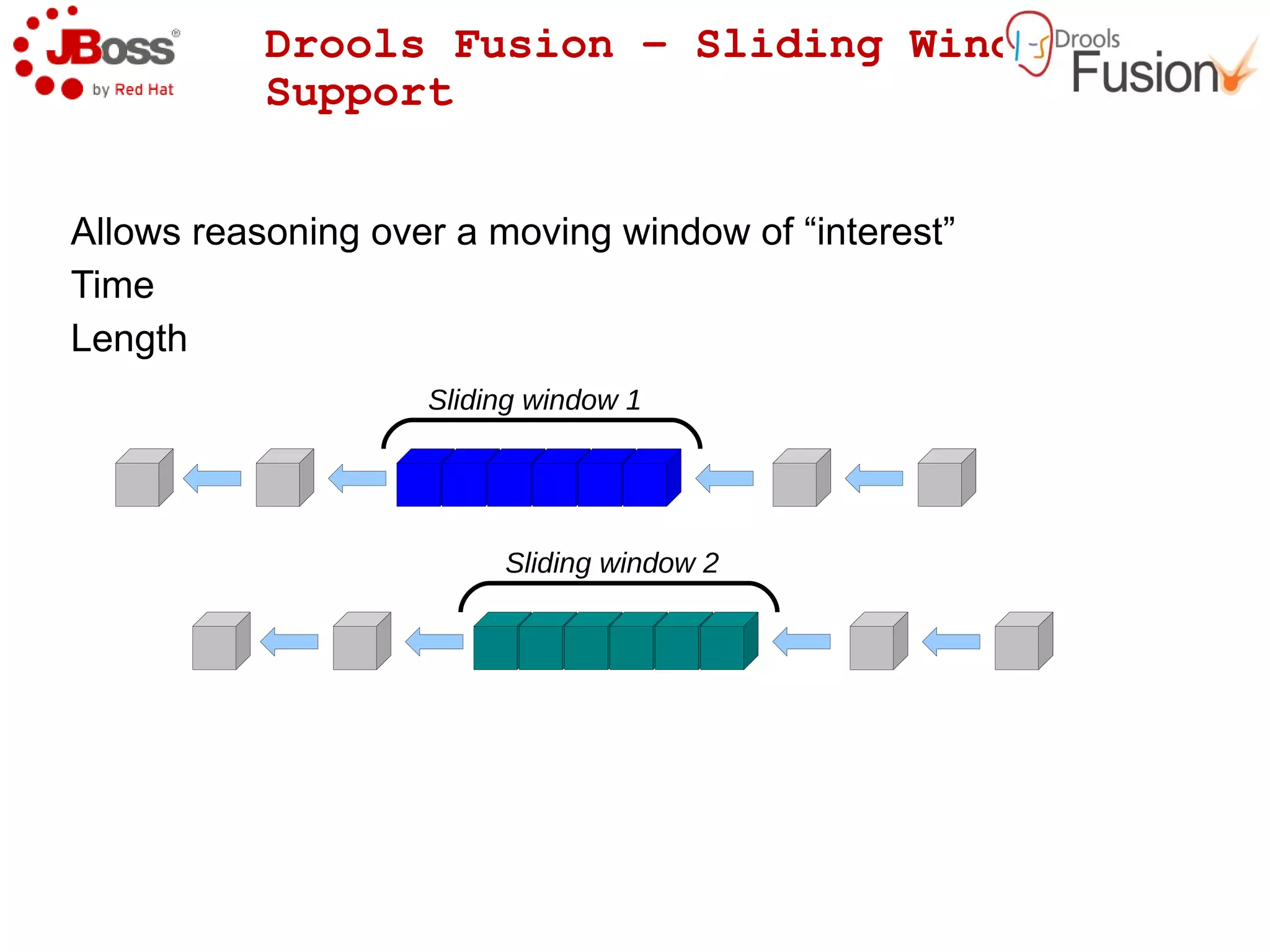
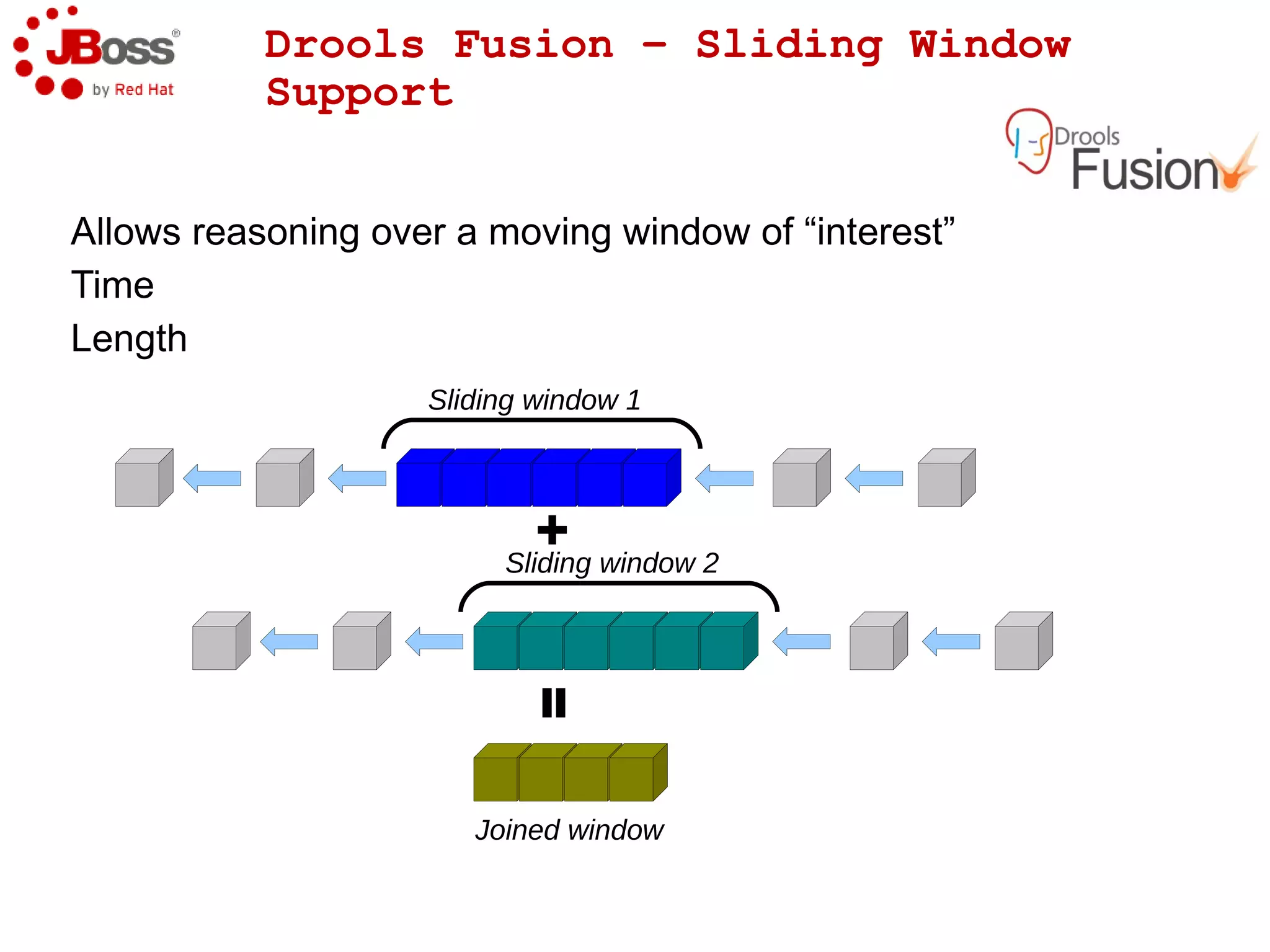
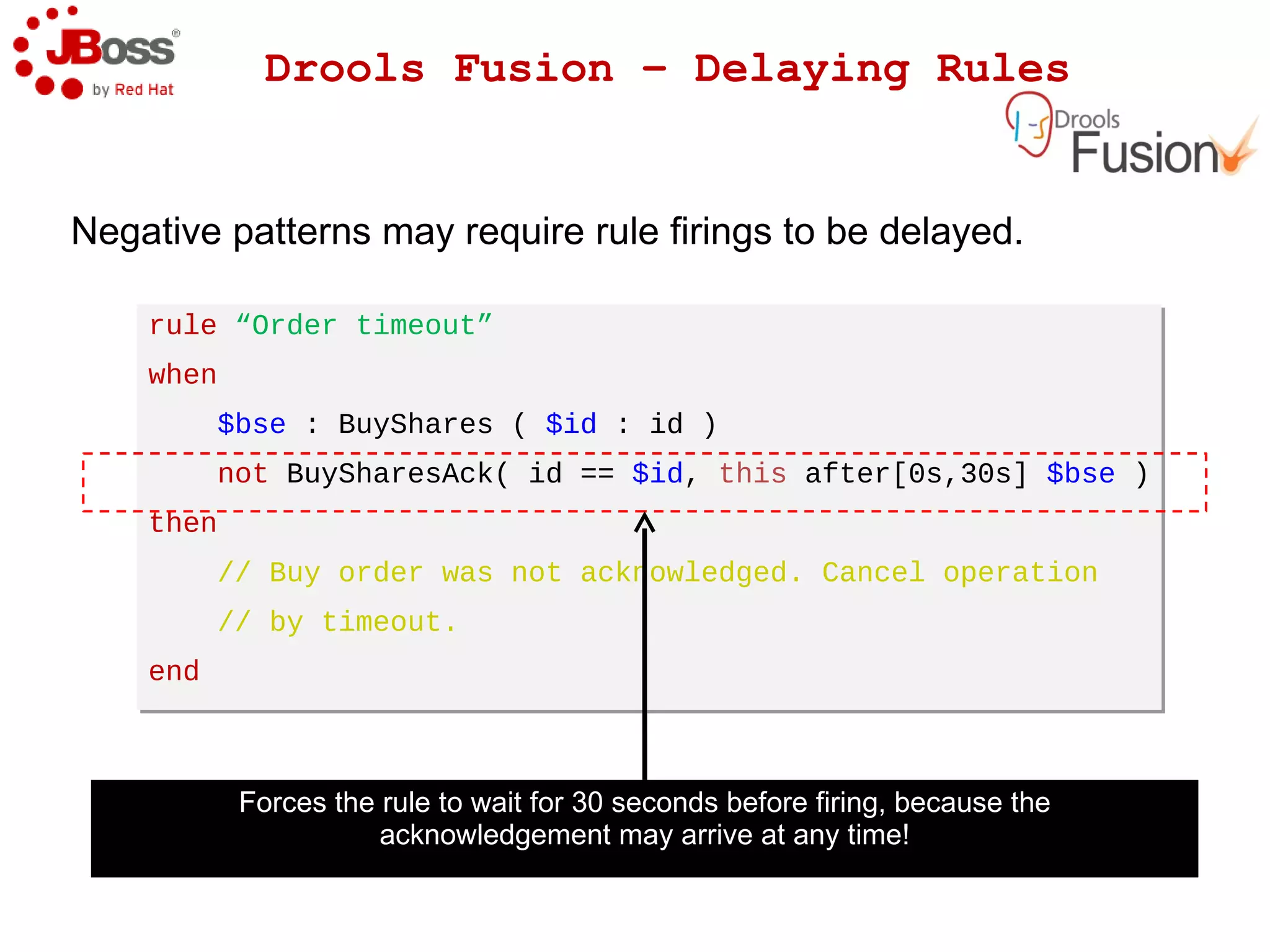
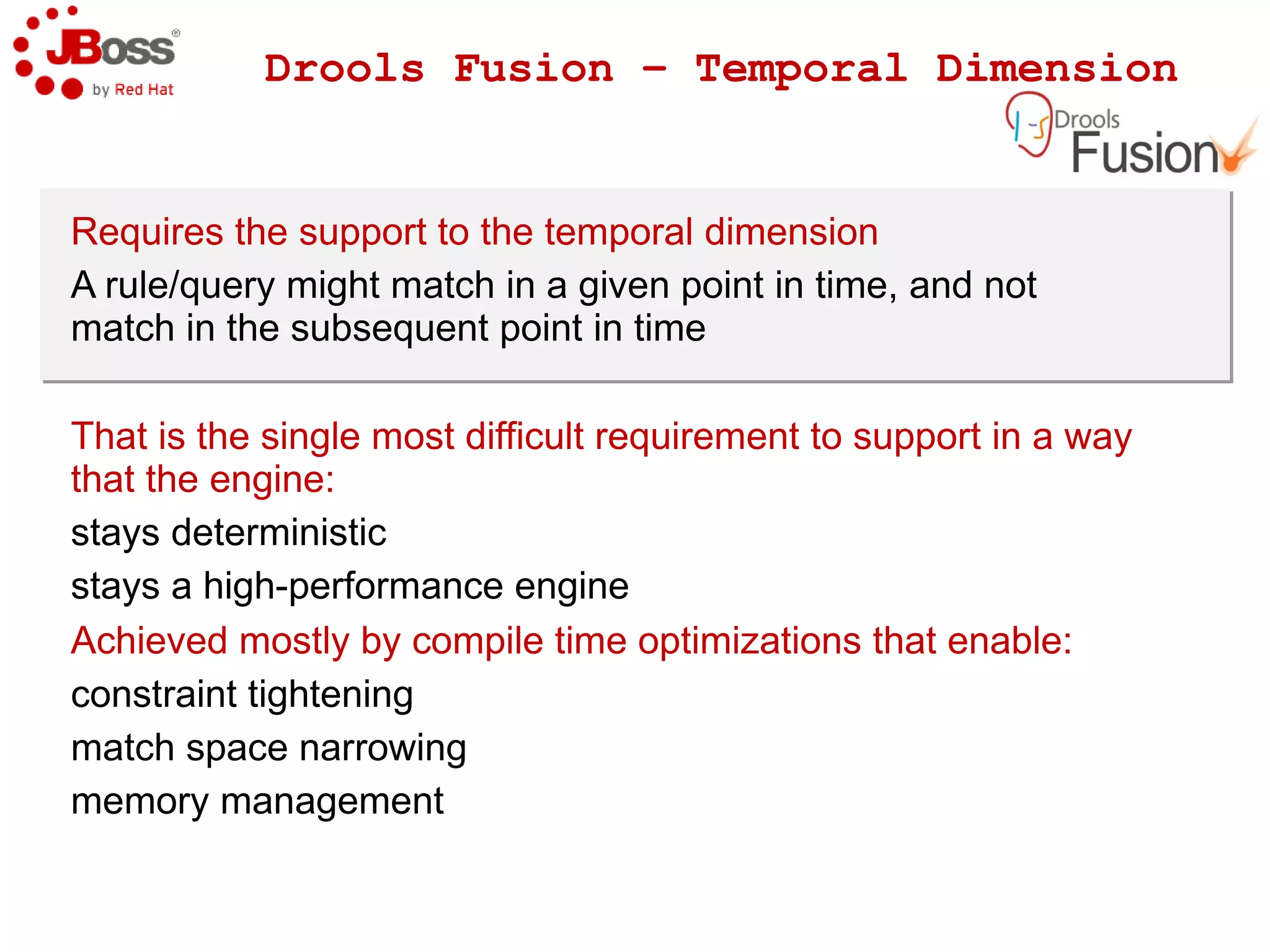
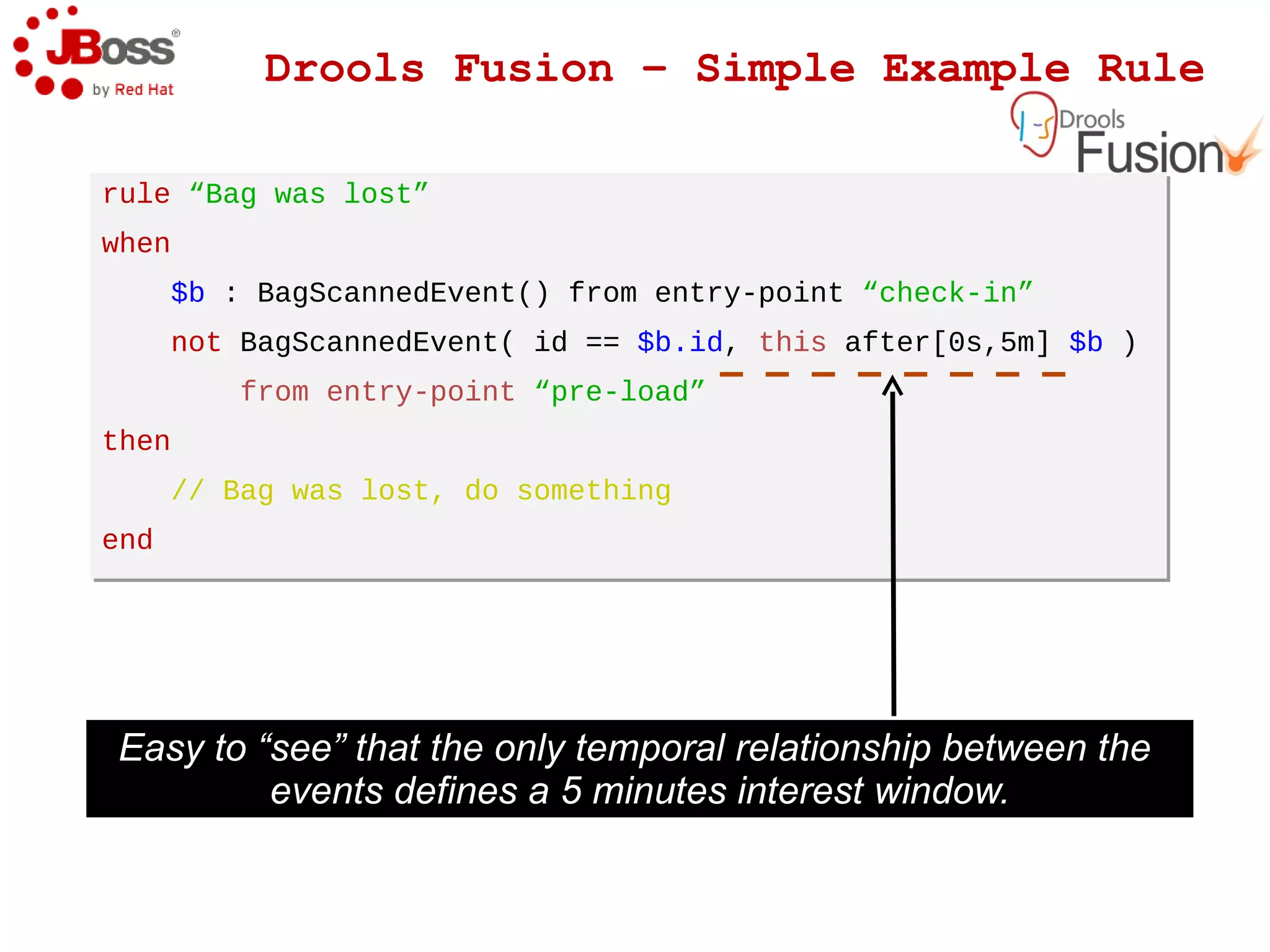
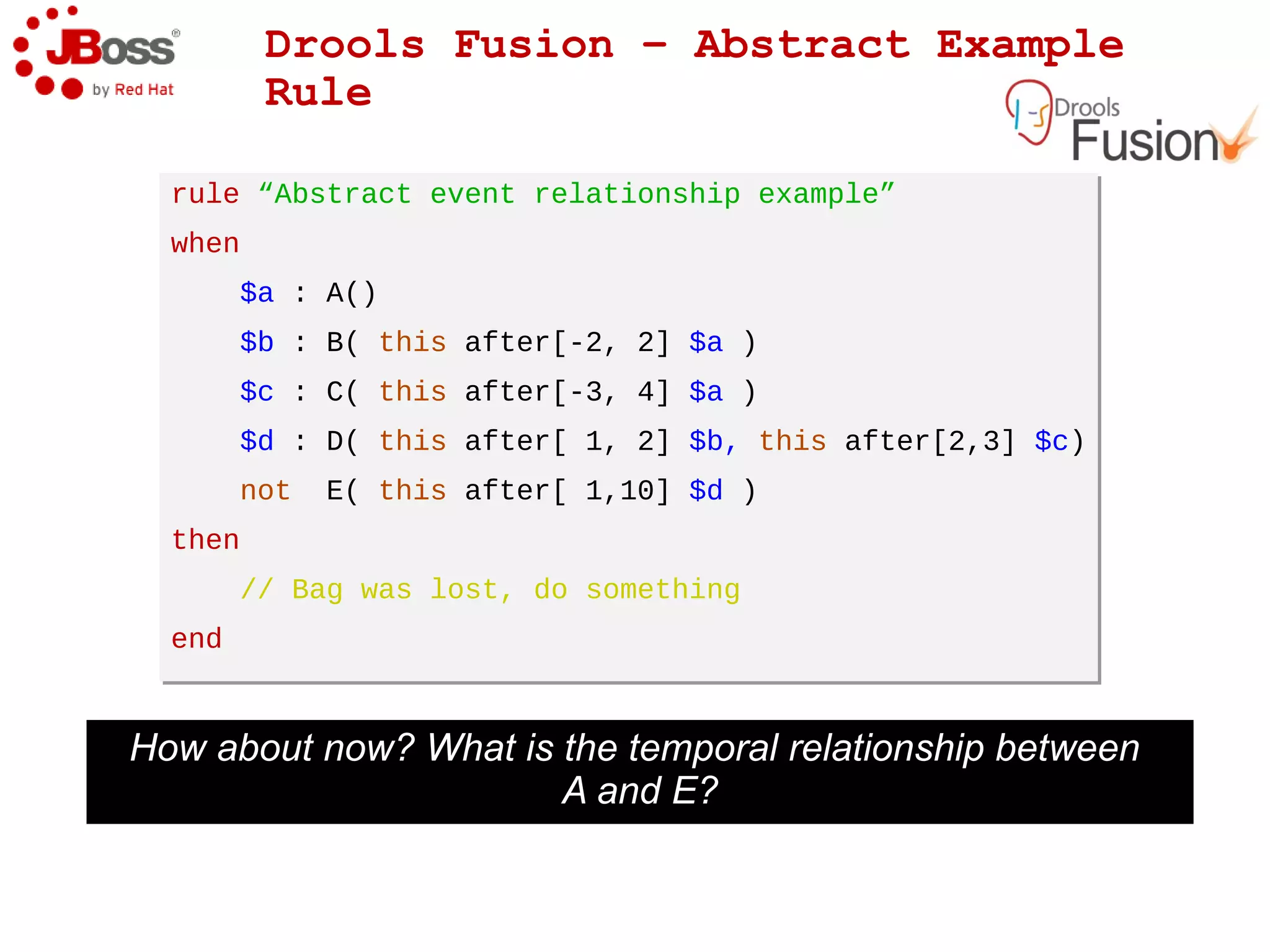
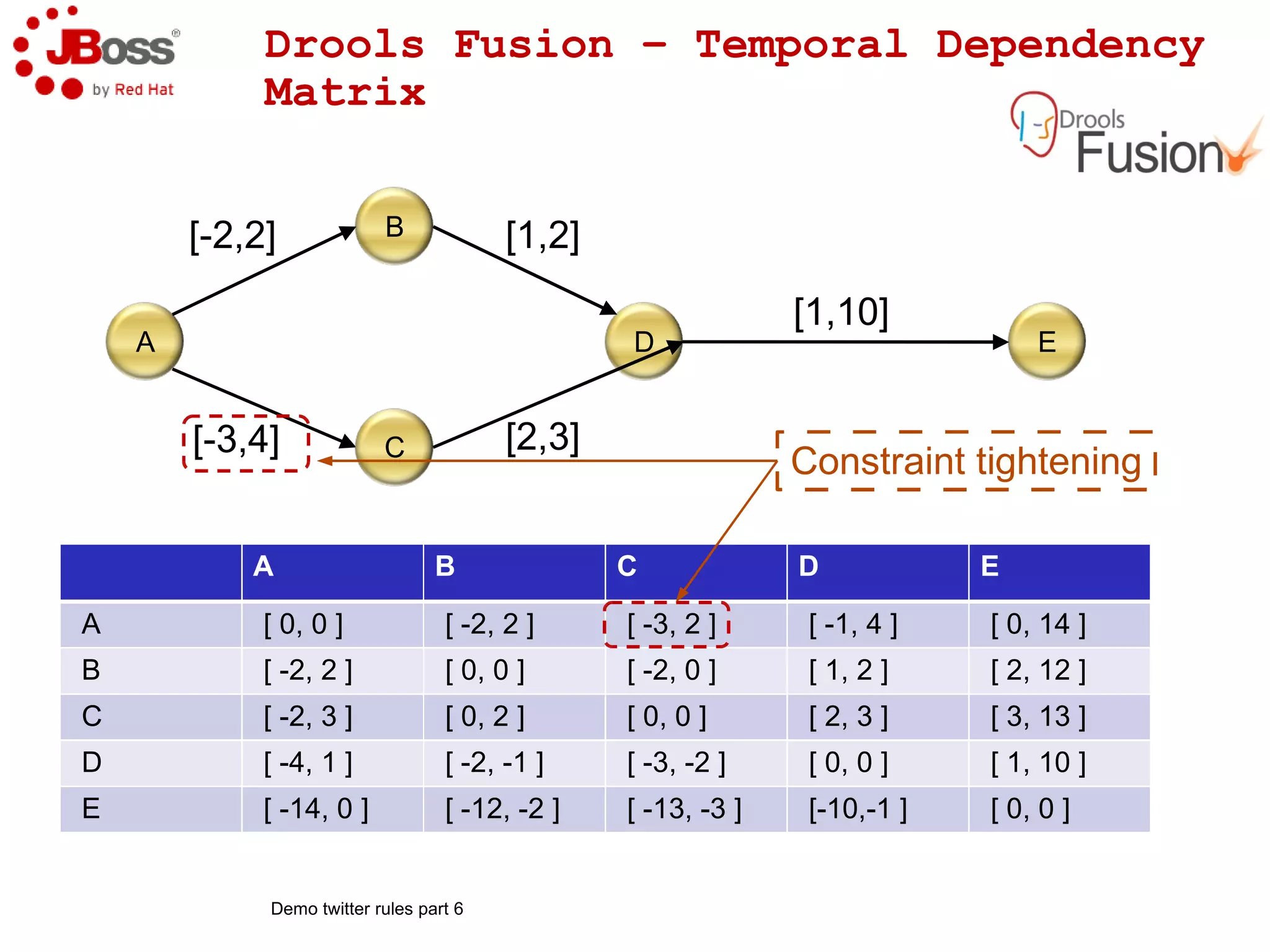
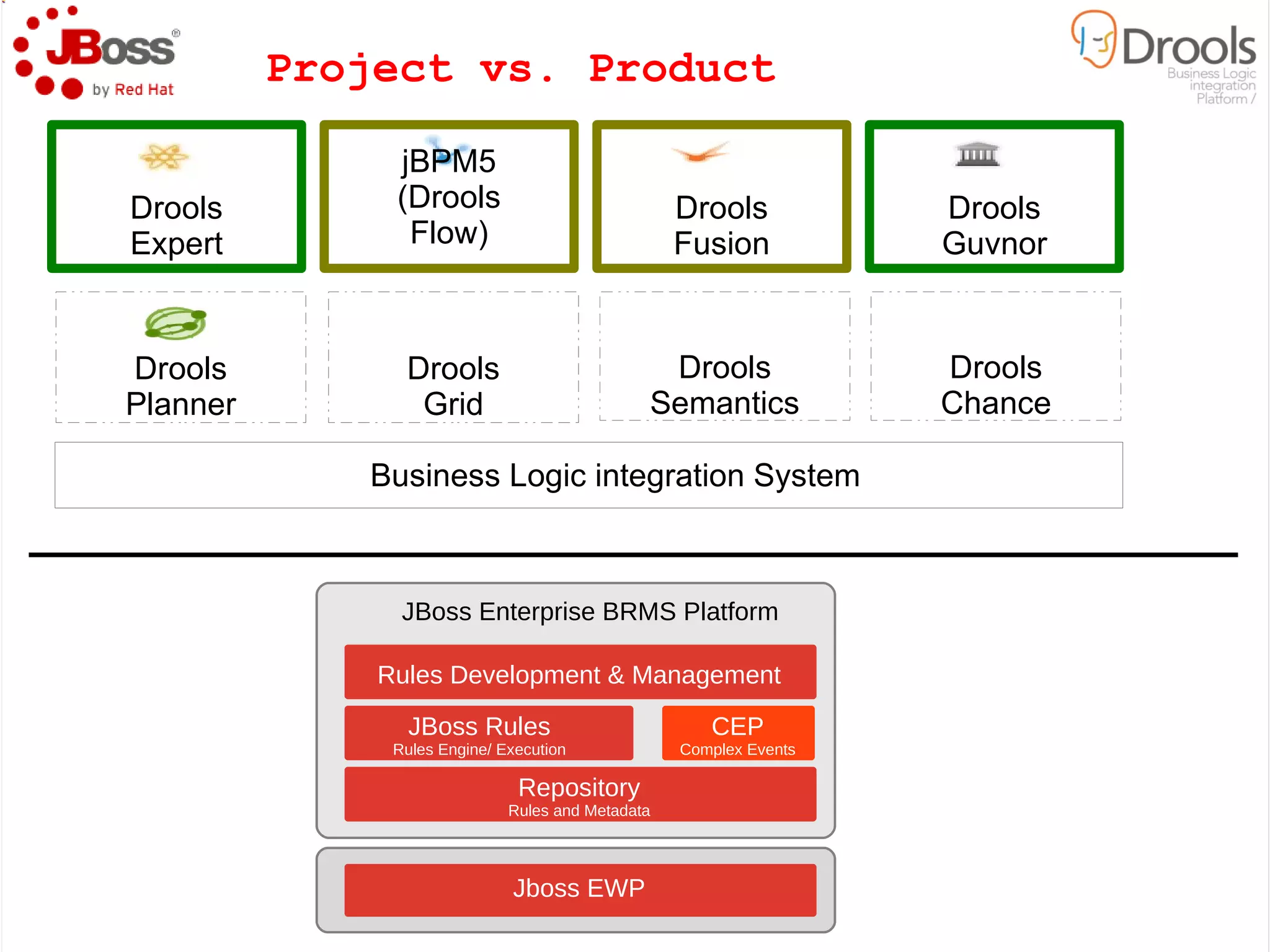
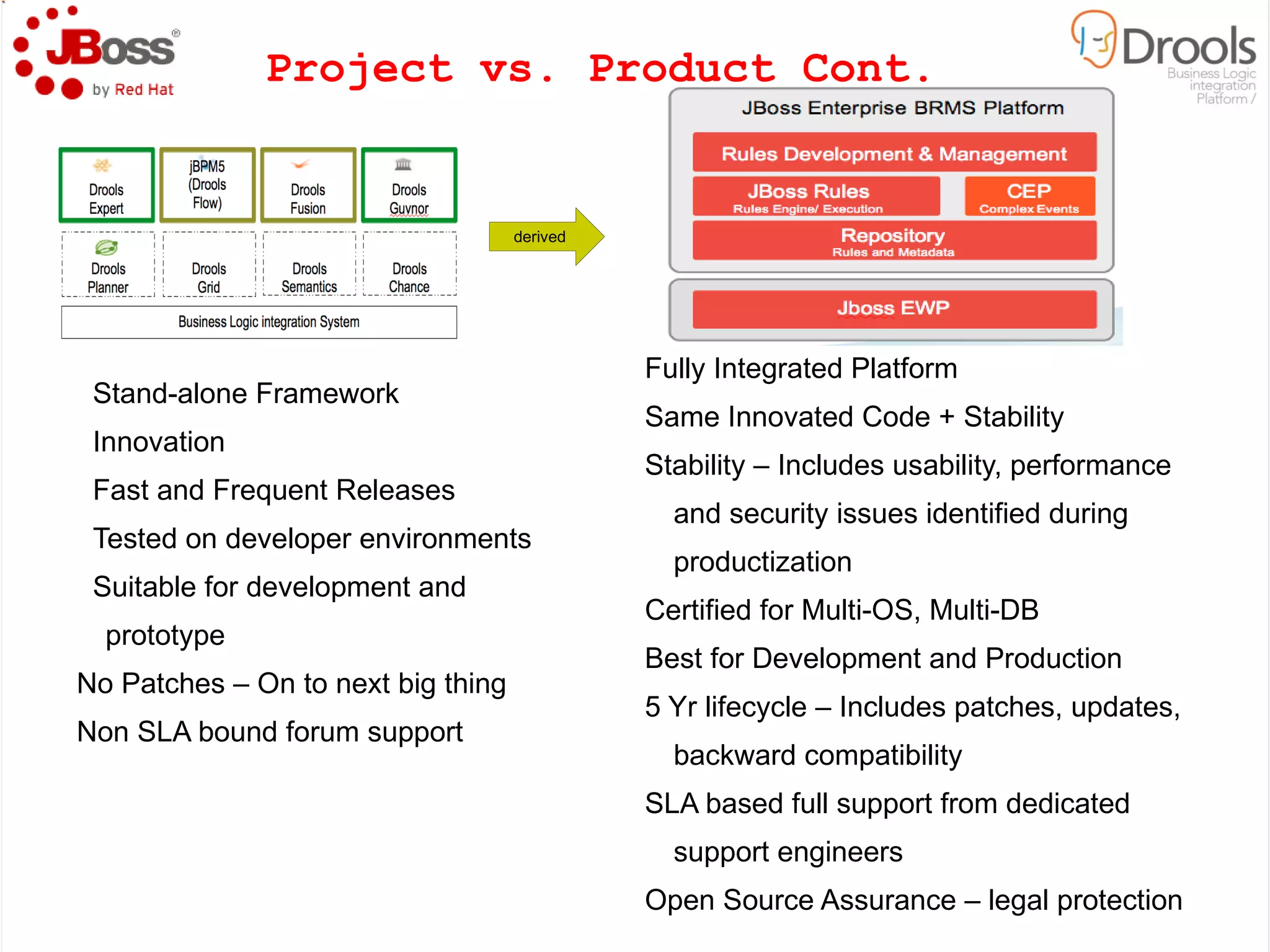
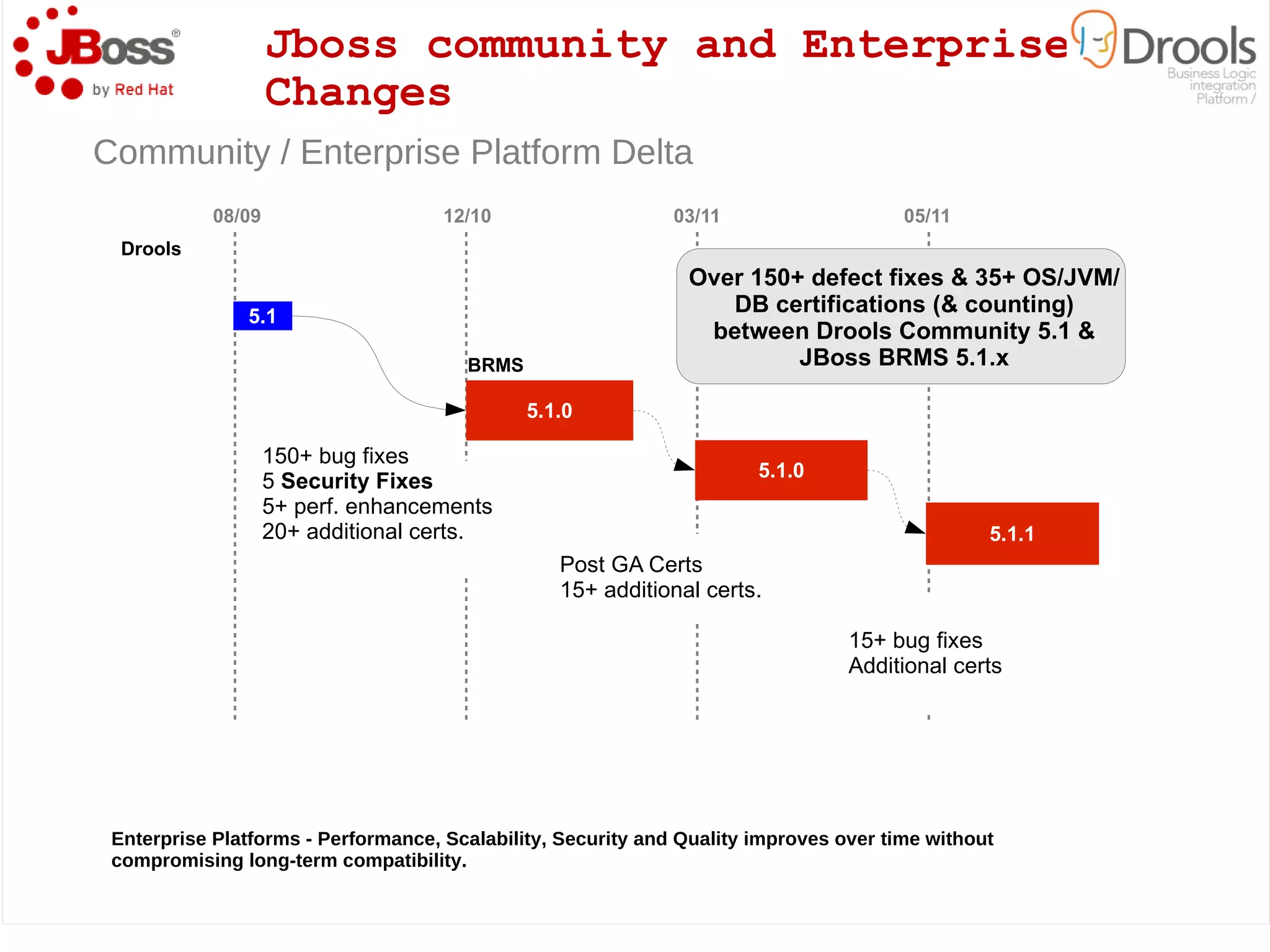
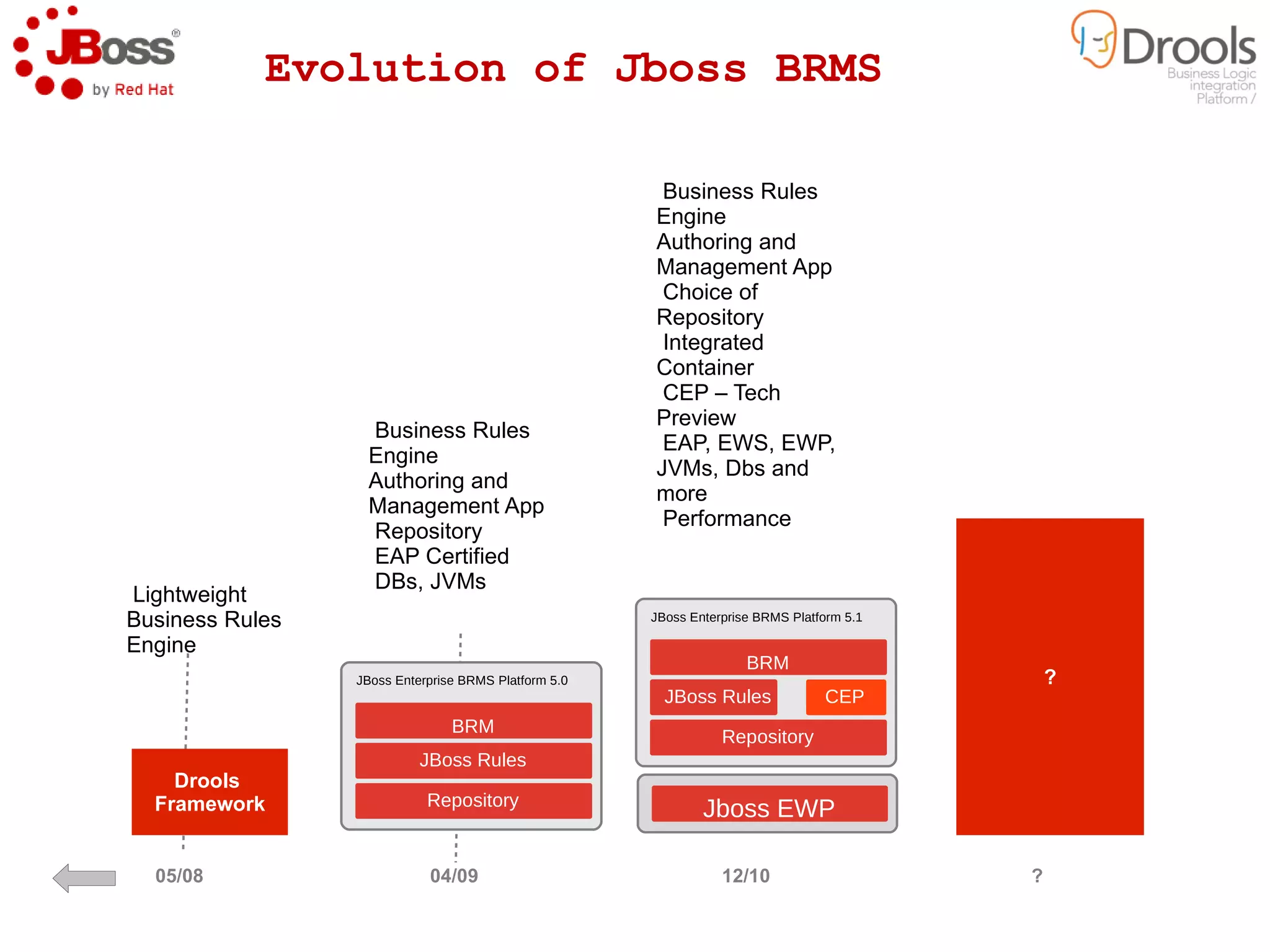
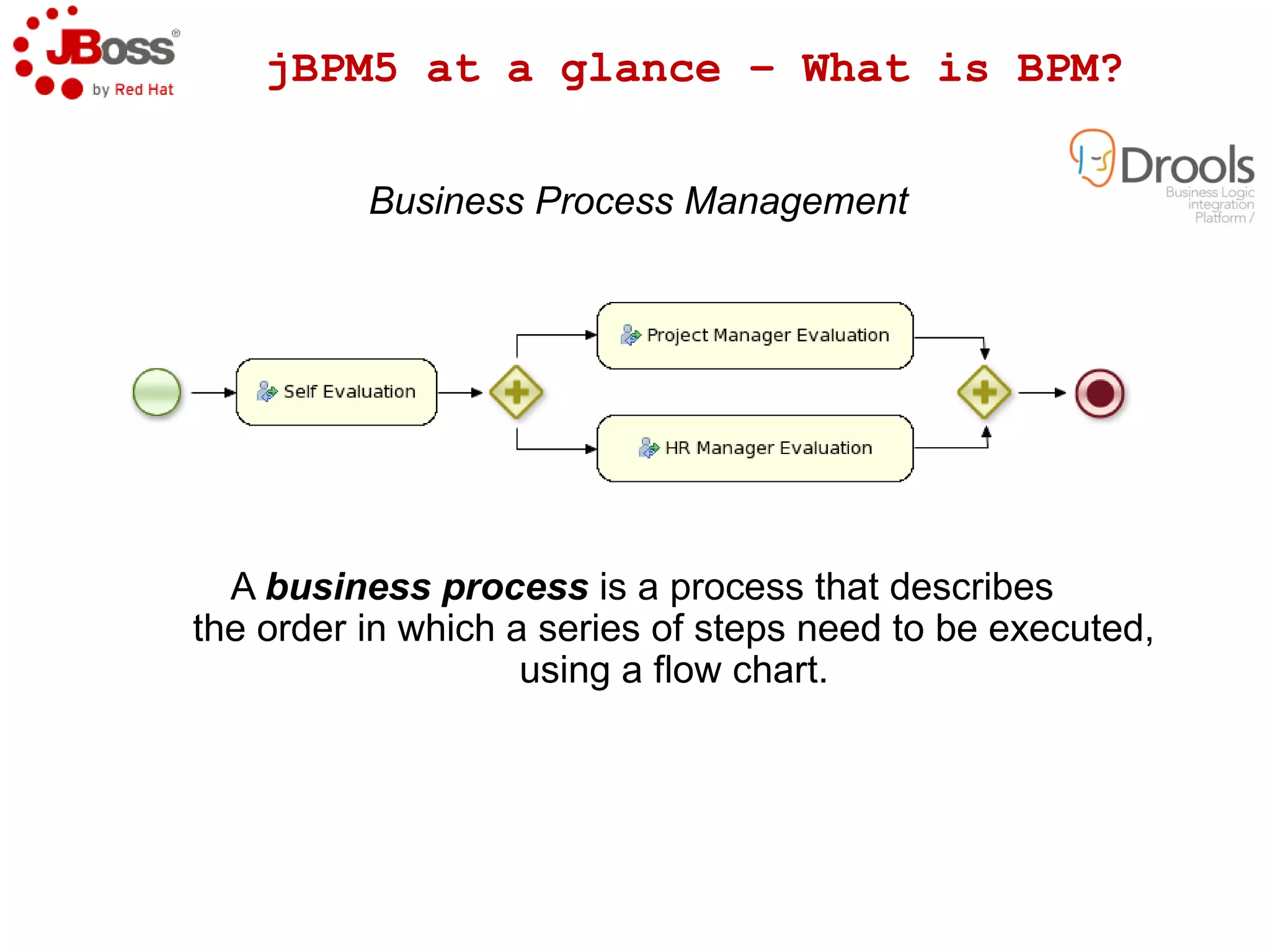
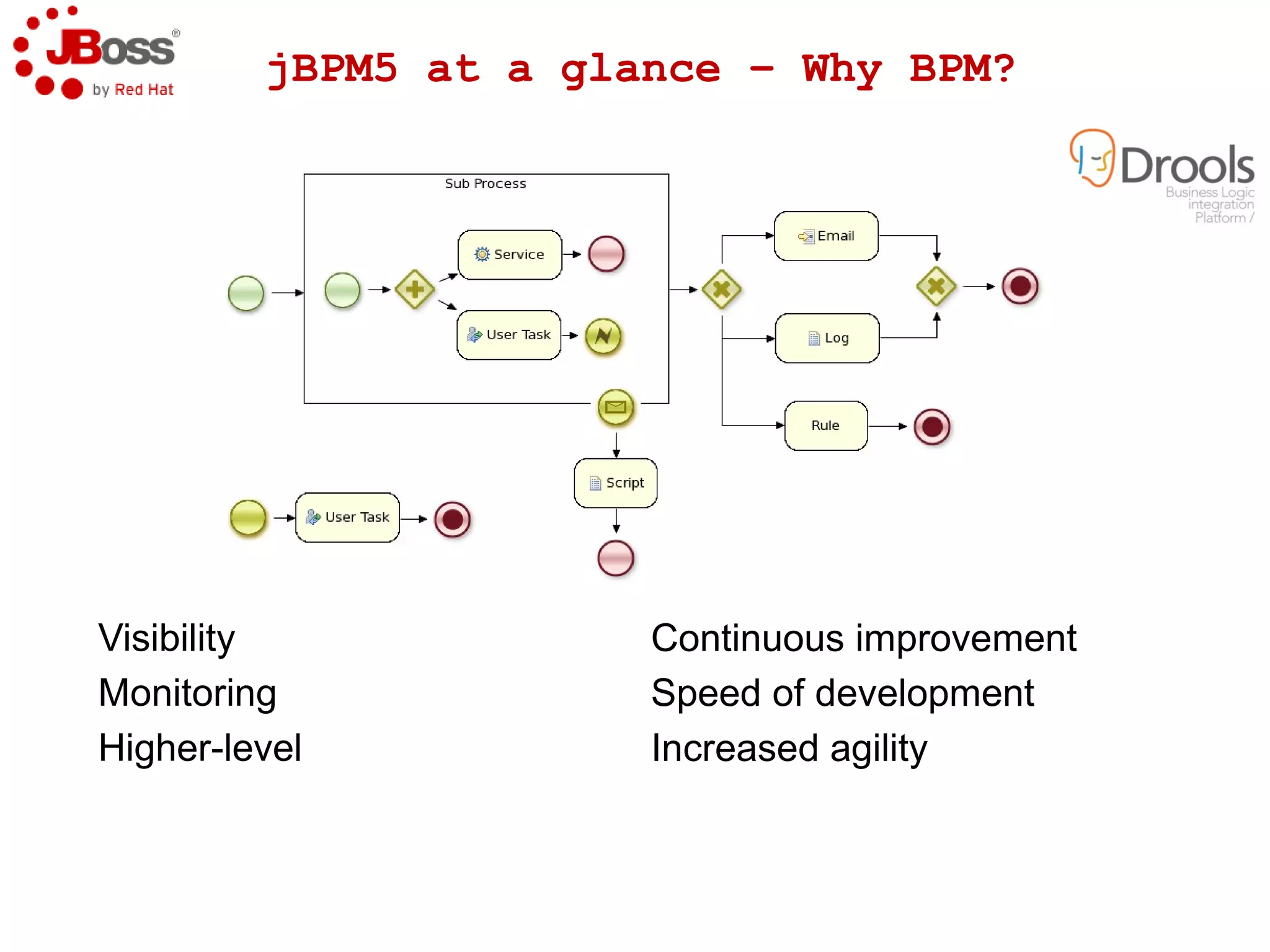
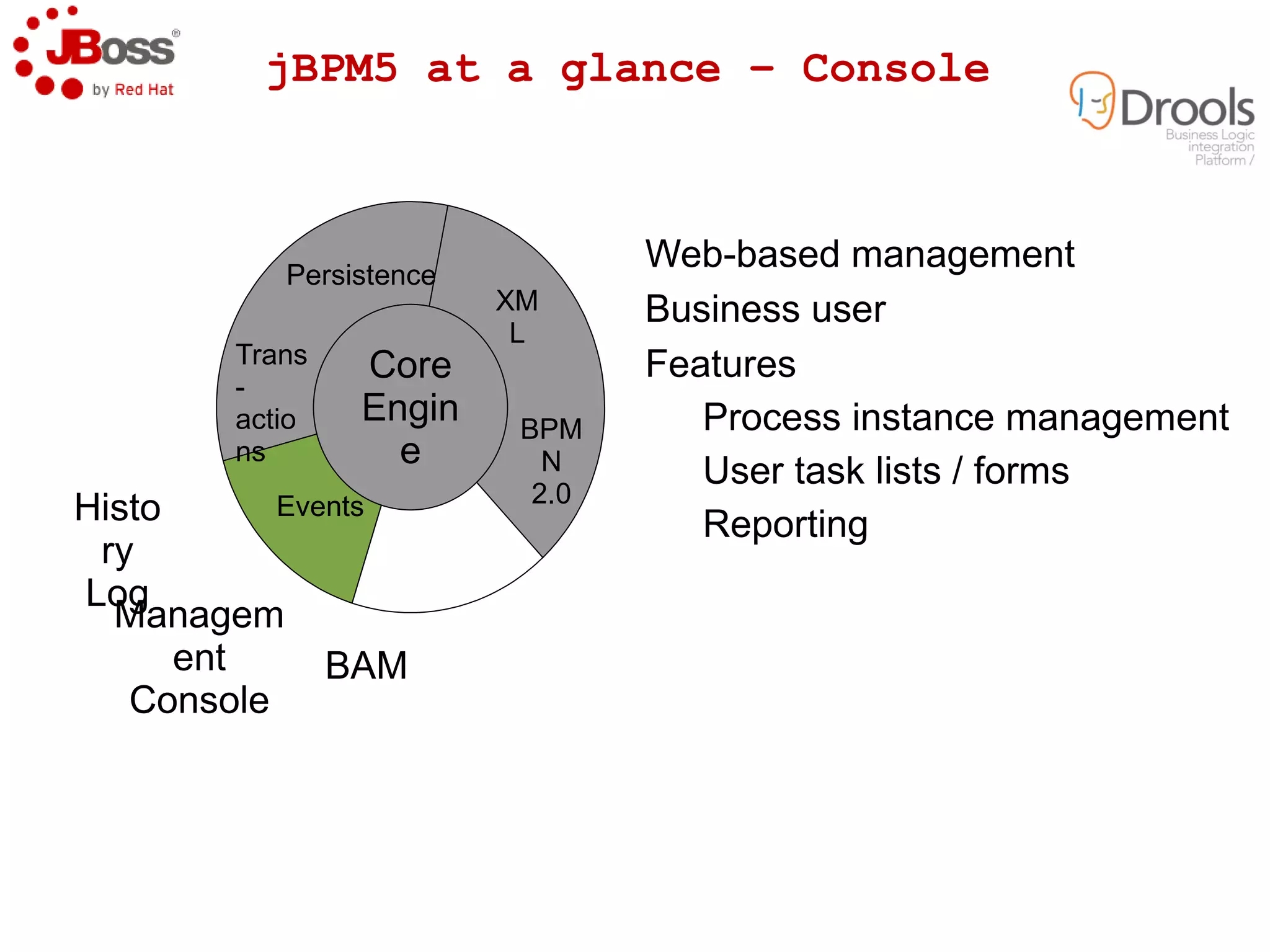
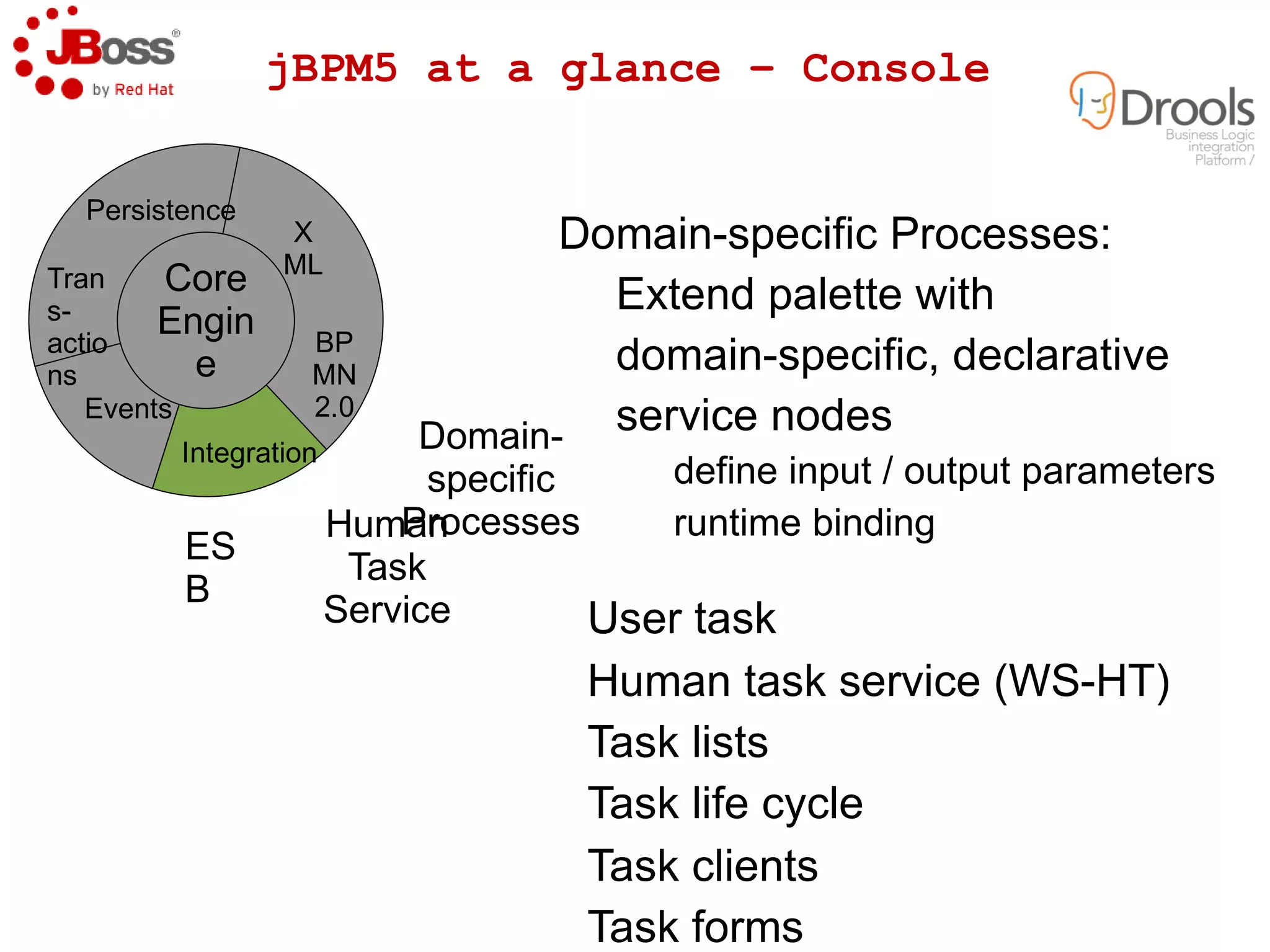
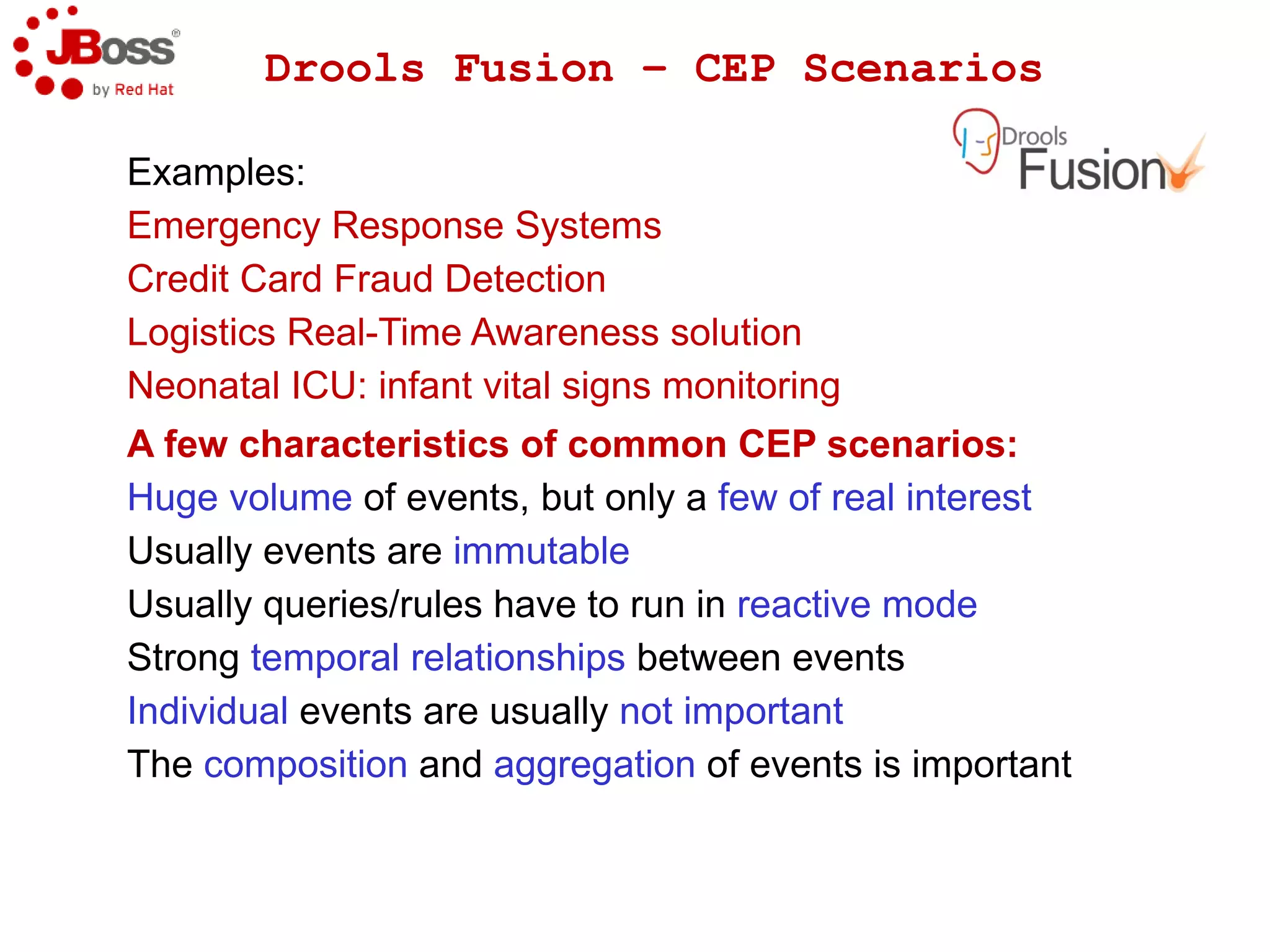
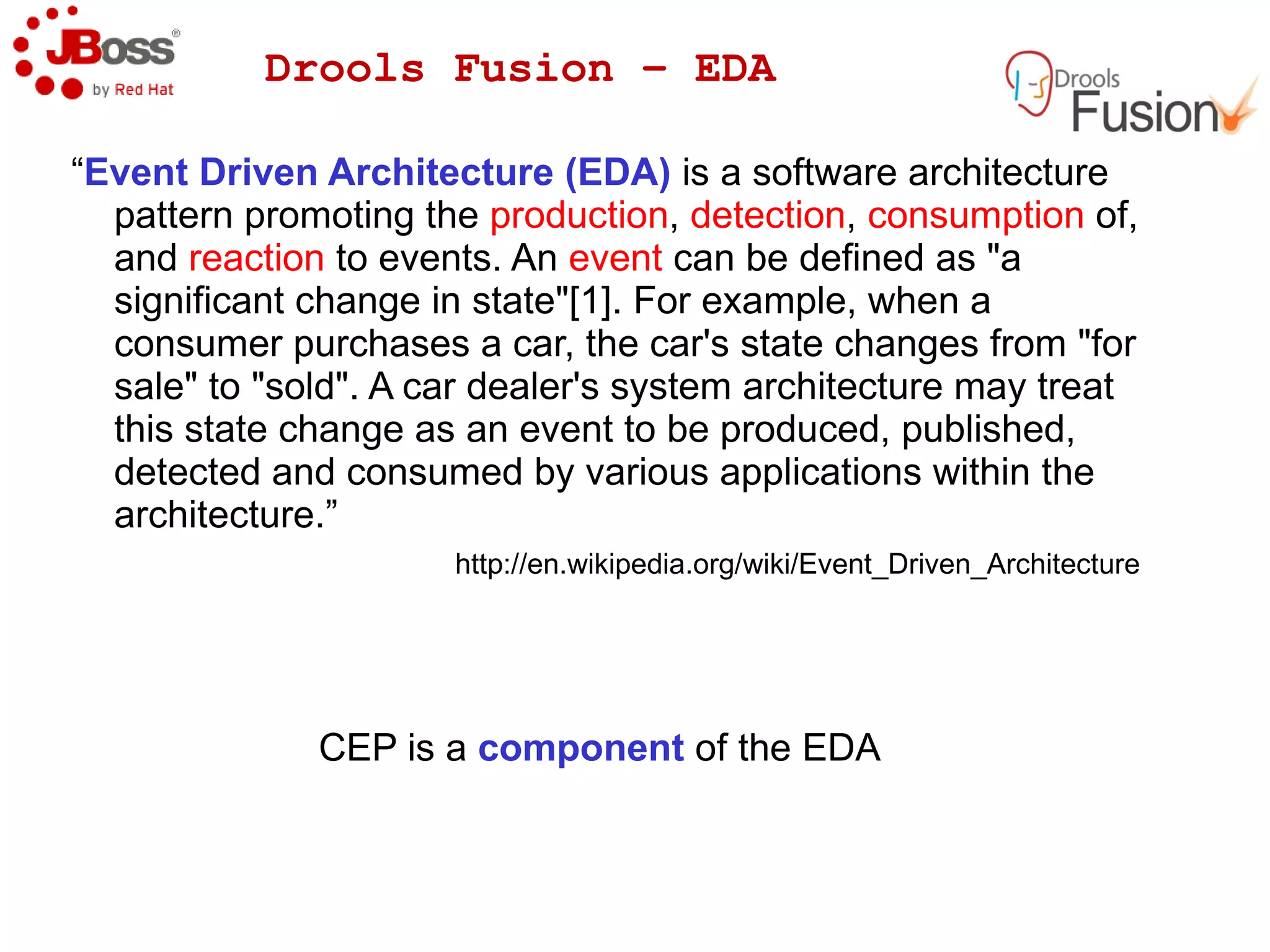
The document discusses JBoss Drools and Drools Fusion, which provide business rules and complex event processing capabilities. It describes the history and vision of Drools, an overview of its rule engine and management tools, and how it has evolved from a standalone framework to an integrated platform. It also introduces jBPM for business process management and how it integrates with Drools for rules and event processing.
![JBoss Drools and Drools Fusion (CEP): Making Business Rules react to RTE Tihomir Surdilovic [email_address] JBoss, a Division of Red Hat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/droolsandcepjax-110619080111-phpapp02/75/JBoss-Drools-and-Drools-Fusion-CEP-Making-Business-Rules-react-to-RTE-1-2048.jpg)



























![avg([12, 16, 4, 6]) Returns single value 9.5 round([10.3, 4.7, 7.8] ) Returns List [10, 5, 8] Description Logic (model concepts, roles, and individuals) Person Has Name and lives at Address](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/droolsandcepjax-110619080111-phpapp02/75/JBoss-Drools-and-Drools-Fusion-CEP-Making-Business-Rules-react-to-RTE-60-2048.jpg)