More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Similar to Biology 7 1
Similar to Biology 7 1 (20)
Cells (The basic unit of life) and Functions. pptx

Cells (The basic unit of life) and Functions. pptx
prokaryoticeukaryoticcells-150419231726-conversion-gate02.pdf

prokaryoticeukaryoticcells-150419231726-conversion-gate02.pdf
More from Tamara
More from Tamara (20)
Biology 7 1
- 1. Life Is Cellular 7.1
- 2. Cell Collection of living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings; basic unit of all forms of life.
- 3. Cell Theory Idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
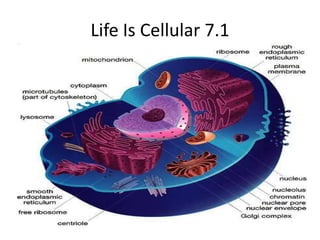
- 4. Nucleus The center of the atom which contains the protons and neutrons; in cells, structure that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell’s activities.
- 5. Eukaryote Organism whose cell contain nuclei.
- 6. Prokaryote Unicellular organism lacking a nucleus.
- 7. Key Concept What is the cell theory? Idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
- 8. Key Concept What are the characteristics of prokaryotes and eukaryotes? Prokaryotes cells have genetic material that is not contained in a nucleus and eukaryotes cells contain a nucleus in which their genetic material is separated from the rest of the cell.