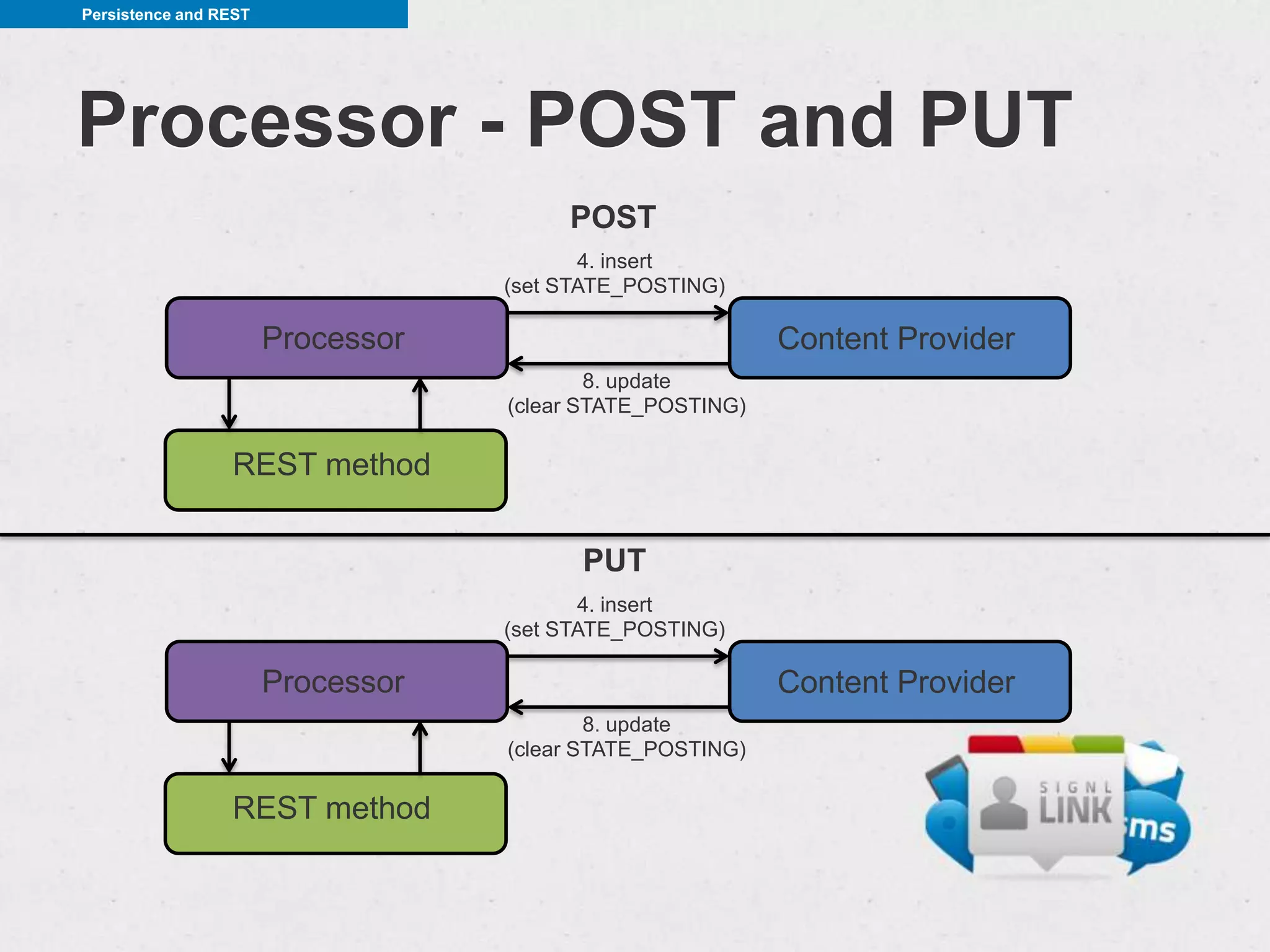
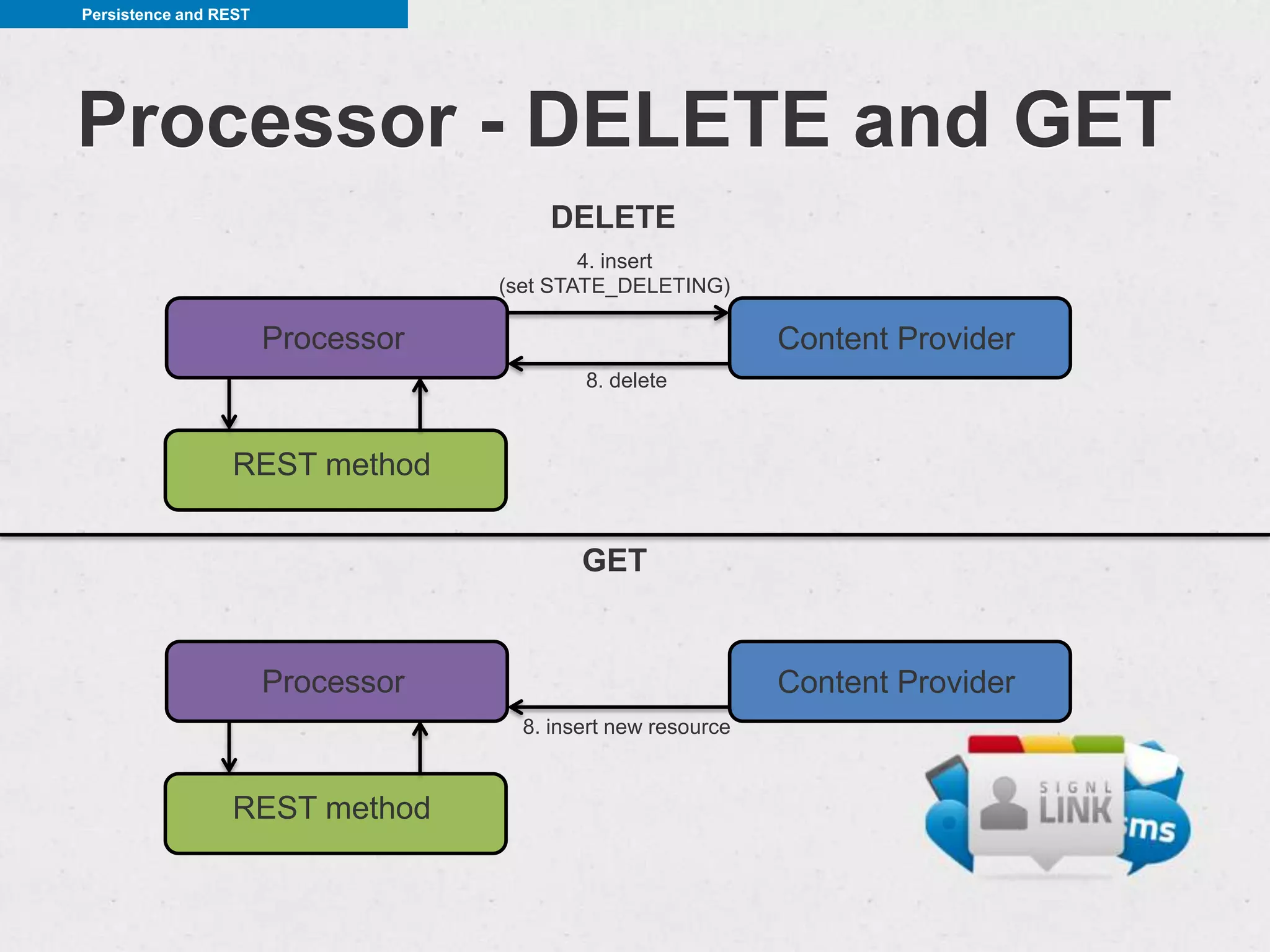
This document discusses REST (REpresentational State Transfer) and how to implement RESTful services on Android. It begins by defining REST and describing its core concepts like client-server architecture, statelessness, uniform interface, and CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations. It then covers how to make HTTP requests in Android using libraries like HttpURLConnection and Apache HTTP Client. Helpful libraries for working with REST APIs are also presented, including Gson for JSON parsing and CRest for declarative REST clients. The document emphasizes best practices like performing HTTP calls in a background thread, persisting data to content providers, and minimizing network usage.








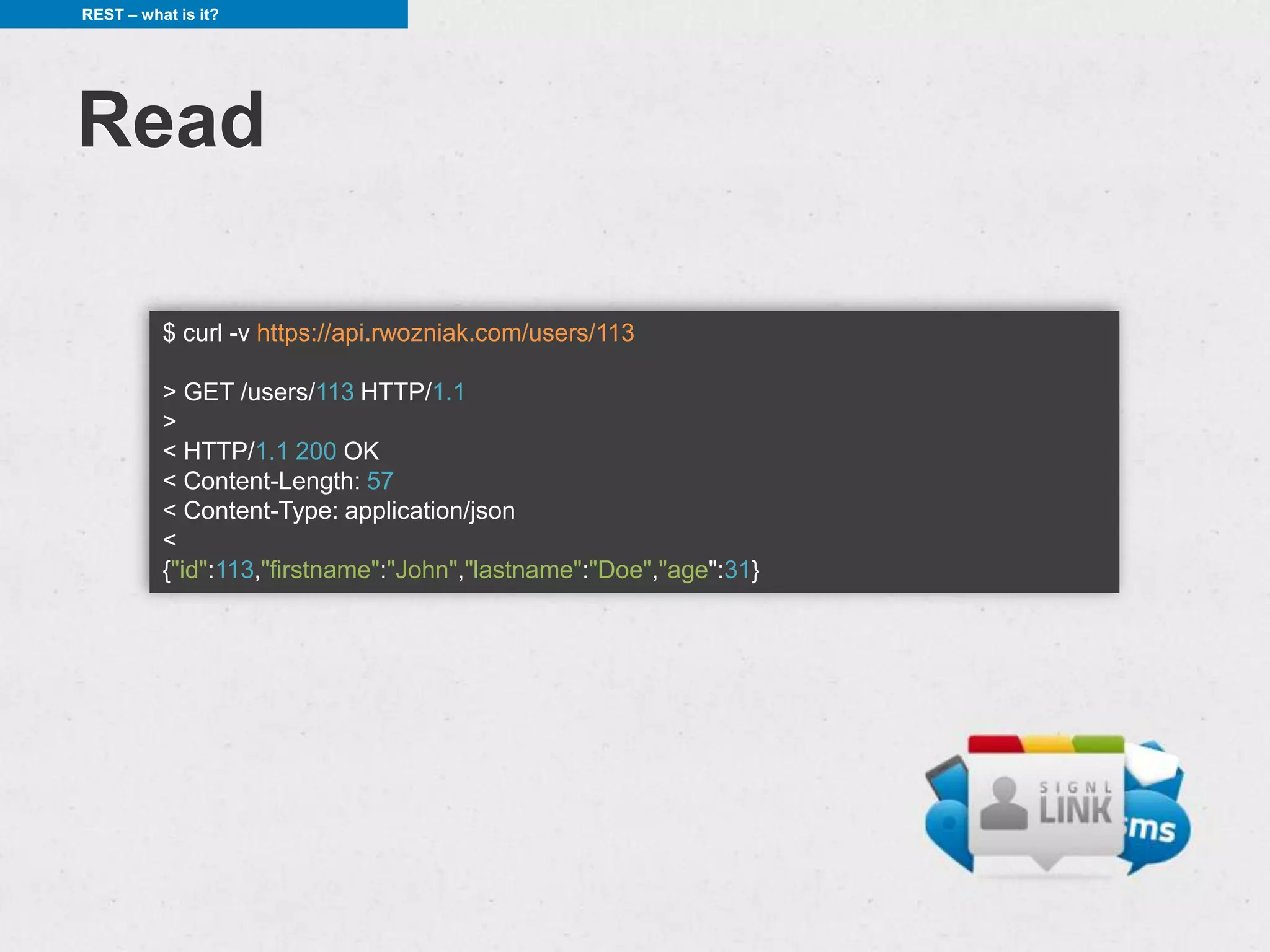
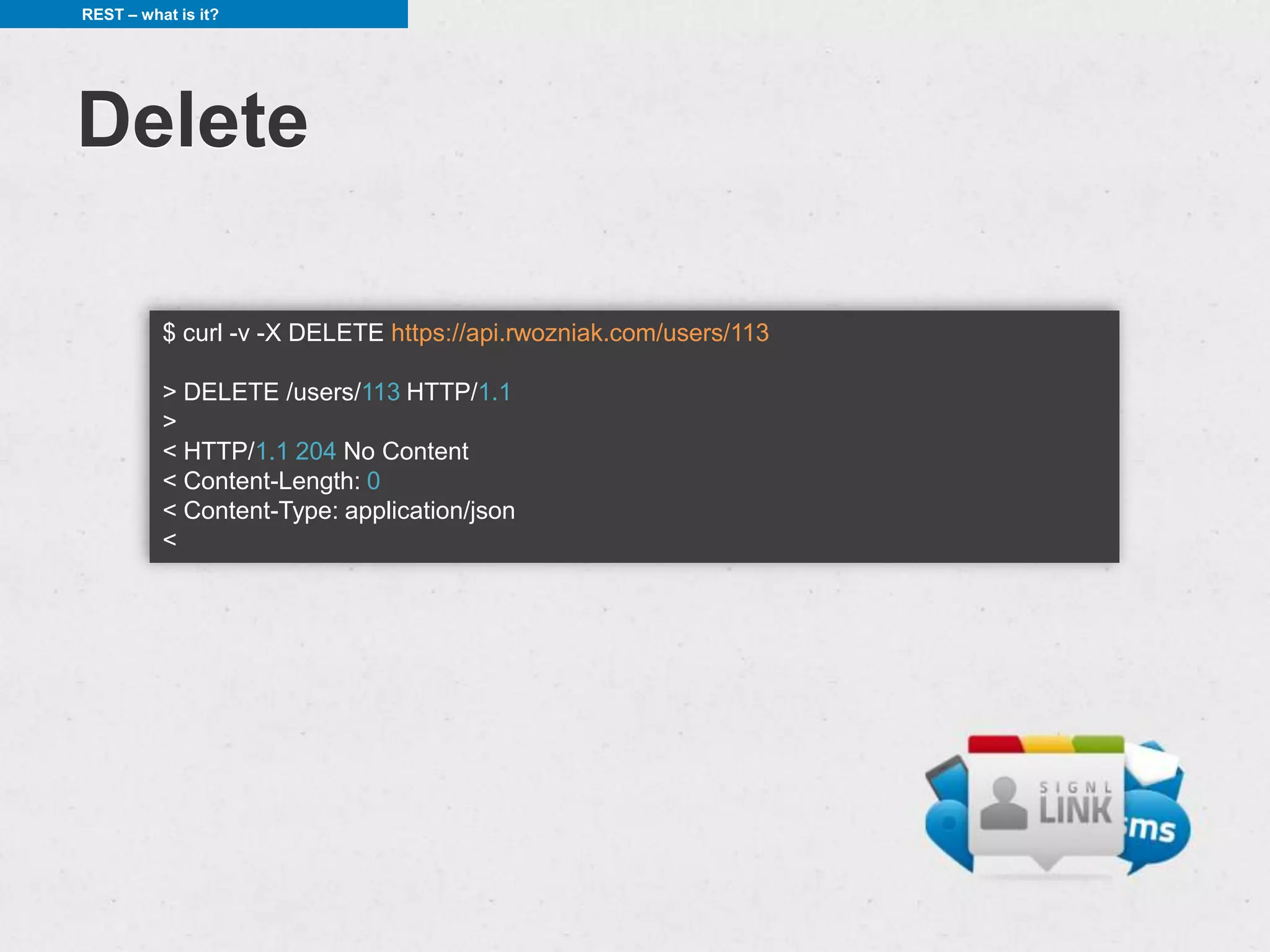
![REST – what is it?
Create
$ curl -v -X POST -d "..." https://api.rwozniak.com/users
> POST /users HTTP/1.1
>
< HTTP/1.1 201 Created
< Location /users/113
< Content-Length: 57
< Content-Type: application/json
<
[{"id":113,"firstname":"John","lastname":"Doe","age":31}]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidresten-121217053553-phpapp01/75/Android-and-REST-9-2048.jpg)




![REST – more
Programmer-friendly
{
"http_code": 400,
"error": "validation_errors",
"error_title": "Set Creation Error",
"error_description": "The following validation errors occurred:nYou must have a
titlenBoth the terms and definitions are mandatory",
"validation_errors": [
"You must have a title",
"Both the terms and definitions are mandatory",
"You must specify the terms language",
"You must specify the definitions language"
]
}
src: https://quizlet.com/api/2.0/docs/api_intro/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidresten-121217053553-phpapp01/75/Android-and-REST-17-2048.jpg)





![Helpful libraries - CRest
Example
@EndPoint("http://api.twitter.com")
@Path("/1/statuses")
@Consumes("application/json")
public interface StatusService {
@POST
@Path("update.json")
Status updateStatus(
@FormParam("status") String status,
@QueryParam("lat") float lat,
@QueryParam("long") float longitude);
@Path("{id}/retweeted_by.json")
User[] getRetweetedBy(
@PathParam("id") long id,
@QueryParam("count") long count,
@QueryParam("page") long page);
@Path("followers.json")
User[] getFollowers(@QueryParam("user_id") long userId);
}
CRest crest = CRest.getInstance();
StatusService statusService = crest.build(StatusService.class);
User[] folowers = statusService.getFollowers(42213);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidresten-121217053553-phpapp01/75/Android-and-REST-29-2048.jpg)