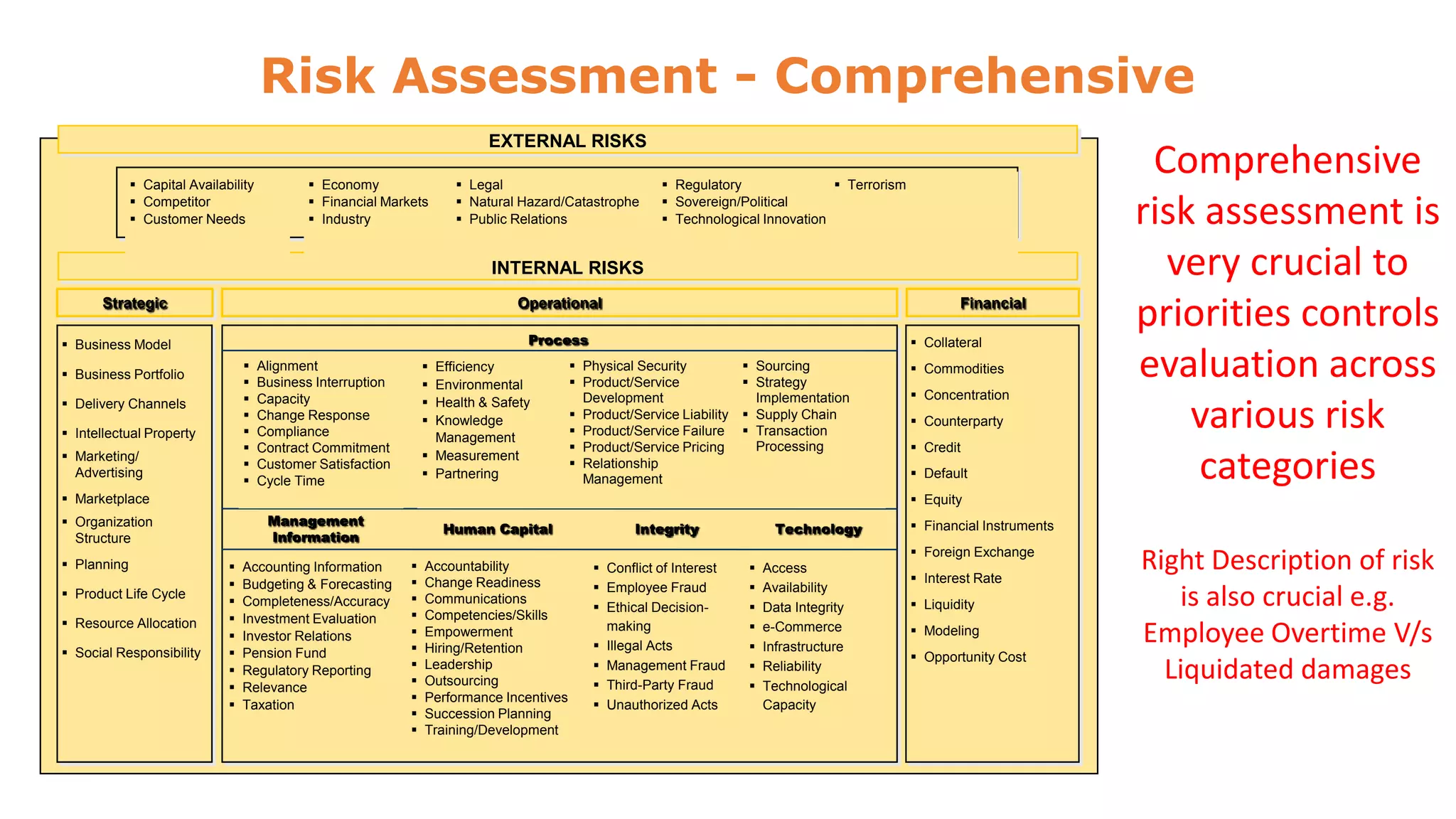
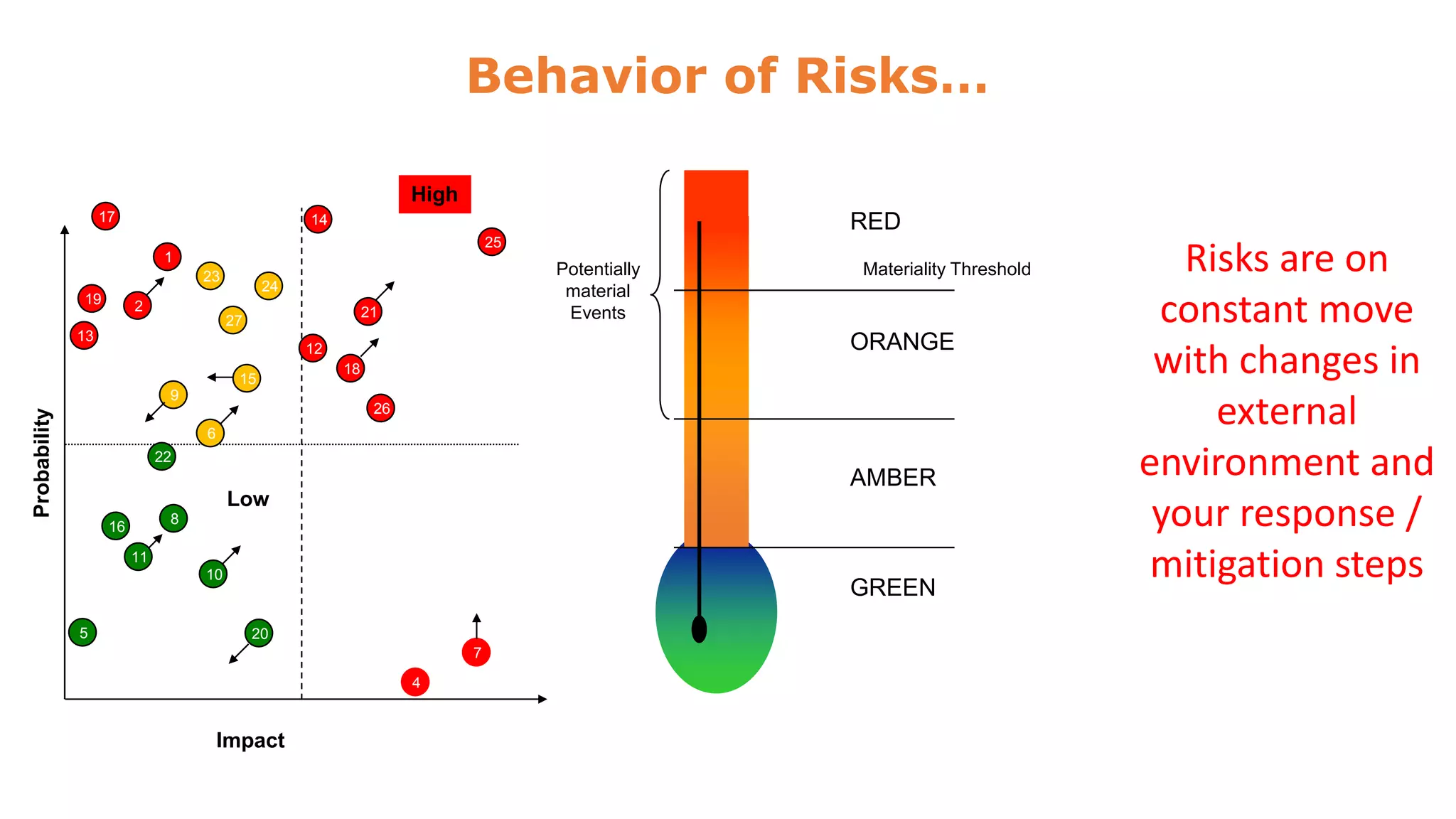
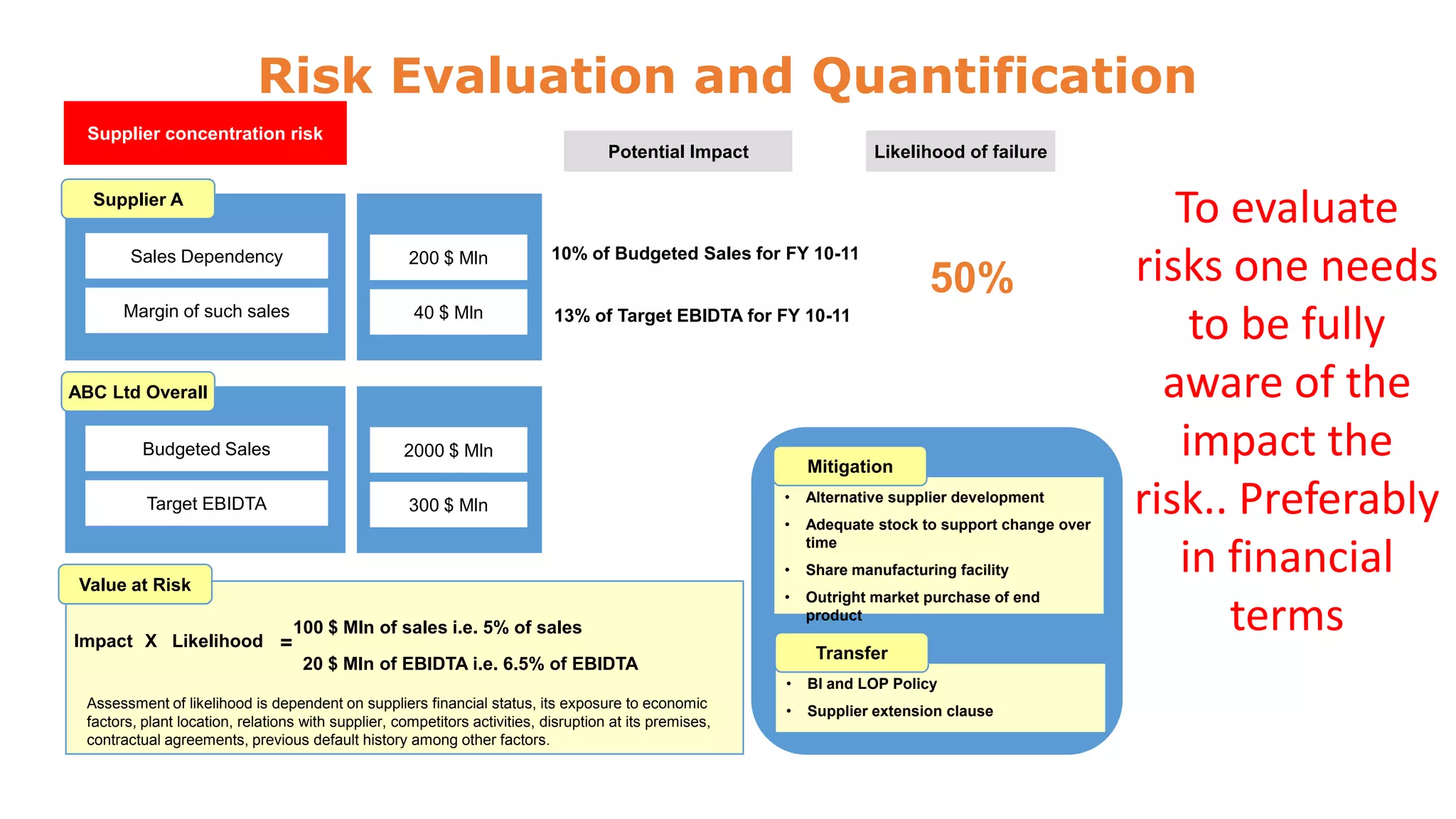
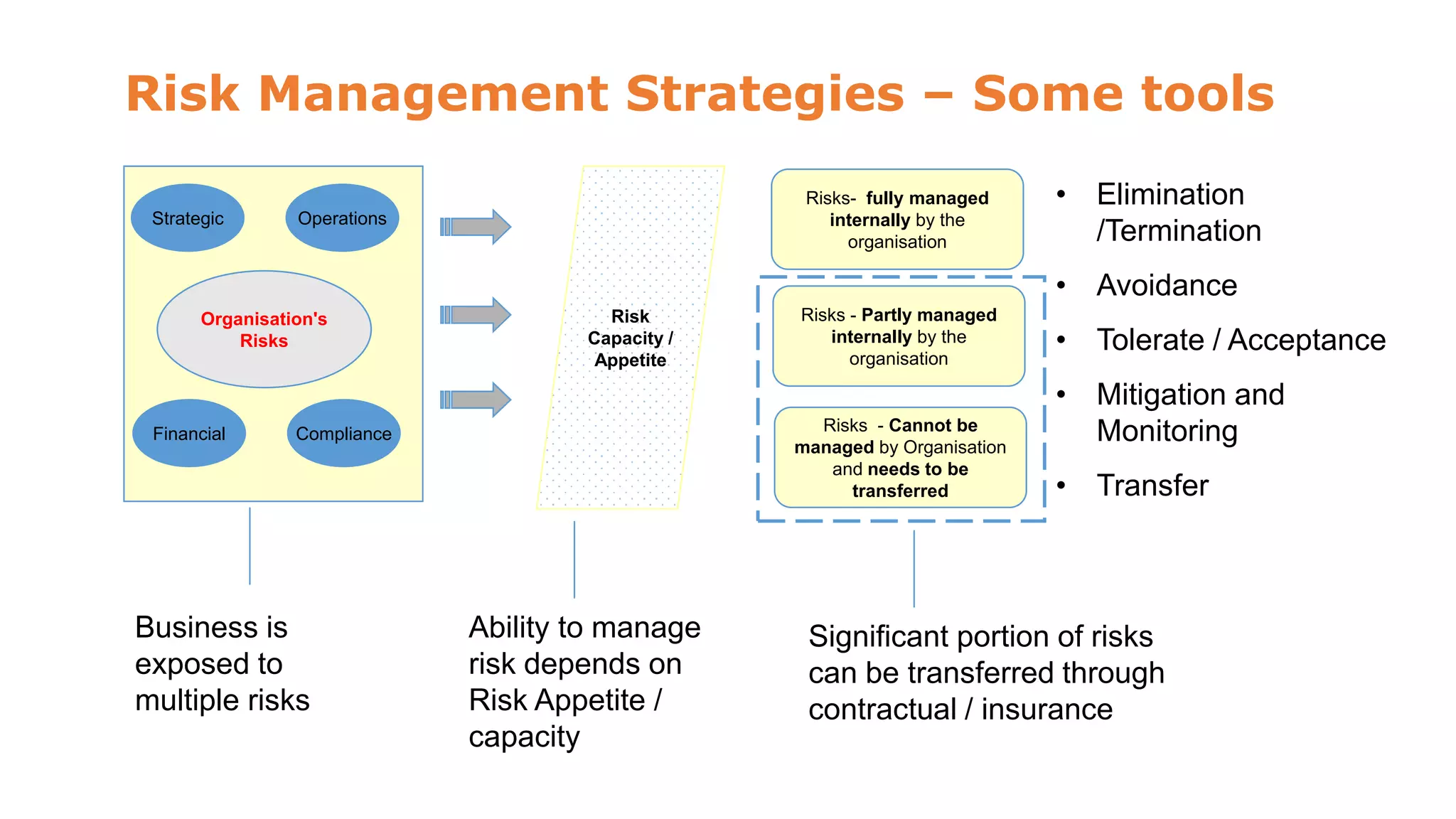
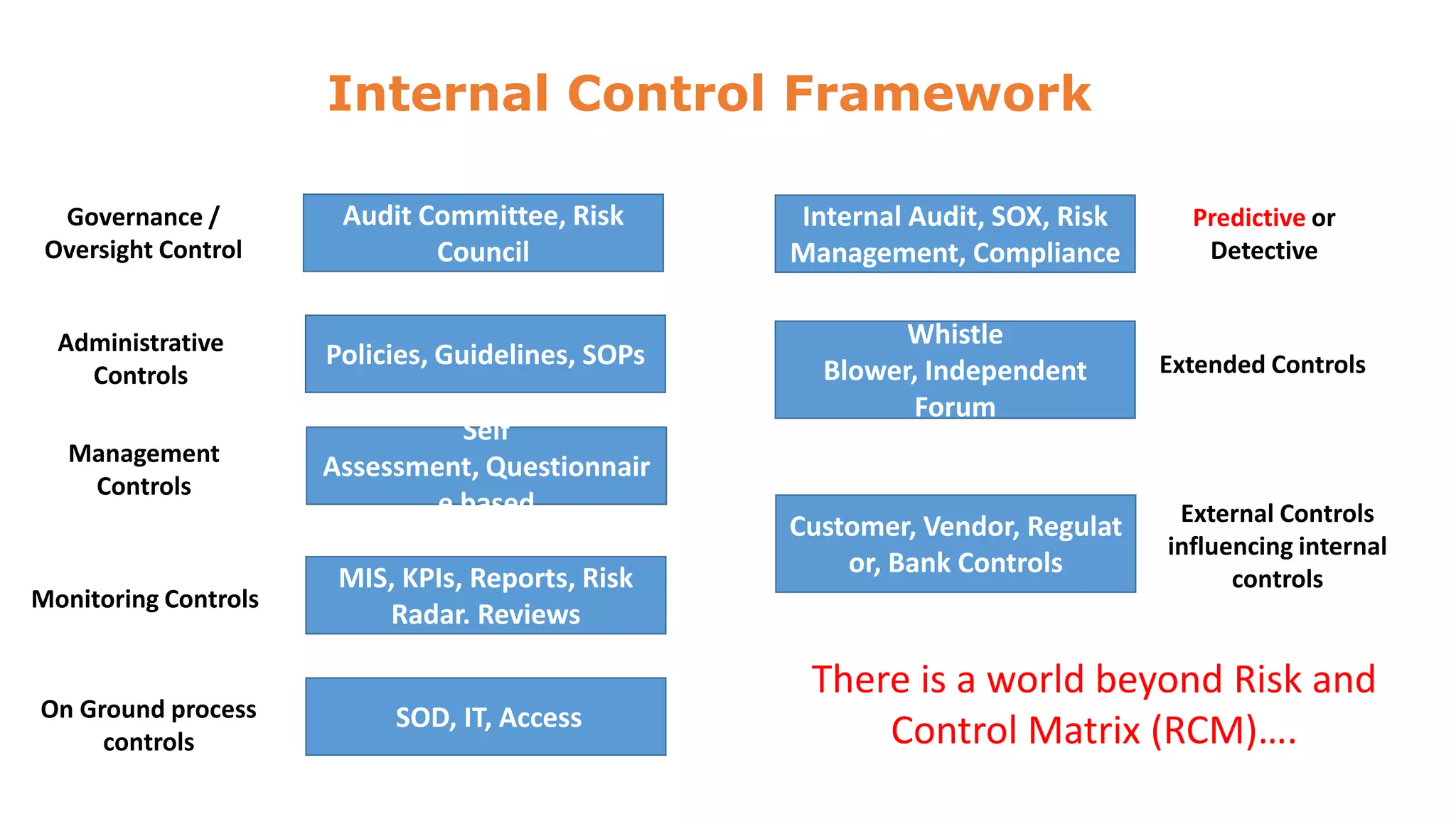
The document discusses risk management and control evaluation, emphasizing the importance of risk assessment as a three-step process involving determining impact, likelihood, and the nature of risks. It outlines both external and internal risks that organizations face, providing a framework for prioritizing controls and evaluating risks. Additionally, it mentions various management strategies, including the transfer of risks and the necessity of an internal control framework for effective governance and oversight.