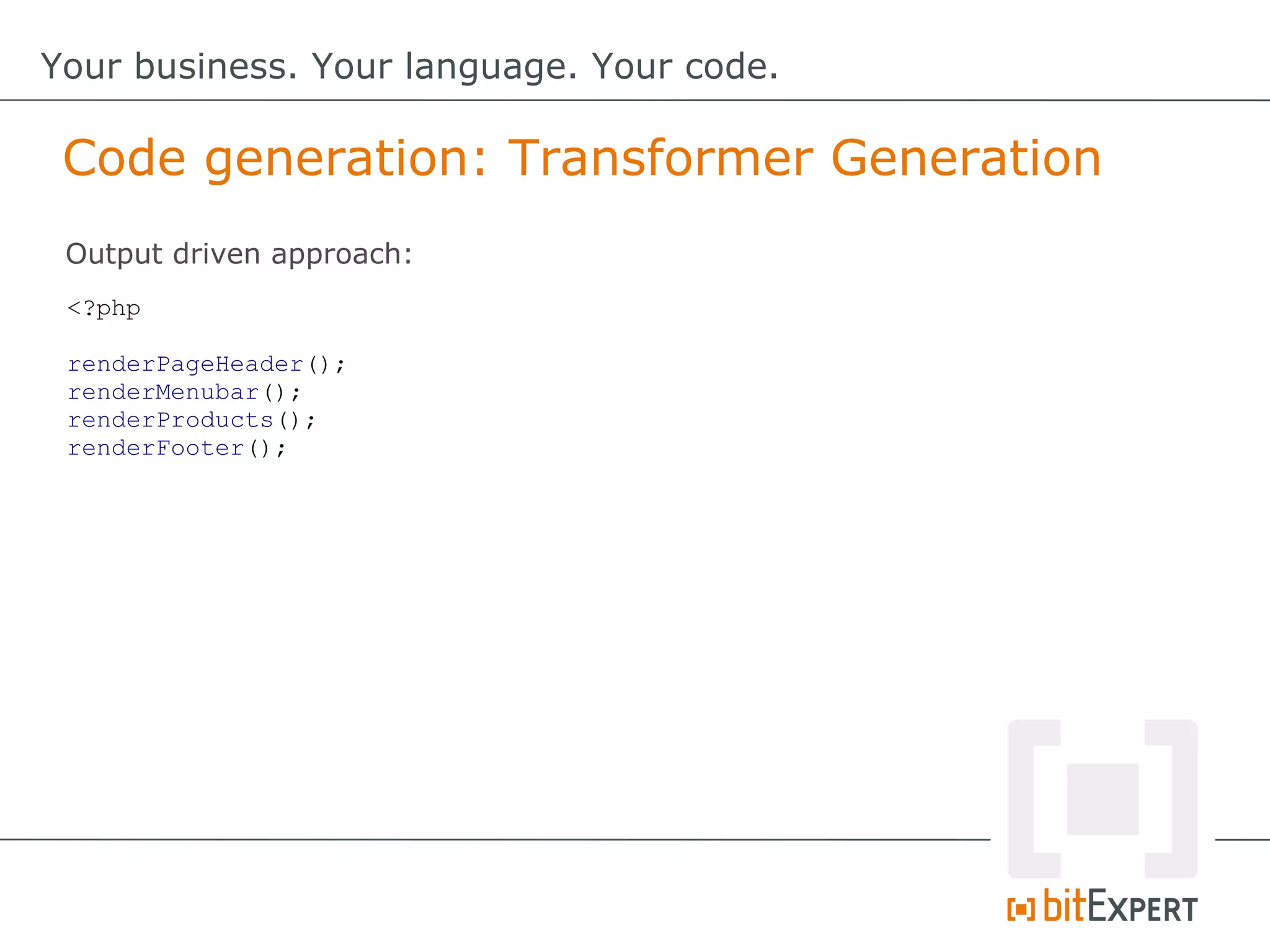
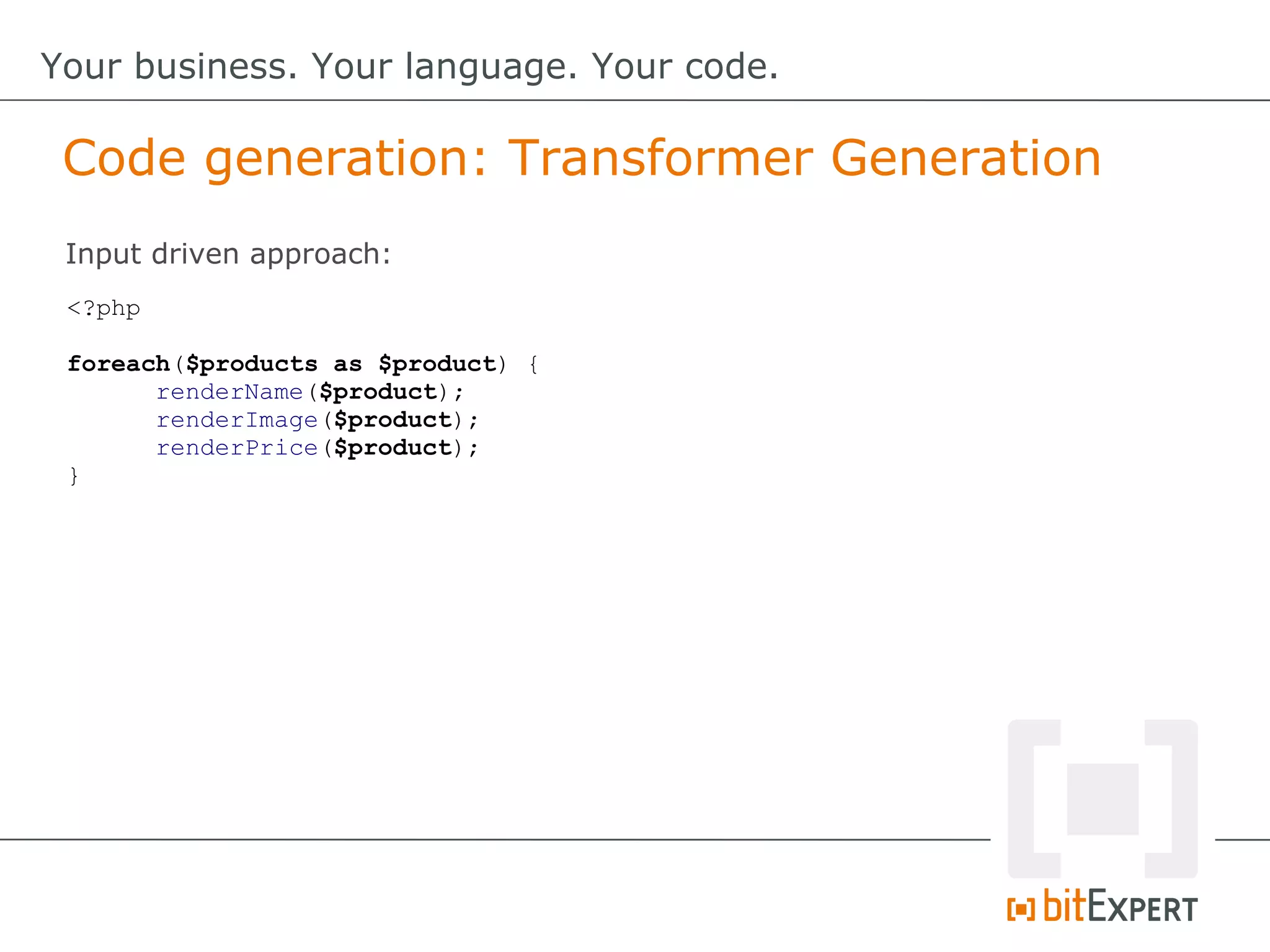
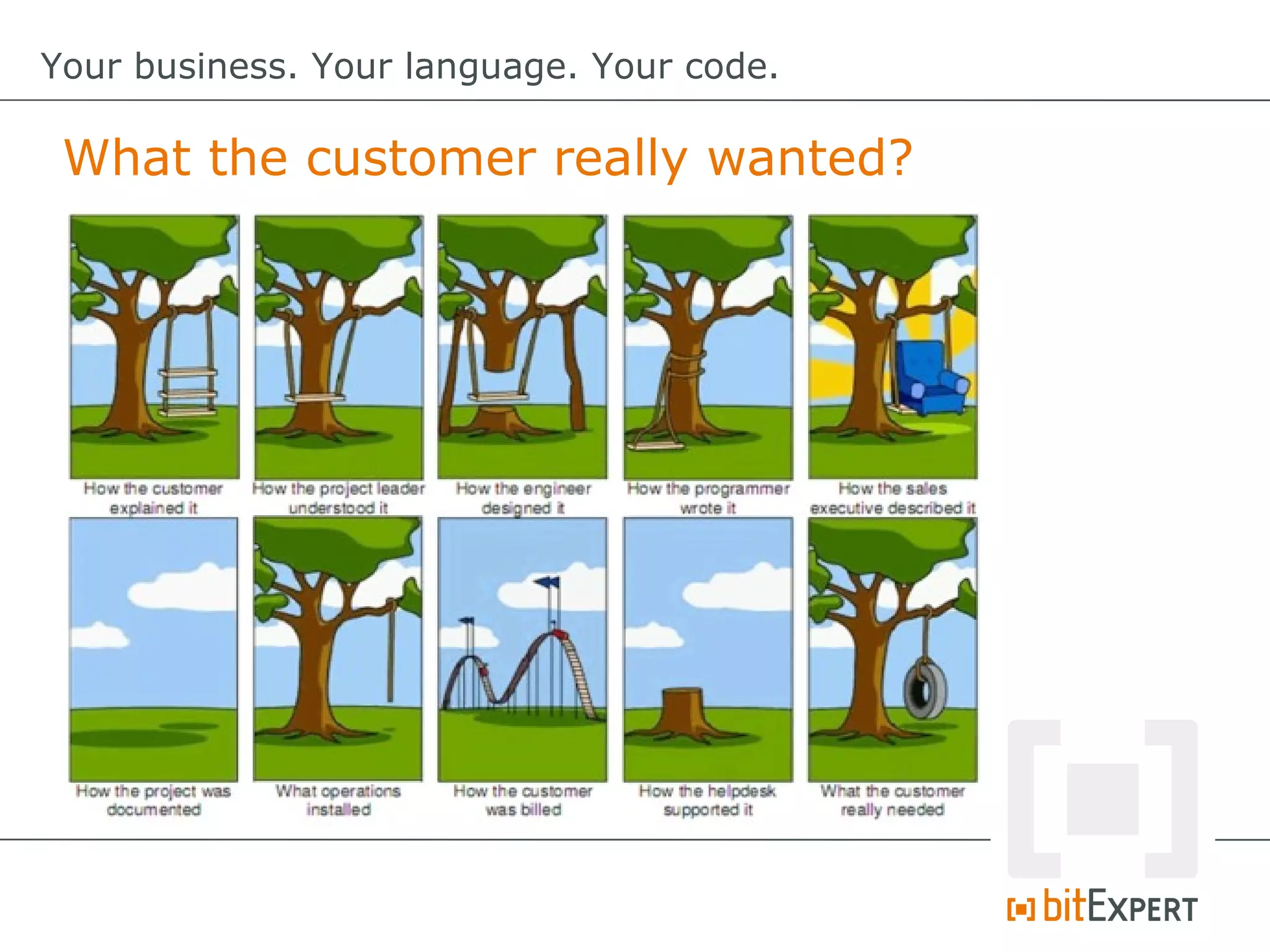
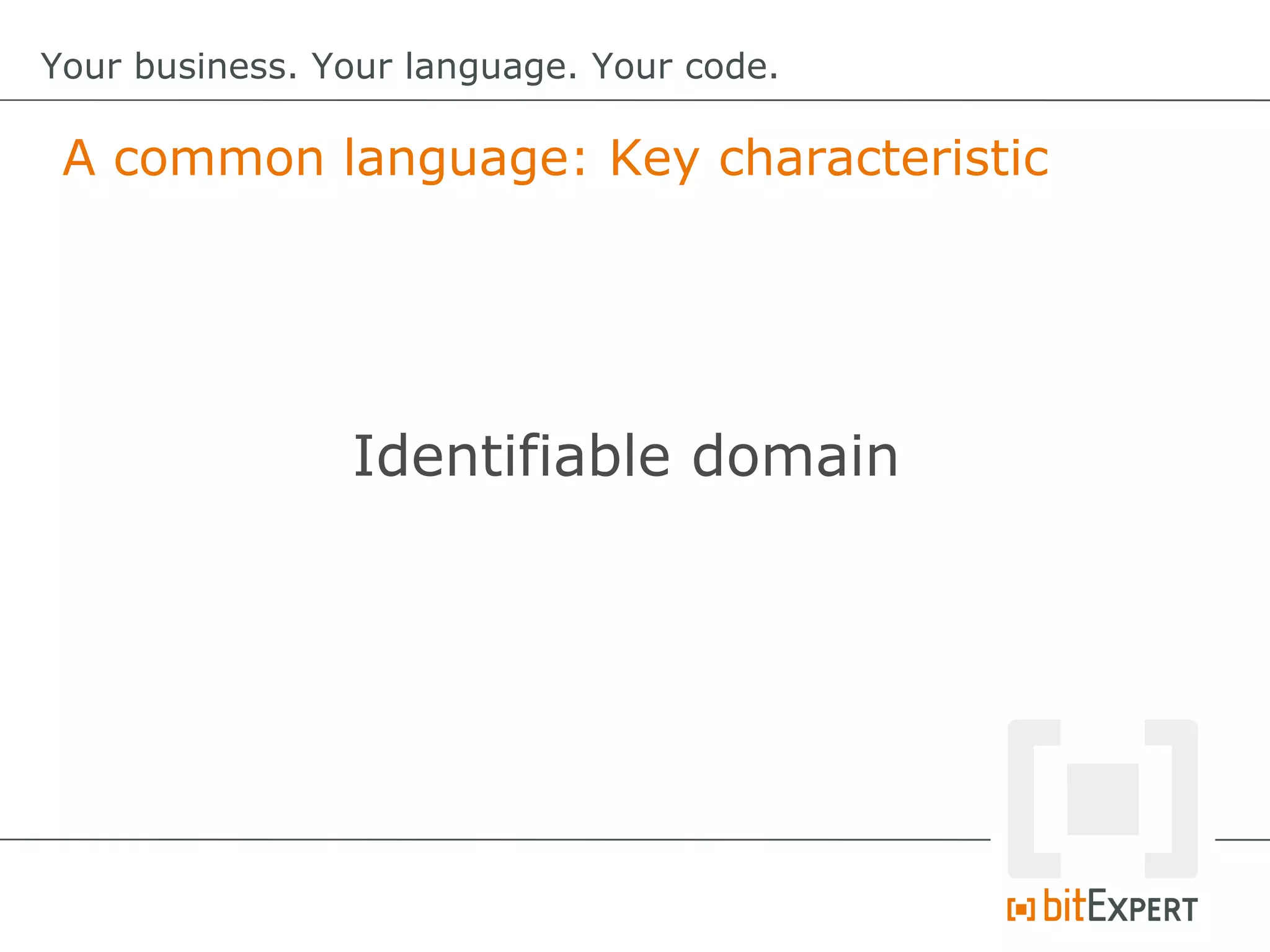
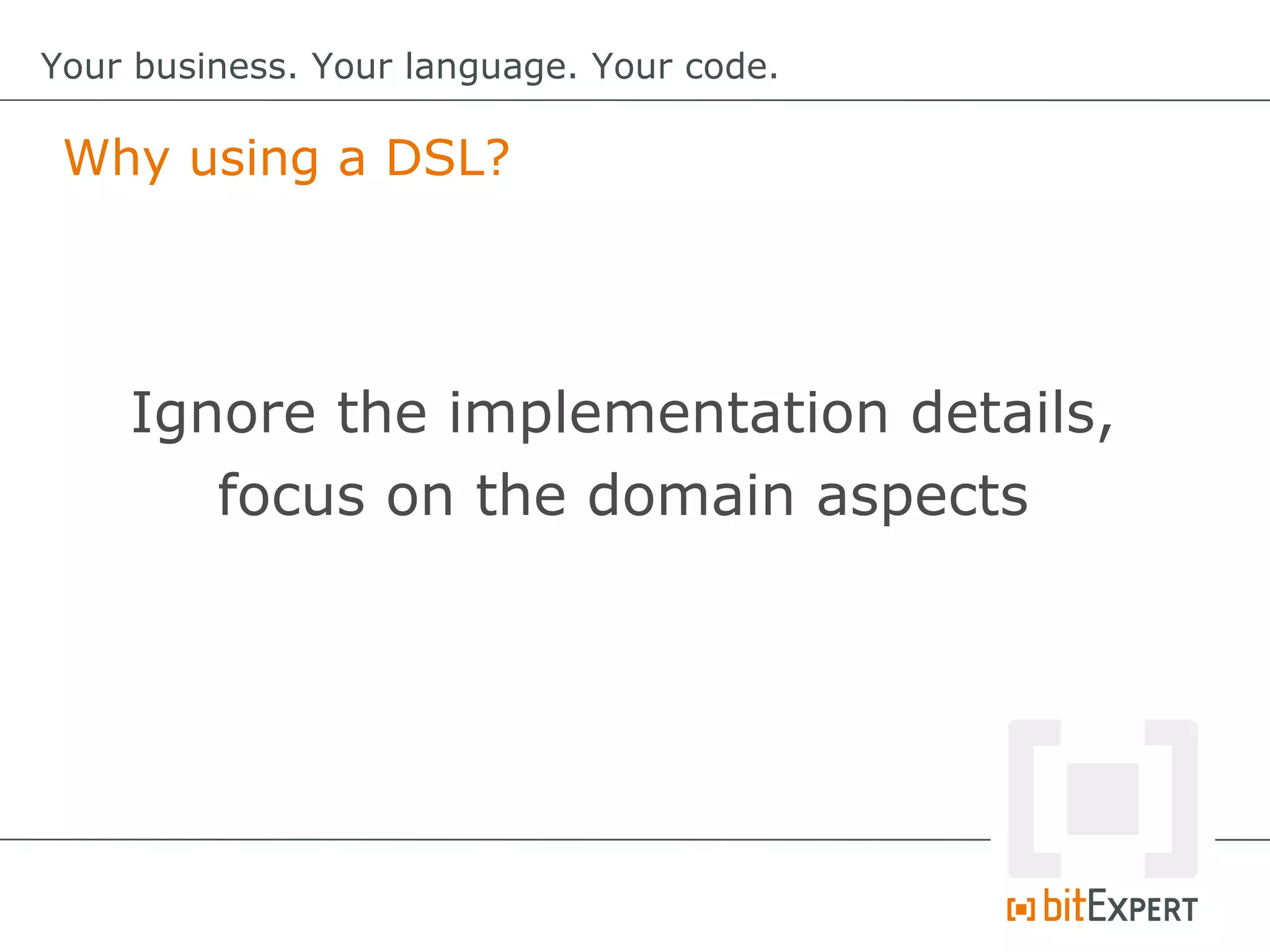
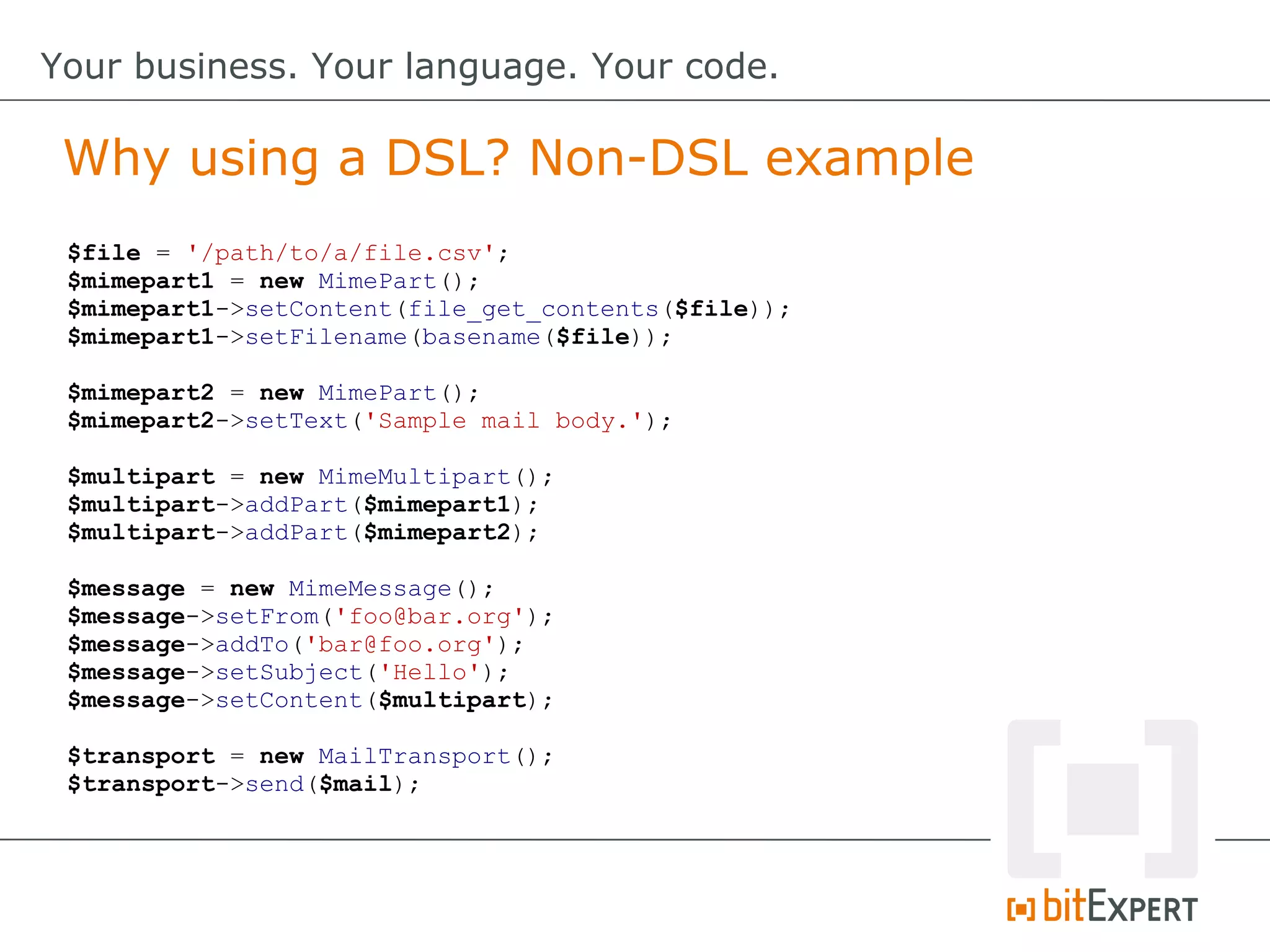
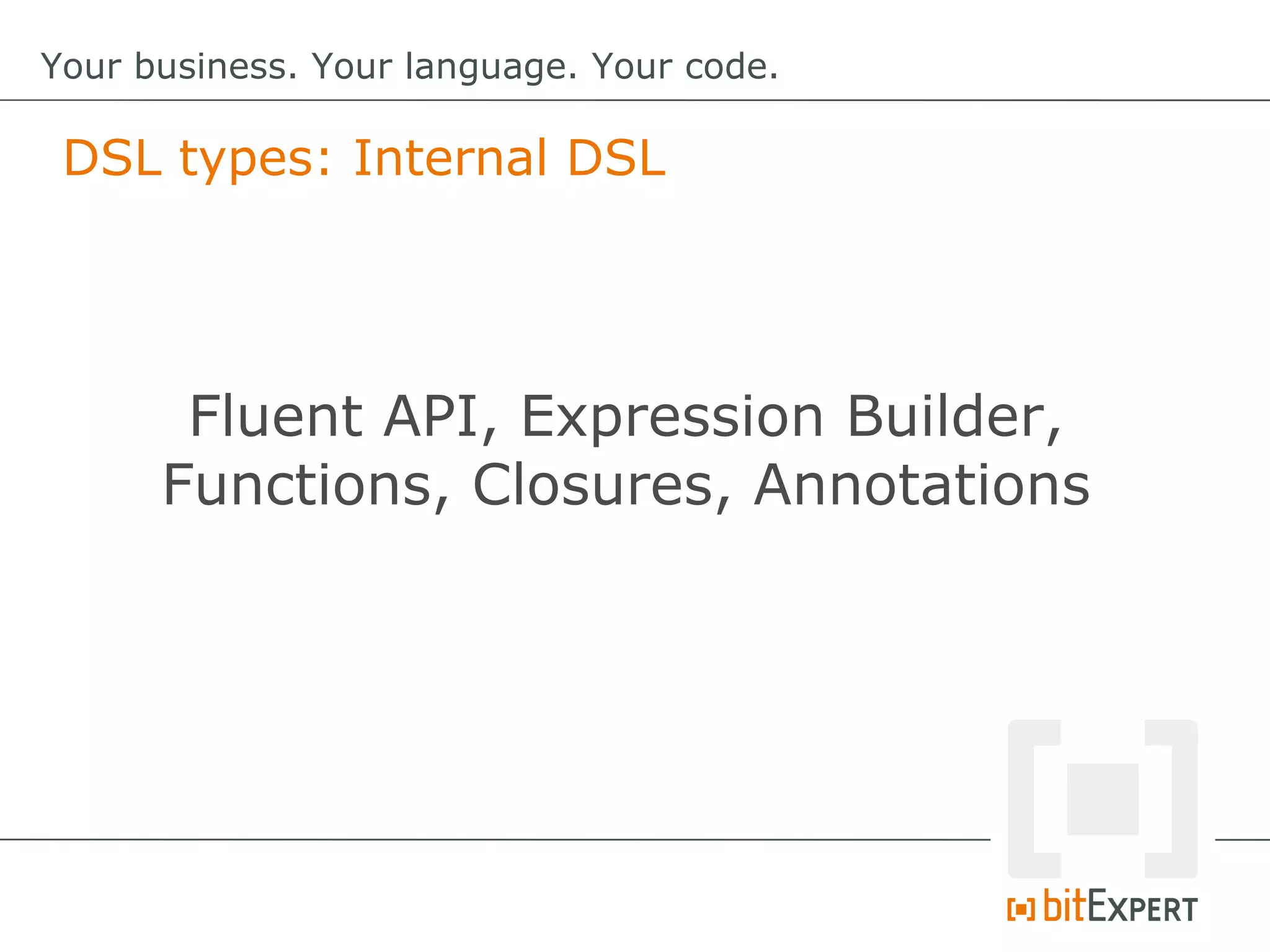
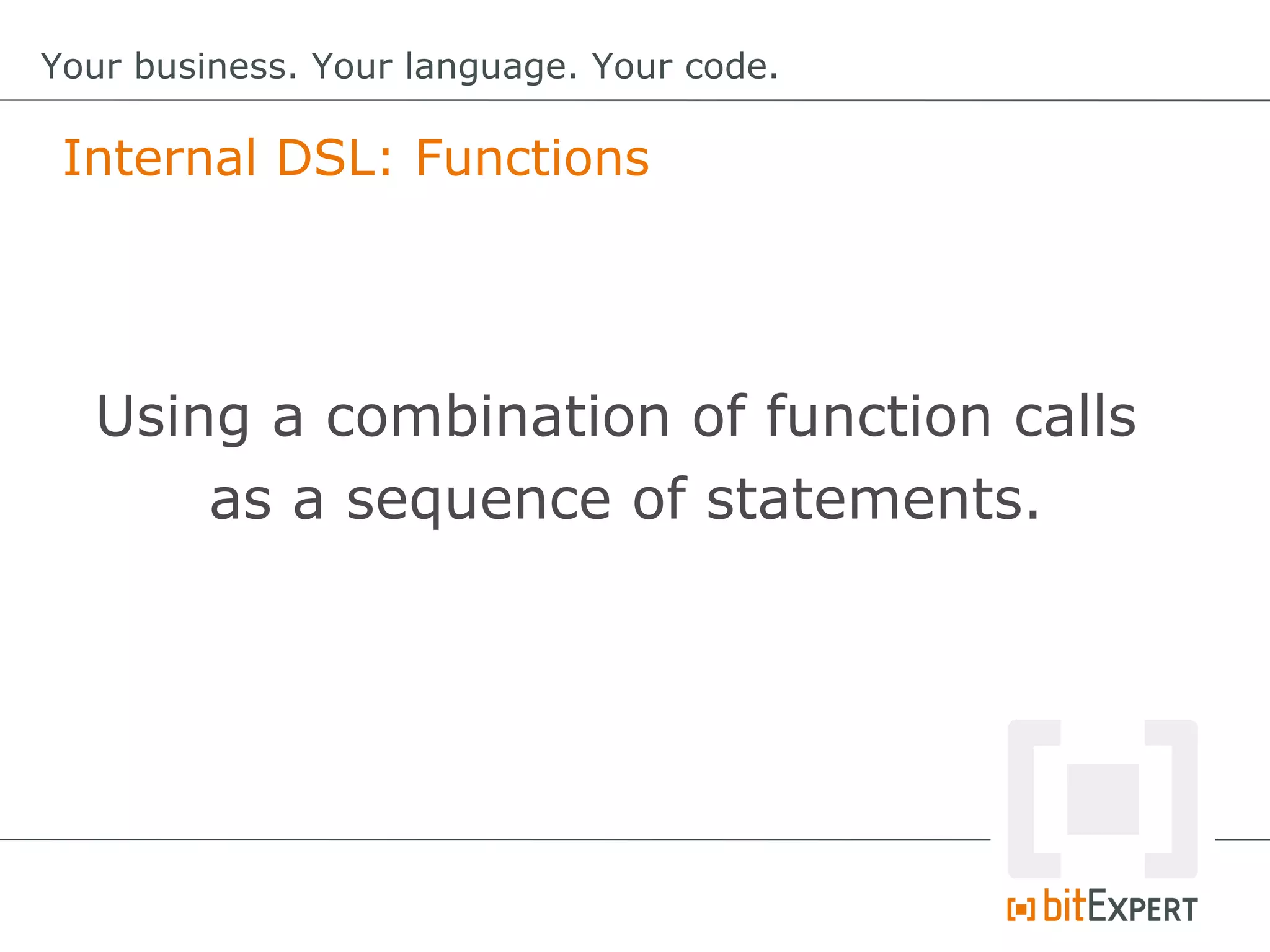
This document discusses domain-specific languages (DSLs) and provides examples of internal and external DSLs. It explains that internal DSLs are implemented within a general-purpose language using techniques like fluent APIs, expression builders, functions, closures, and annotations. External DSLs have greater syntactic freedom but require developing a new language. Both types of DSLs aim to increase productivity by focusing on the domain rather than implementation details. The document also covers code generation from a DSL to executable code.










![A common language
Your business. Your language. Your code.
"[…] I do think that the greatest
potential benefit of DSLs comes when
business people participate [...]"
(Martin Fowler)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-15-2048.jpg)












![Internal DSL: The Fluent API
Your business. Your language. Your code.
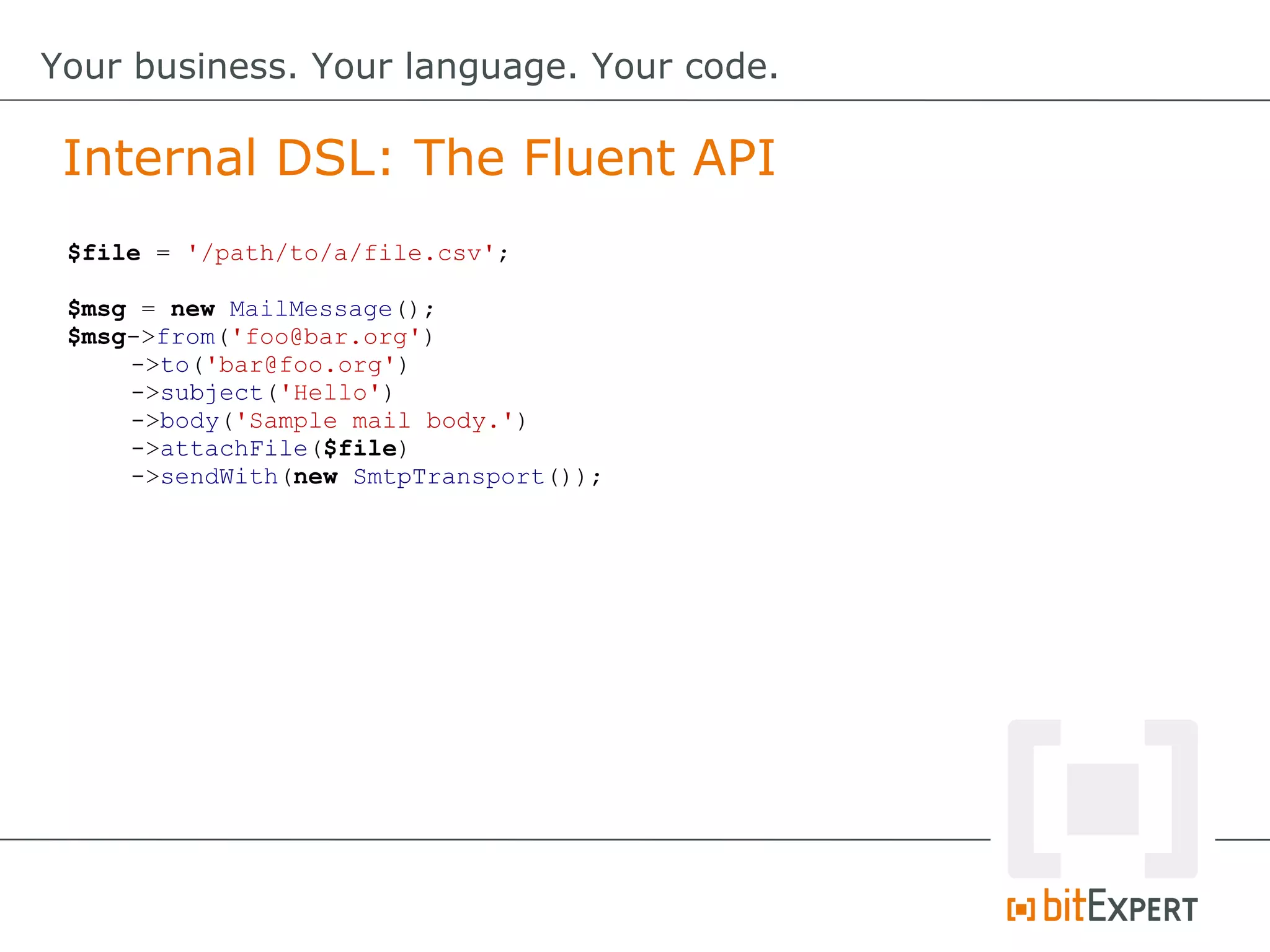
class MailMessage {
protected $from;
protected $to;
public function from($from) {
$this->from = $from;
return $this;
}
public function to($to) {
$this->to = $to;
return $this;
}
// [...]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-36-2048.jpg)
![Internal DSL: The Fluent API
Your business. Your language. Your code.
class MailMessage {
protected $from;
protected $to;
public function from($from) {
$this->from = $from;
return $this;
}
public function to($to) {
$this->to = $to;
return $this;
}
// [...]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-37-2048.jpg)
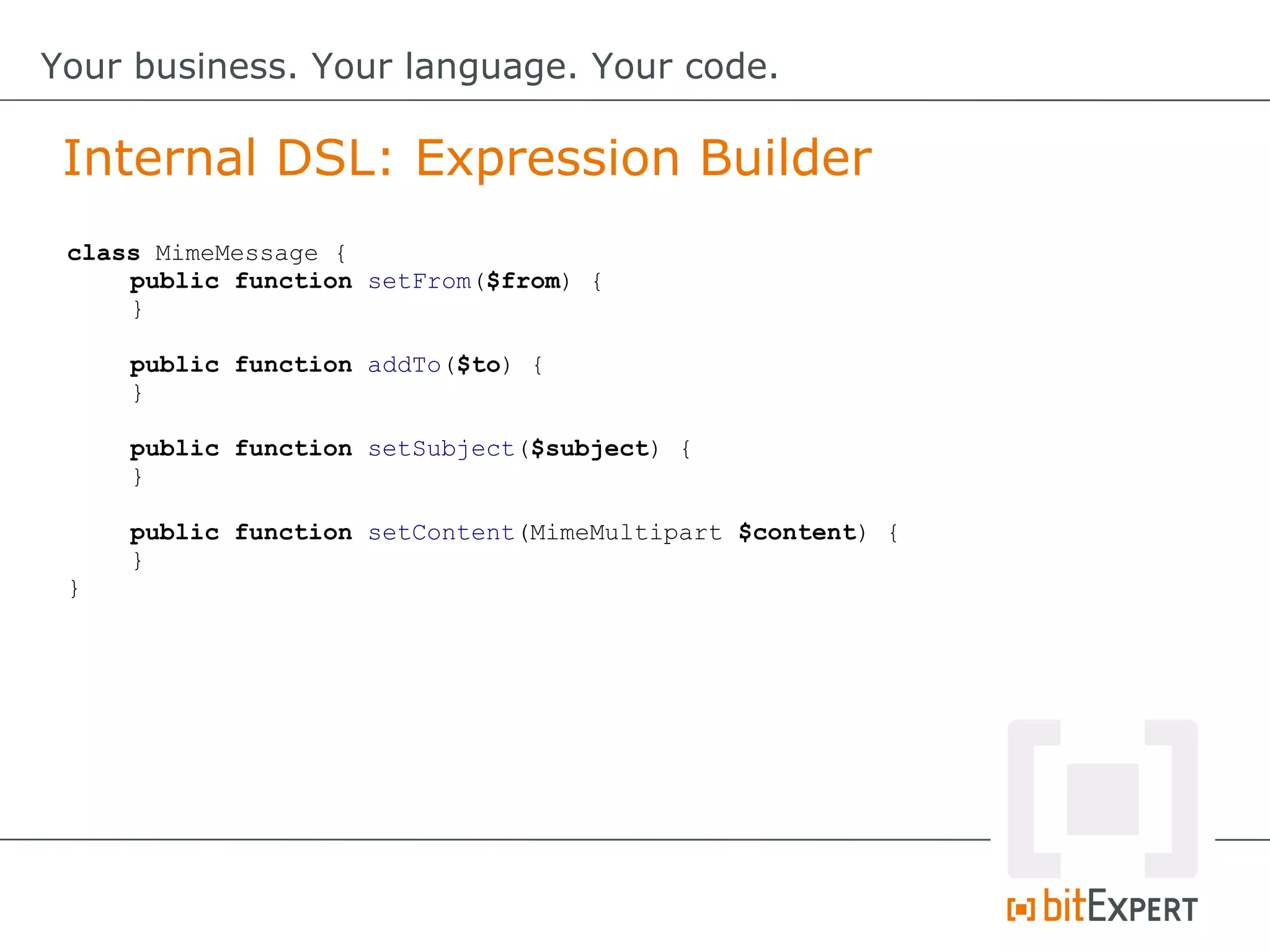
![class MailBuilder {
protected $msg;
protected $multipart;
public function __construct() {
$this->msg = new MimeMessage();
$this->multipart = new MimeMultipart();
}
public function from($from) {
$this->msg->setFrom($from);
return $this;
}
public function attachFile($file) {
$part = new MimePart();
$part->setContent(file_get_contents($file));
$part->setFilename(basename($file));
$this->multipart->addPart($part);
return $this;
}
// [...]
}
Internal DSL: Expression Builder
Your business. Your language. Your code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-41-2048.jpg)

![Internal DSL: Expression Builder (Improved)
Your business. Your language. Your code.
class MailBuilder {
protected $msg;
protected $parts;
public function __construct() {
$this->msg = new MimeMessage();
$this->parts = array();
}
public function from($from) {
$this->msg->setFrom($from);
return $this;
}
public function attachFile($file) {
$builder = new PartBuilder($this);
$this->parts[] = $builder;
return $builder;
}
// [...]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-43-2048.jpg)
![class PartBuilder {
protected $part;
public function __construct() {
$this->part = new MimePart();
}
public function content($content) {
$this->part->setContent($content);
return $this;
}
public function filename($filename) {
$this->part->setFilename($filename);
return $this;
}
// [...]
}
Internal DSL: Expression Builder (Improved)
Your business. Your language. Your code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-44-2048.jpg)
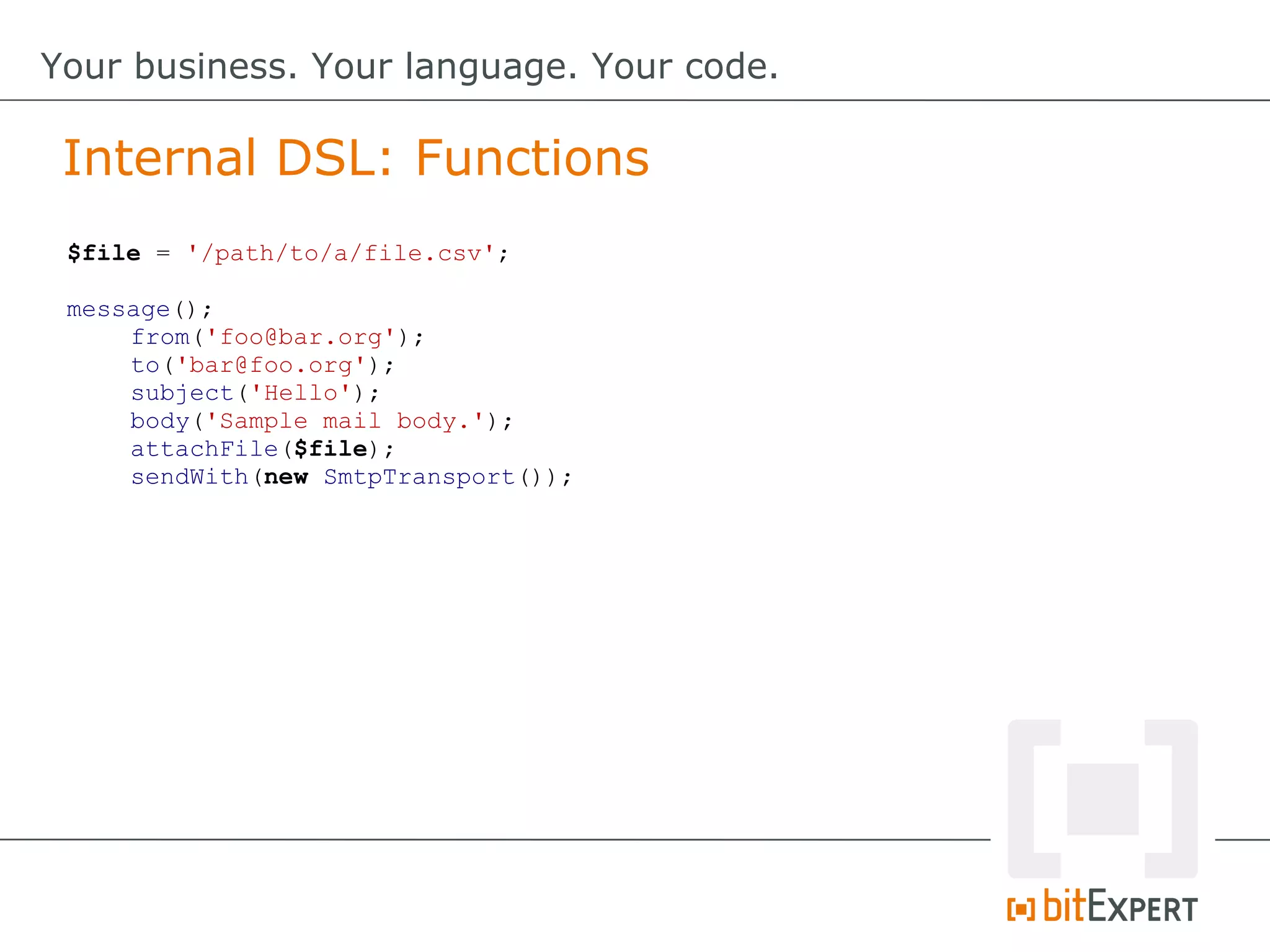

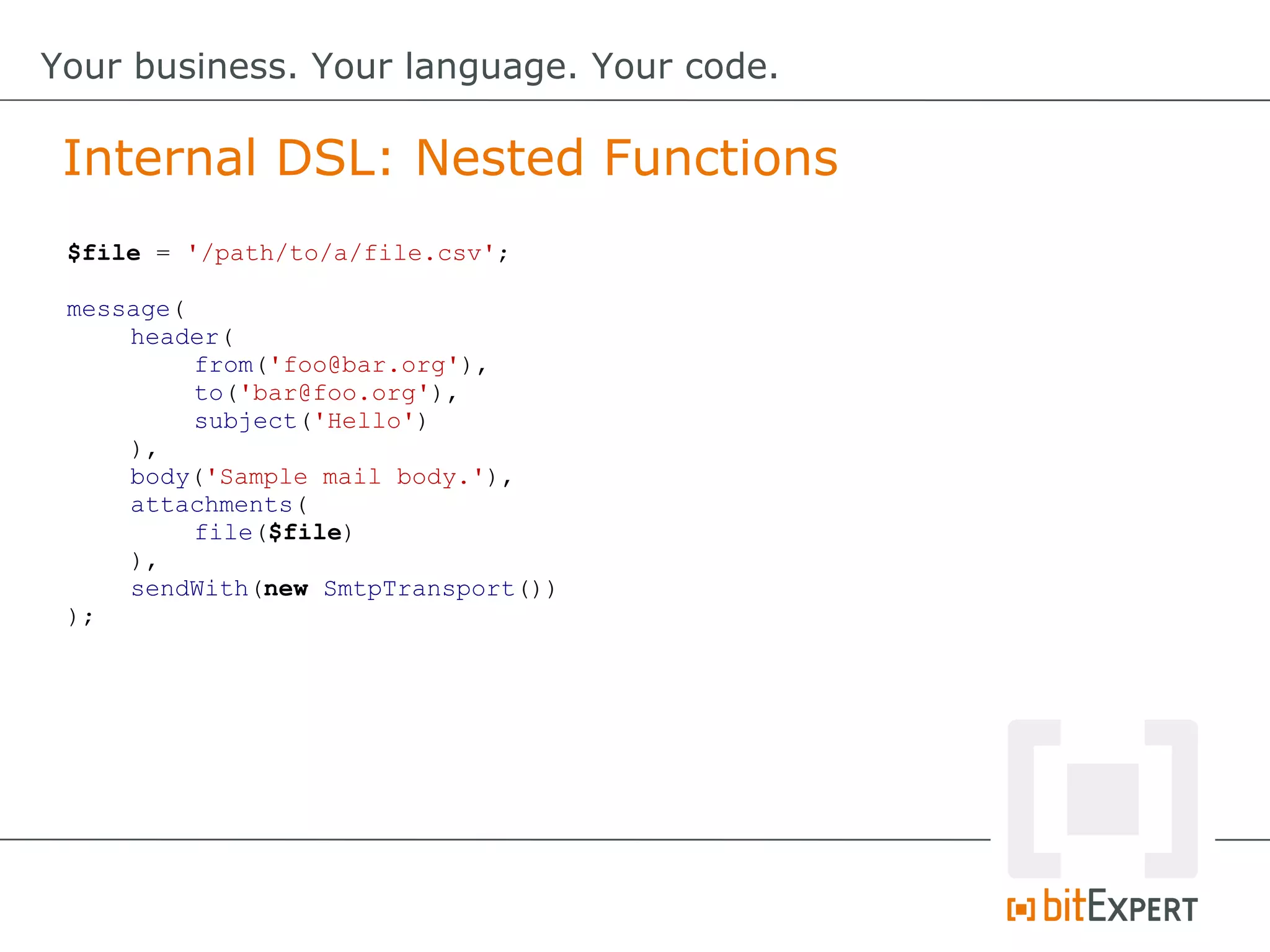
![$file = '/path/to/a/file.csv';
$file2 = '/path/to/a/file2.csv';
message(
header(
[
from('foo@bar.org'),
to('bar@foo.org'),
subject('Hello')
]
),
body('Sample mail body.'),
attachments(
[
file($file),
file($file2)
]
),
sendWith(new SmtpTransport())
);
Internal DSL: Nested Functions (Improved)
Your business. Your language. Your code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-51-2048.jpg)



![class MyCustomController {
// [...]
public function adminAction() {
$user = $this->authService->getLoggedInUser();
if(!$user->hasRole('ROLE_ADMIN')) {
throw new AccessDeniedException();
}
// proceed with main logic...
}
}
Internal DSL: Annotations
Your business. Your language. Your code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-58-2048.jpg)
![class MyCustomController {
// [...]
/**
* @Allow(roles="ROLE_ADMIN")
*/
public function adminAction() {
// proceed with main logic...
}
}
Internal DSL: Annotations
Your business. Your language. Your code.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-59-2048.jpg)


![Code generation: Template Generation
Your business. Your language. Your code.
<?php
class [className] {
protected $service;
public function __construct([serviceType] $service) {
$this->service = $service;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20130608yourbusinessyourlanguageyourcode-130609140100-phpapp02/75/Your-Business-Your-Language-Your-Code-dpc13-66-2048.jpg)