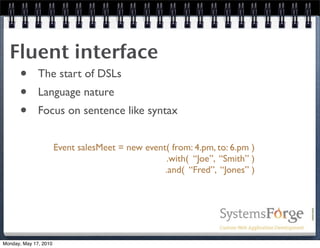
The document discusses domain-specific languages (DSLs), outlining their definition, benefits, and when to use them. It covers key concepts like types of DSLs, design approaches, implementation strategies, and additional considerations such as testing and documentation. The presentation aims to equip participants with a comprehensive understanding of DSL engineering and its application in software development.