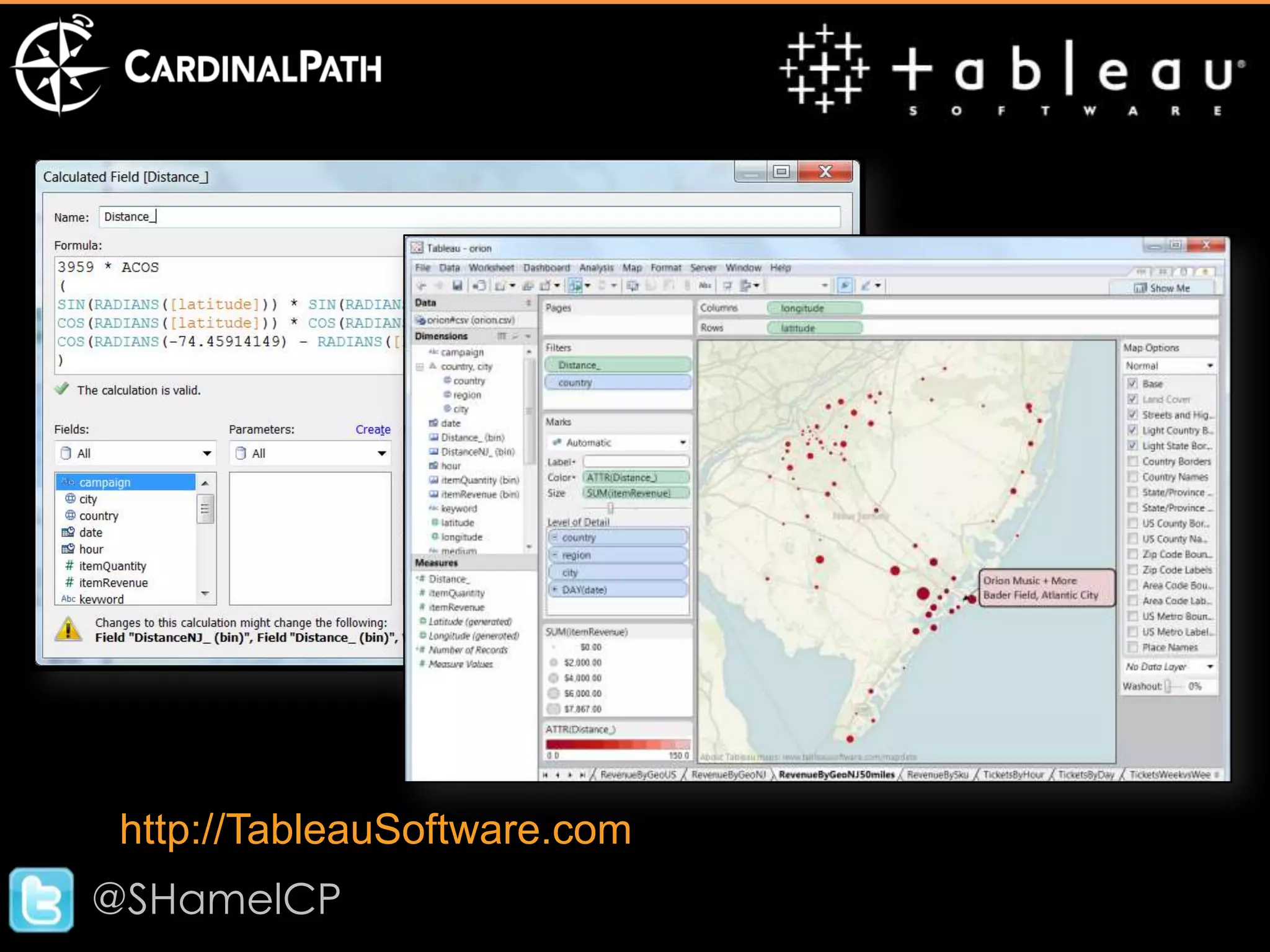
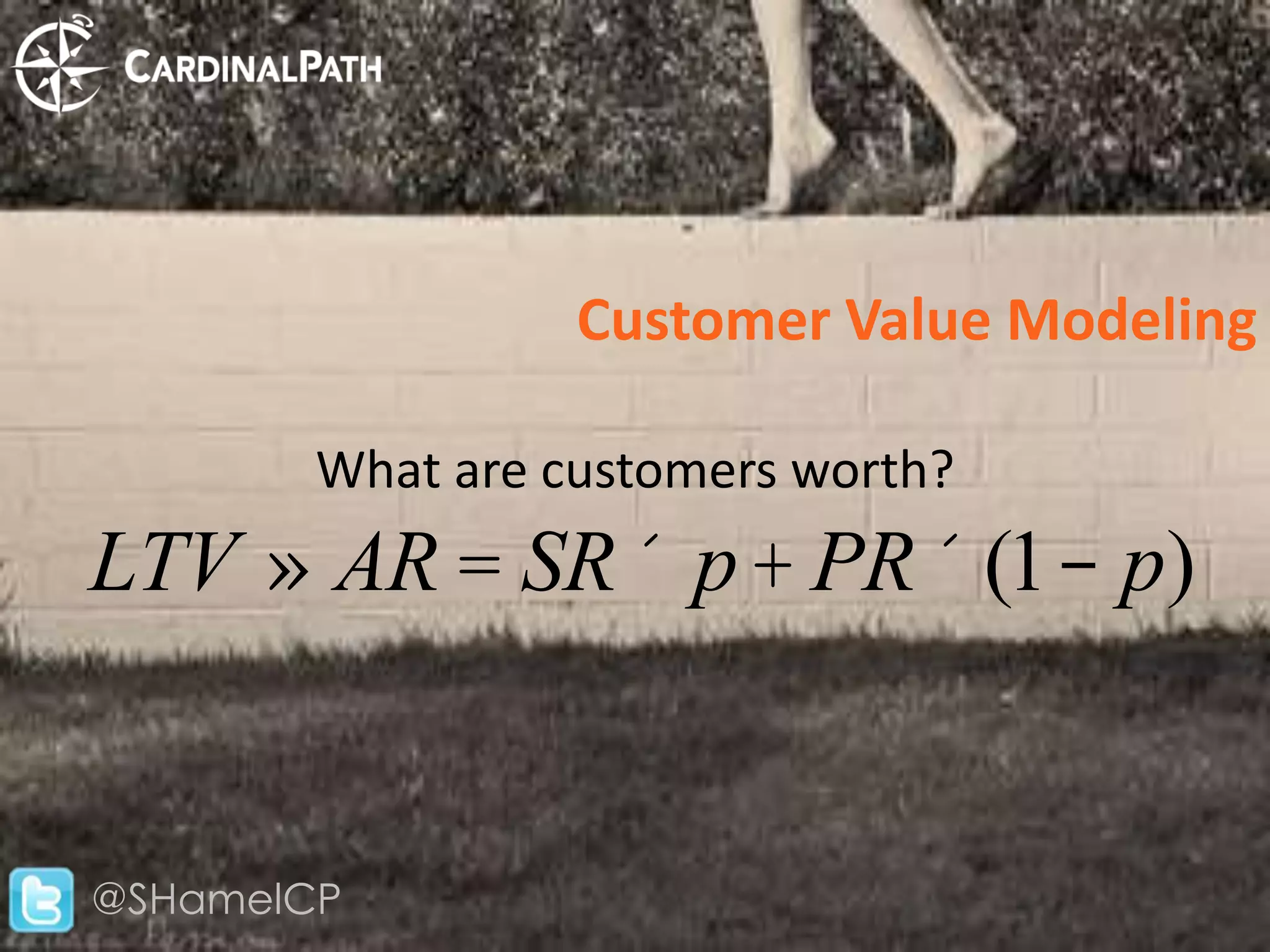
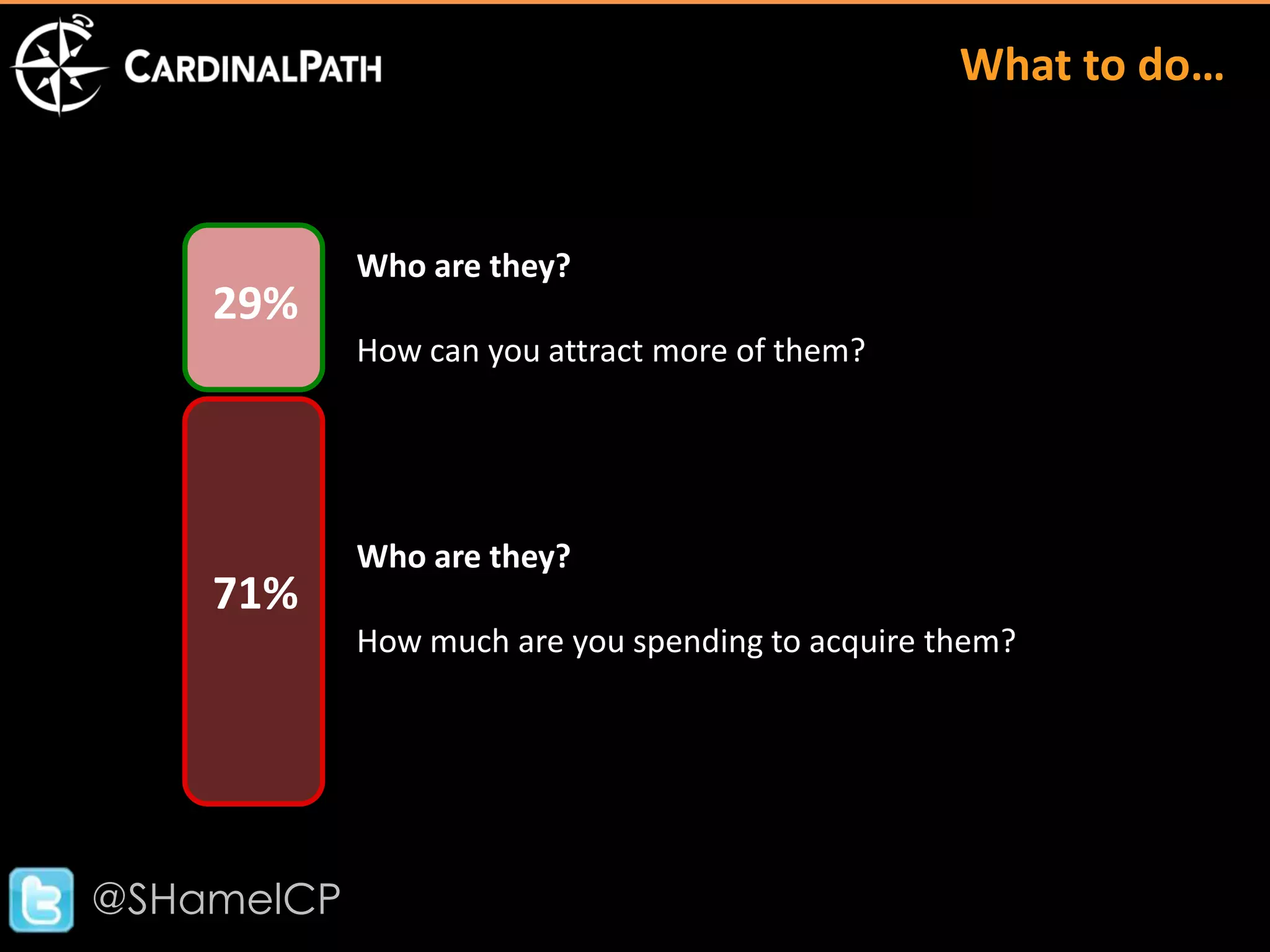
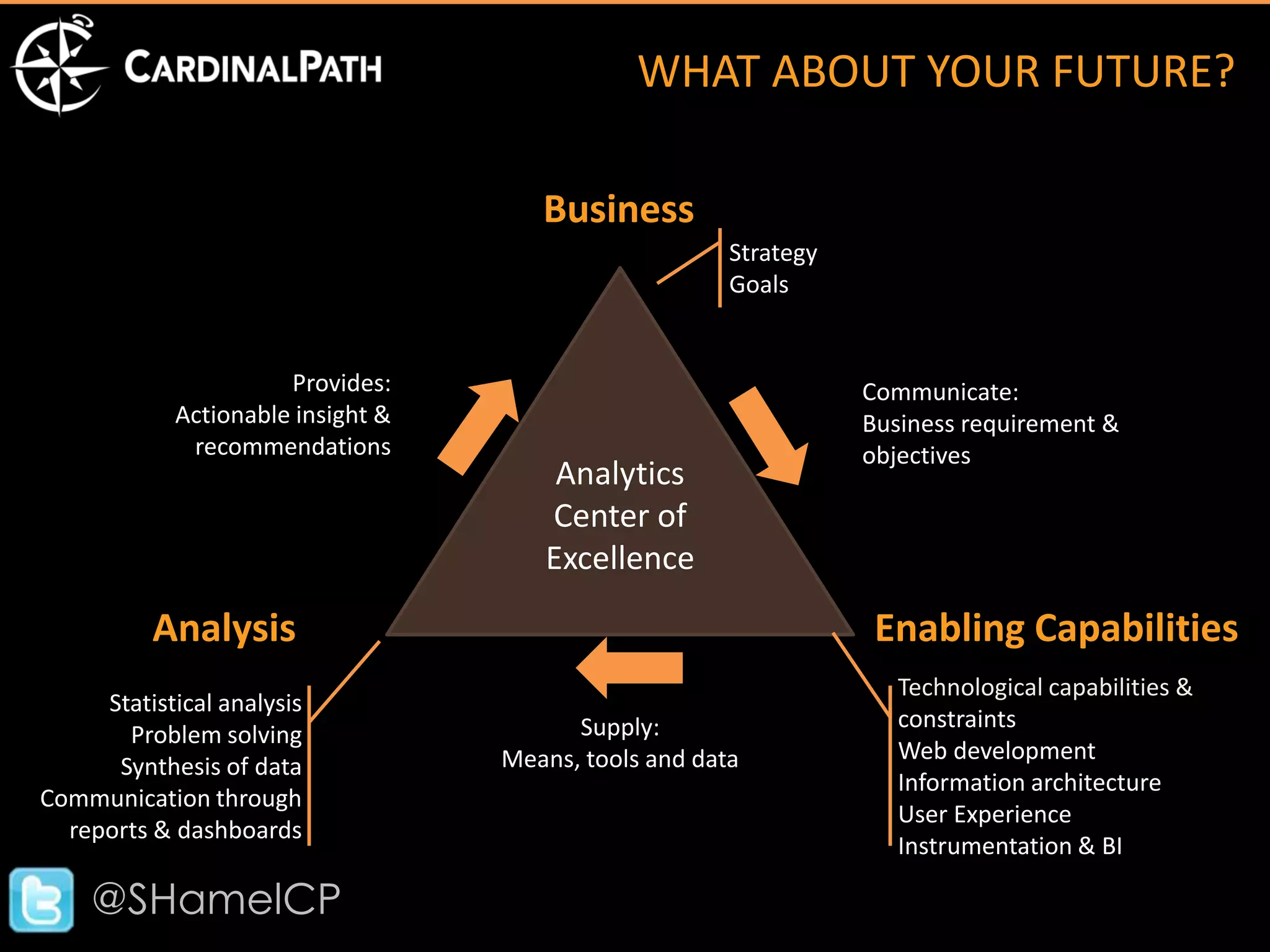
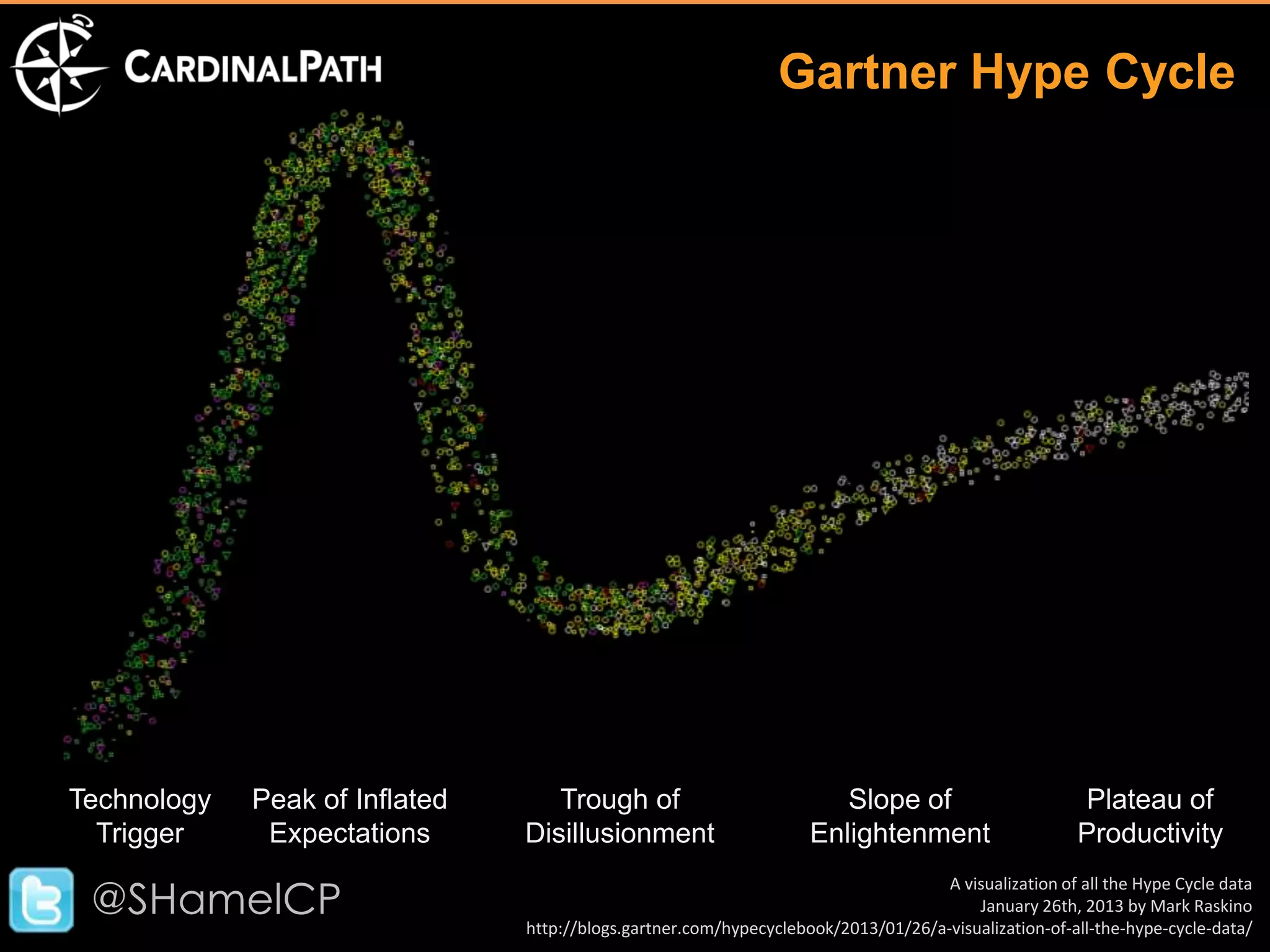
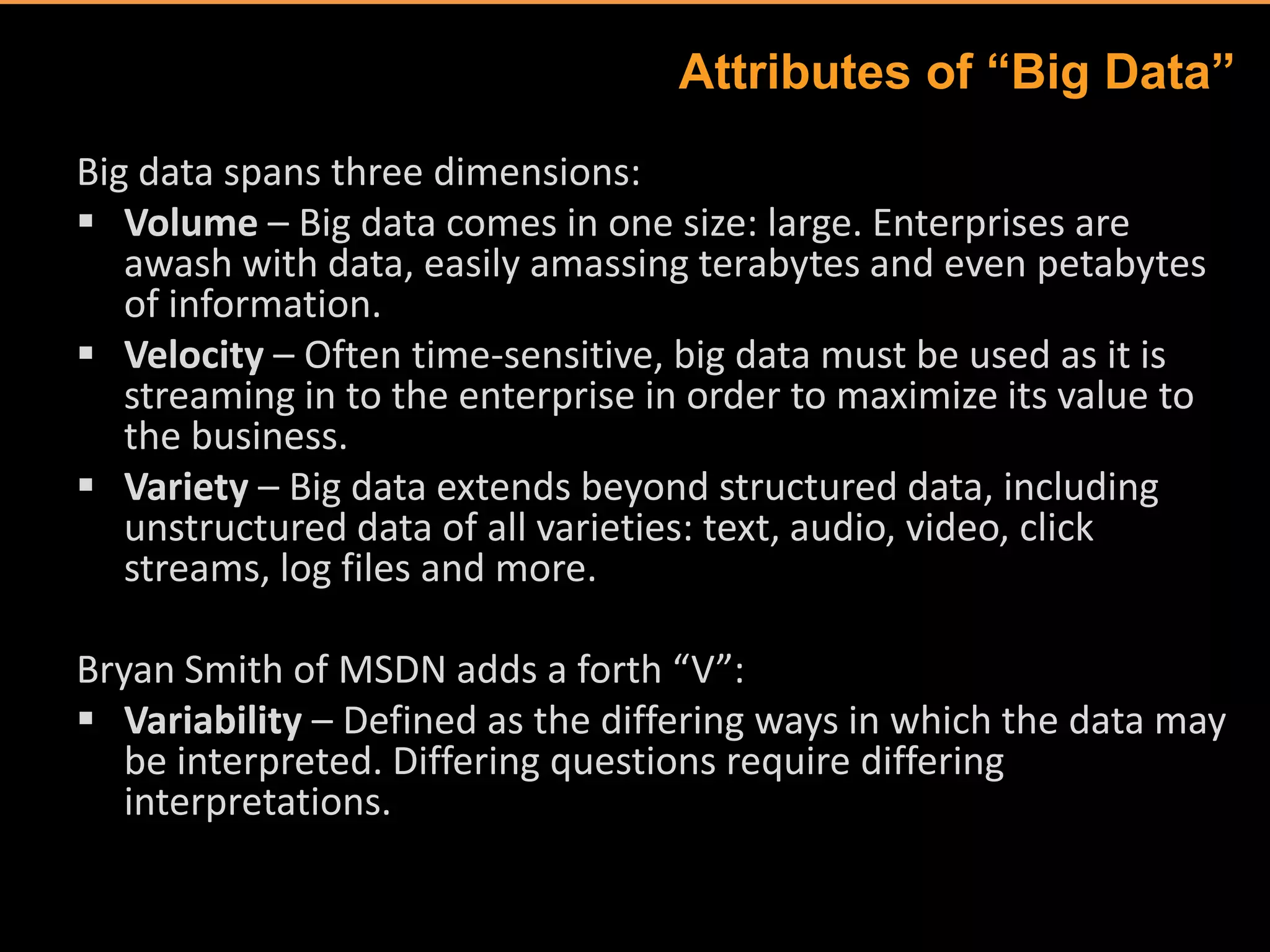
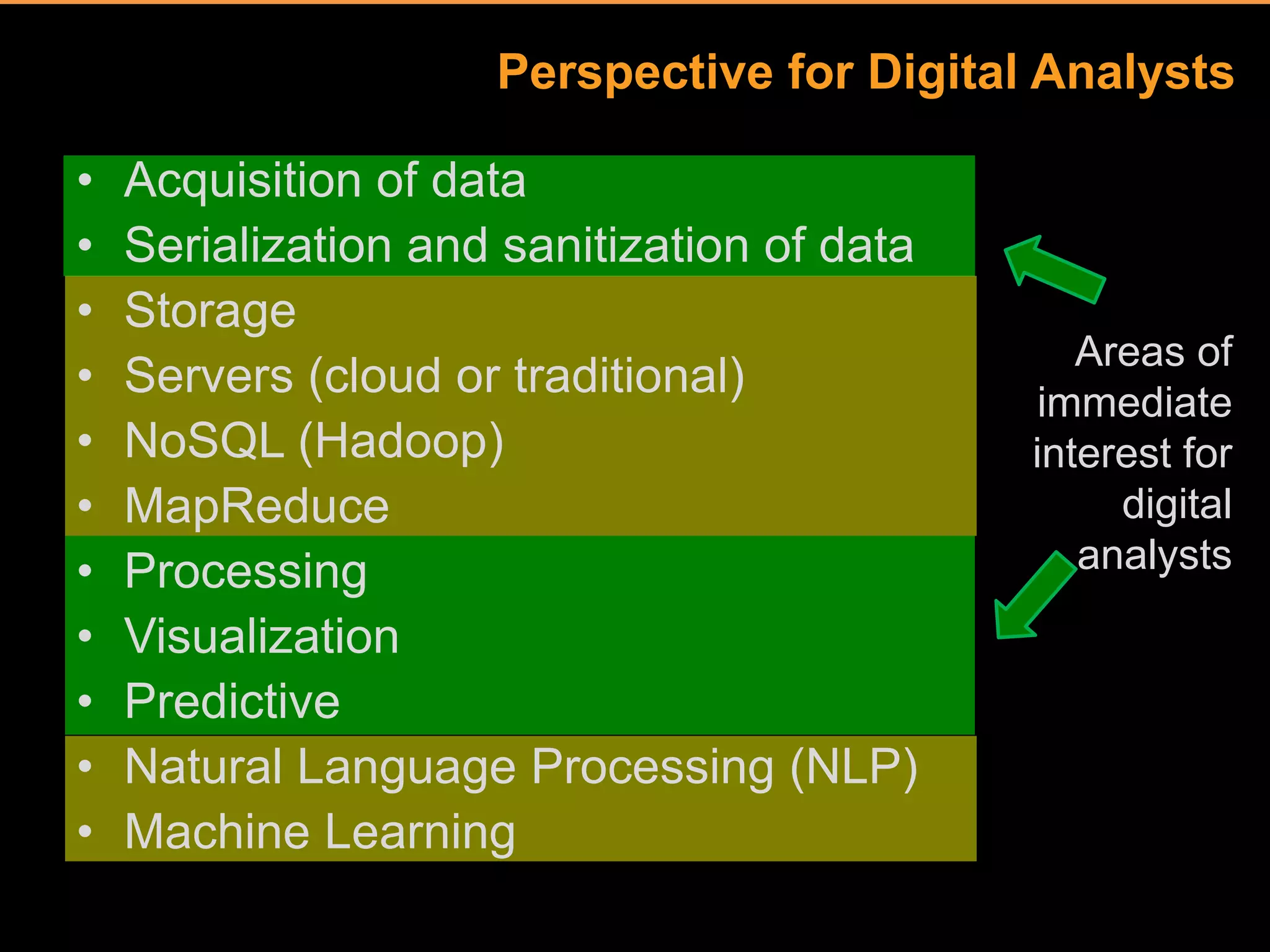
The document discusses big data and its implications for digital analysts. It covers the volume, velocity, and variety of big data. It also discusses areas of immediate interest for digital analysts related to acquiring, storing, processing, visualizing, and analyzing big data. The future of digital analysts involves making sense of large and complex data through creativity and context.