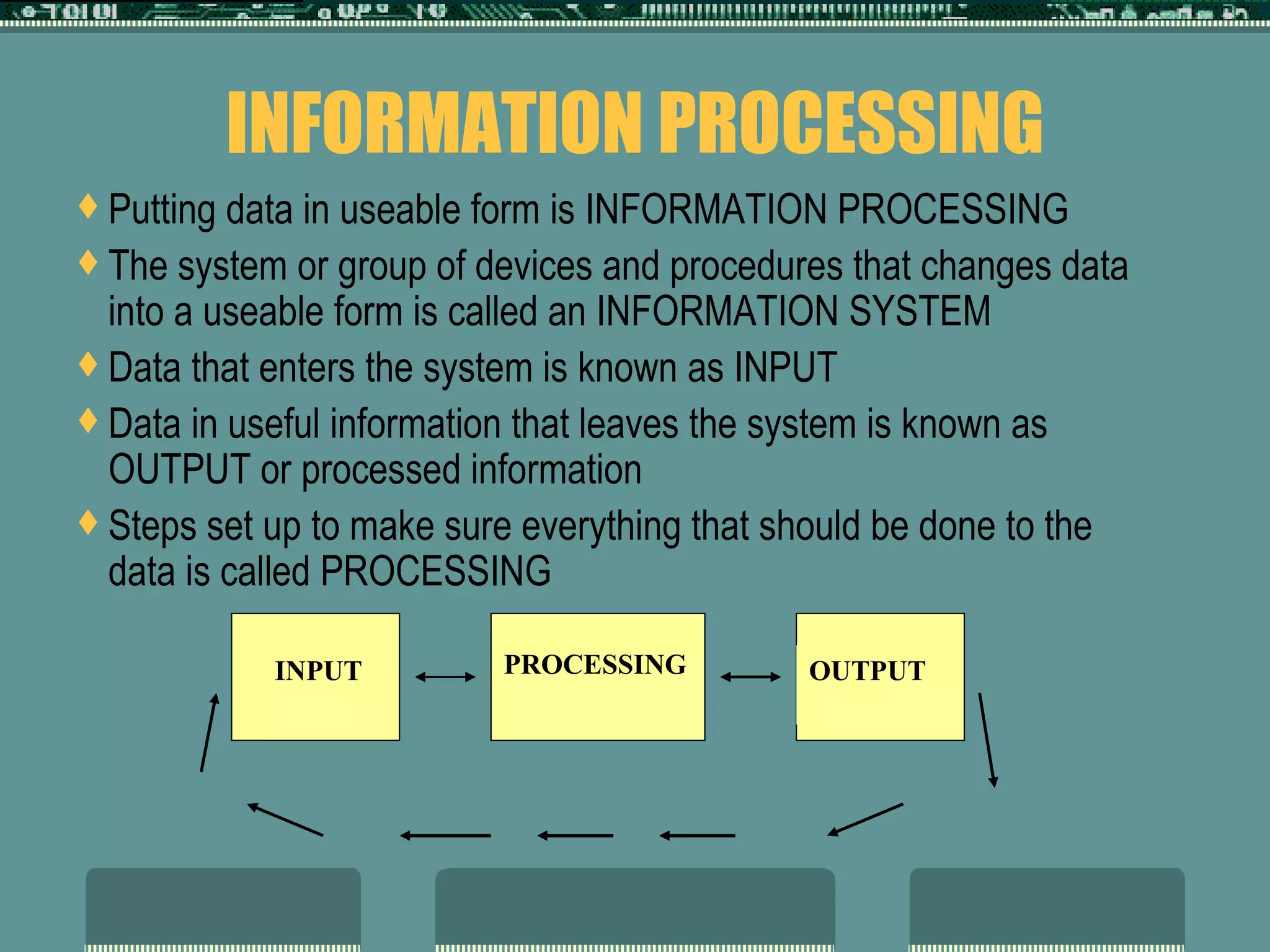
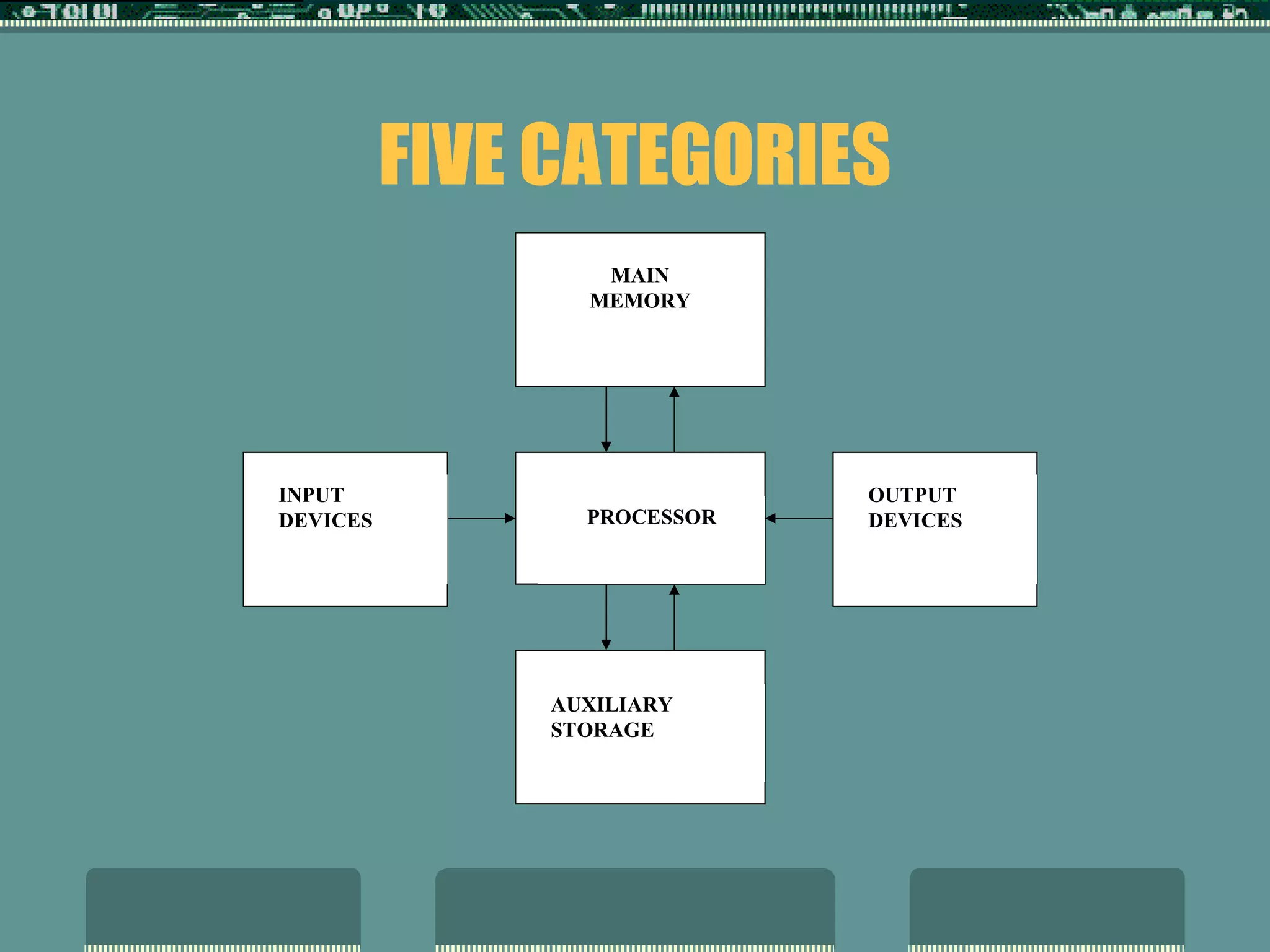
The document provides an introduction to computers and essential information about their basic components and functions. It explains that computers perform four basic operations: input, processing, output, and storage. Data is input and then processed before being output in a usable form. The main hardware components are the processor, main memory, auxiliary storage, input devices, and output devices. Software includes operating systems, utilities, and applications.