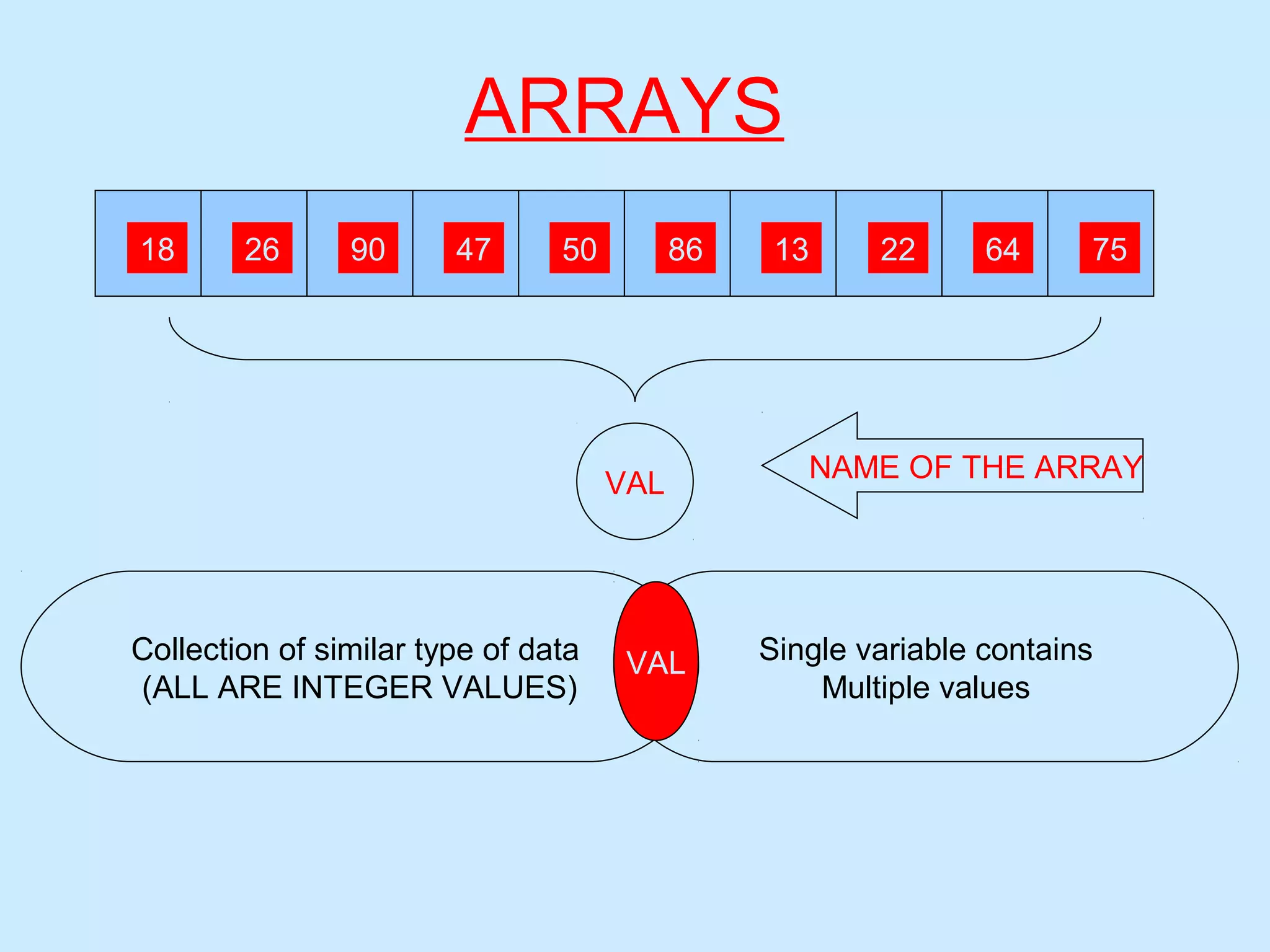
This document provides information about arrays in C/C++. It defines arrays as a collection of similar data types that uses a single variable name to represent multiple values. The key types of arrays discussed are one-dimensional and two-dimensional arrays. Memory representation and declaration of arrays is explained, including how to initialize arrays of integers, characters, and strings. Examples of programs that demonstrate entering and displaying array values, bubble sorting arrays, and using a two-dimensional character array are also provided.
![ARRAY DECLARATION
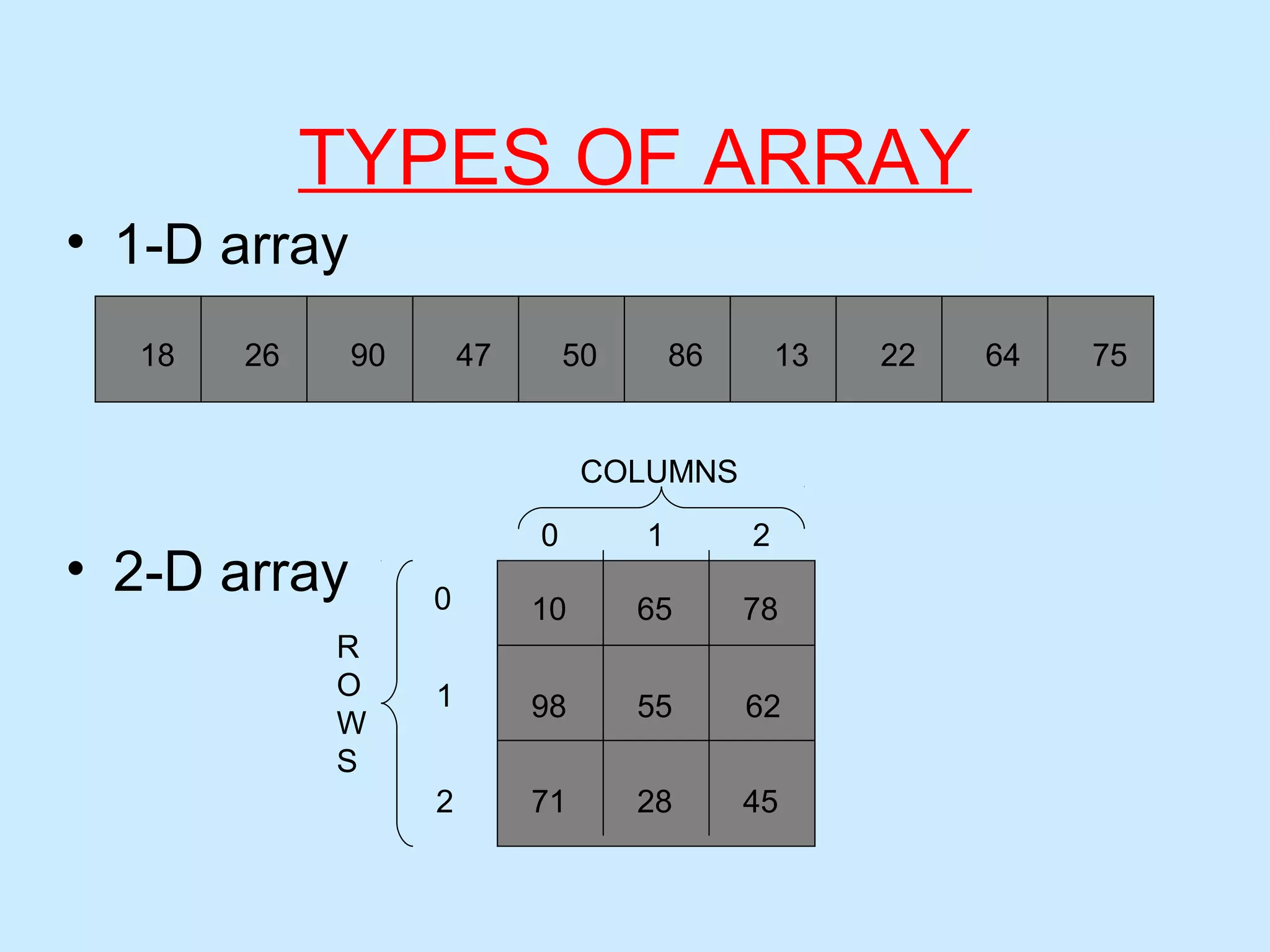
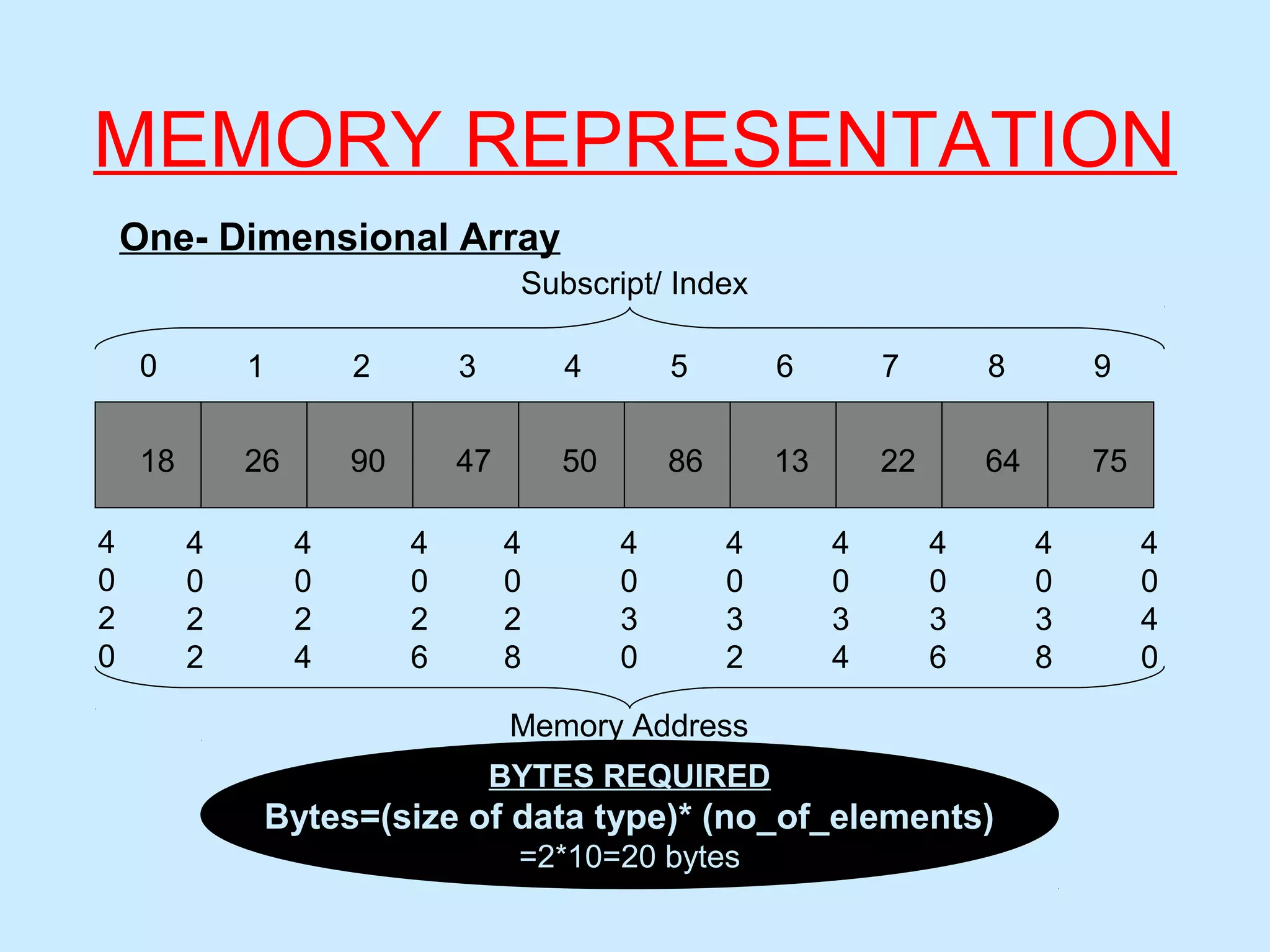
One-Dimensional Array
int arr[5]; contains 5 numbers
char name[15]; 15 characters (including 0)
float salary[10]; 10 floating point (decimal) values
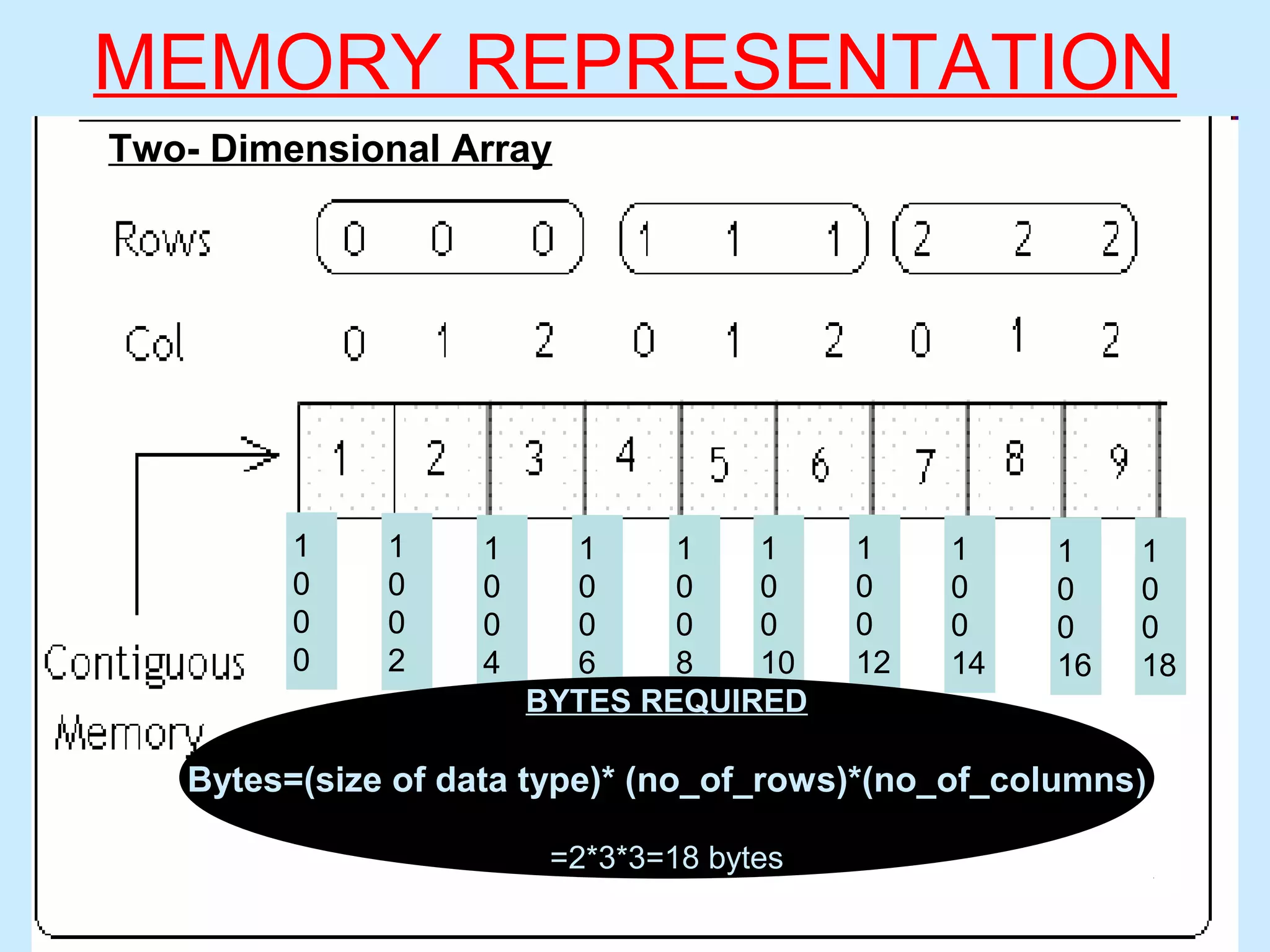
Two-Dimensional Array
int arr[5][5]; contains 25(5x5) numbers
char names[15][10]; 15 names with 10 characters each
float salary[10][5]; contains 50(10x5) floating point (decimal) values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-5-2048.jpg)
![ARRAY INITIALIZATION
INTEGERS
1. int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
2. int a[ ]={1,2,3,4,5};
3. int a[3][3] = { {1,2,3}, {4,5,6}, {7,8,9} };
4. int marks[ ][2]={ 10, 15,
20, 12,
14, 16};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-6-2048.jpg)
![ARRAY INITIALIZATION
CHARACTER ARRAY/ STRINGS
1. char str[6] = “Radha”;
2. char str[ ] = “Radha”;
3. char str[ ]={ ‘r’, ’a’ ,’d’ ,’h’ ,’a’ , ’0’};
4. char days[3][15]={“Monday”, “Tuesday”, “Wednesday”};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-7-2048.jpg)

![#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[10],i;
cout<<“n ENTER 10 NUMBERS”;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
cout<<“nNUMBERS ENTERED BY YOU ARE”;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cout<<“n”<<a[i];
}
getch();
}
Initial value of i=0 ???
Loop
???
BACK](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-9-2048.jpg)
![#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a[20],i,j,size,temp;
cout<<"n ENTER THE SIZE OF THE ARRAY";
cin>>size;
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<size-i-1;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=temp;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-10-2048.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<size;i++)
{
cout<<"n"<<a[i];
}
getch();
}
If array is
i=0j<size-i-1(size=8) j<8-0-1=7 j<7
j= 0 No change as a[0] > a[0+1] 10 > 46 (false)
j=1 Swapping as a[1]>a[1+1] 46 >12 (true)
10 46 12 5 30 2 24 17
10 46 12 5 30 2 24 17
10 46 12 5 30 2 24 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-11-2048.jpg)
![j=2 Swapping as a[2]>a[2+1] 46 > 5 (true)
j=3 Swapping as a[3]>a[3+1] 46 > 30 (true)
J=4 Swapping as a[4]>a[4+1] 46>24(true)
10 12 46 5 30 2 24 17
10 12 5 46 30 2 24 17
10 12 5 30 46 2 24 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-12-2048.jpg)
![J=5 Swapping as a[5]>a[5+1] 46 > 24 (true)
J=6 Swapping as a[6]>a[6+1] 46 > 30 (true)
ARRAY AFTER Ist PASS
10 12 5 30 2 46 24 17
10 12 5 30 2 24 46 17
10 12 5 30 2 24 17 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-13-2048.jpg)
![i=1 j<size-i-1(size=8) j<8-1-1=6 j<6
j=0 No change as a[0] > a[0+1] 10 > 12 (false)
j=1 Swapping as a[1]>a[1+1] 12 >5 (true)
j=2 No change as a[2]>a[2+1] 12>30(false)
10 12 5 30 2 24 17 46
10 12 5 30 2 24 17 46
10 5 12 30 2 24 17 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-14-2048.jpg)
![j=3 Swapping as a[3]>a[3+1] 30 > 2 (true)
j=4 Swapping as a[4]>a[4+1] 30 > 24 (true)
J=5 Swapping as a[5]>a[5+1] 30>17(true)
10 5 12 30 2 24 17 46
10 5 12 2 30 24 17 46
10 5 12 2 24 30 17 46](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-15-2048.jpg)
![ARRAY AFTER IInd PASS
i=2 j<size-i-1(size=8) j<8-2-1=6 j<5
j=0 Swapping as a[0] > a[0+1] 10 > 5 (true)
j=1 No change as a[1]>a[1+1] 10 >12 (false)
10 5 12 2 24 17 30 46
10 5 12 2 24 17 30 46
5 10 12 2 24 17 30 46
PERFORM THE DRY RUN ON YOUR OWN TO GET SORTED LIST](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-16-2048.jpg)
![#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char name[10][15];
int I;
cout<<“nENTER 10 NAMES”;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
gets(name[i]);
}
cout<<“nNAMES ENTERED BY YOU ARE”;
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
cout<<“n”<<name[i];
}
getch();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arrays-160211175158/75/Arrays-17-2048.jpg)