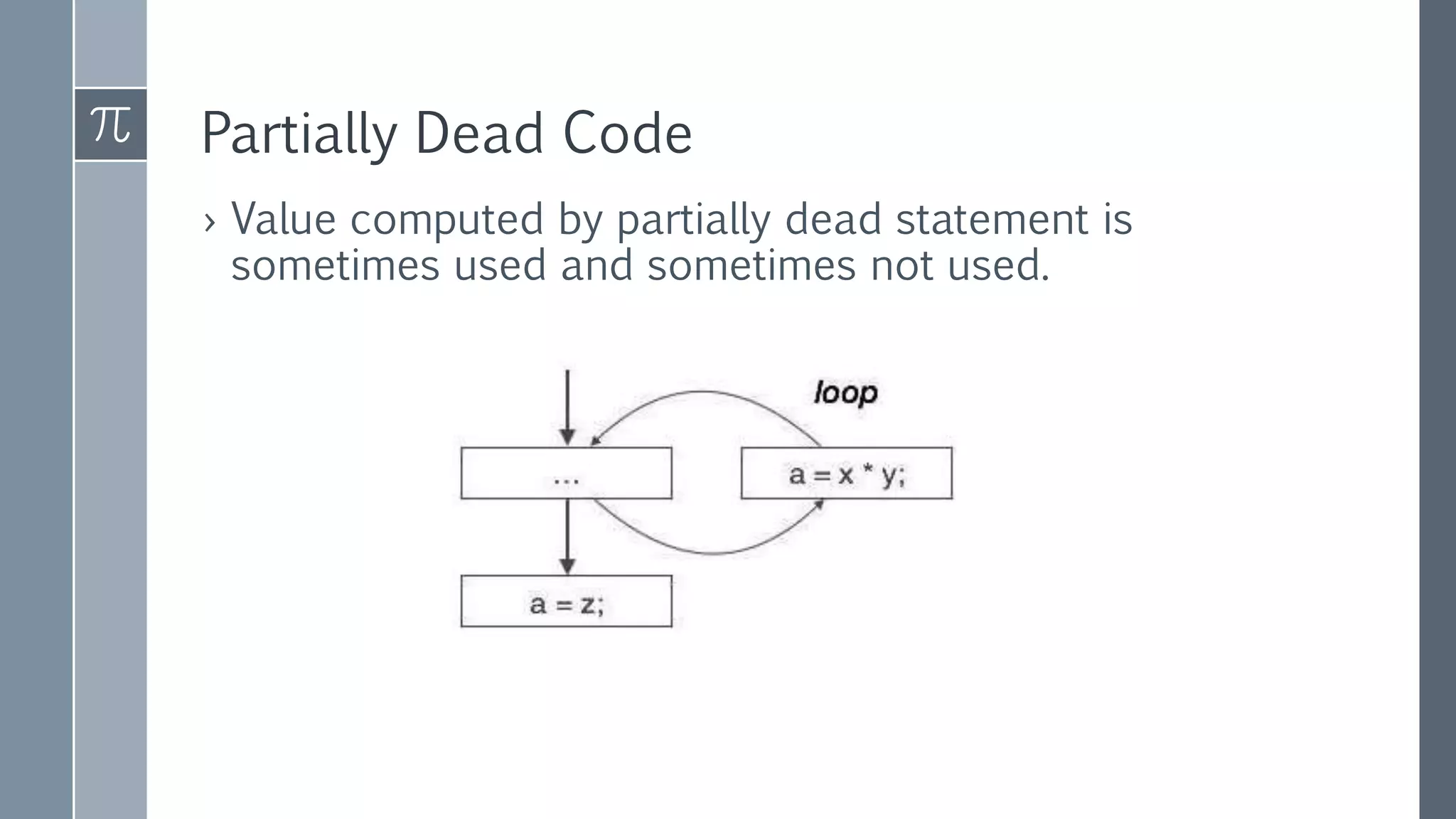
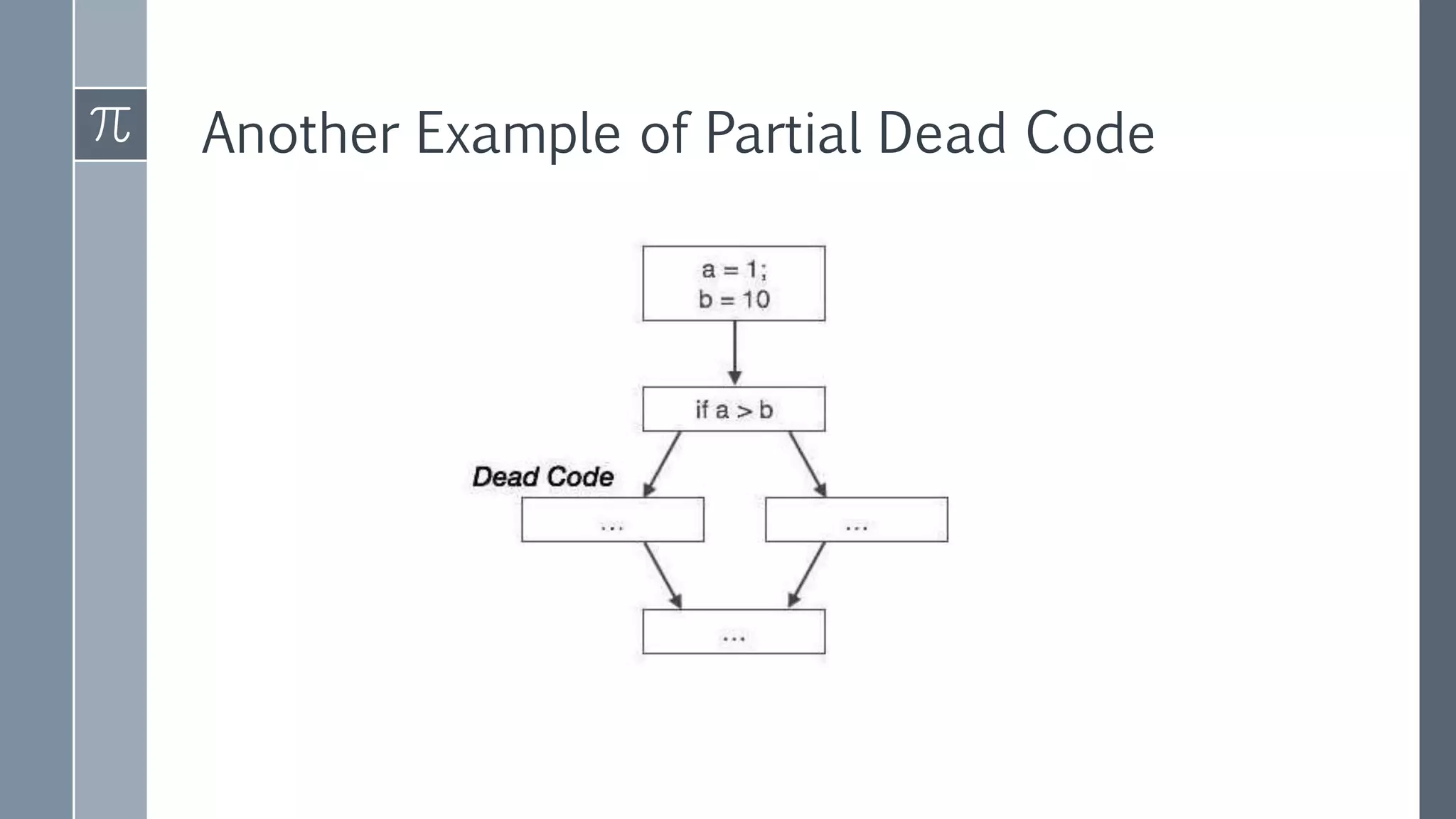
Dead code elimination is a compiler optimization technique that removes code that can never be executed, such as unreachable code, or code with outputs that are never used. Removing dead code shrinks program size and reduces runtime. It works by analyzing the control flow and data dependencies of a program to identify code that is deemed dead. Both static and dynamic dead code elimination techniques exist.