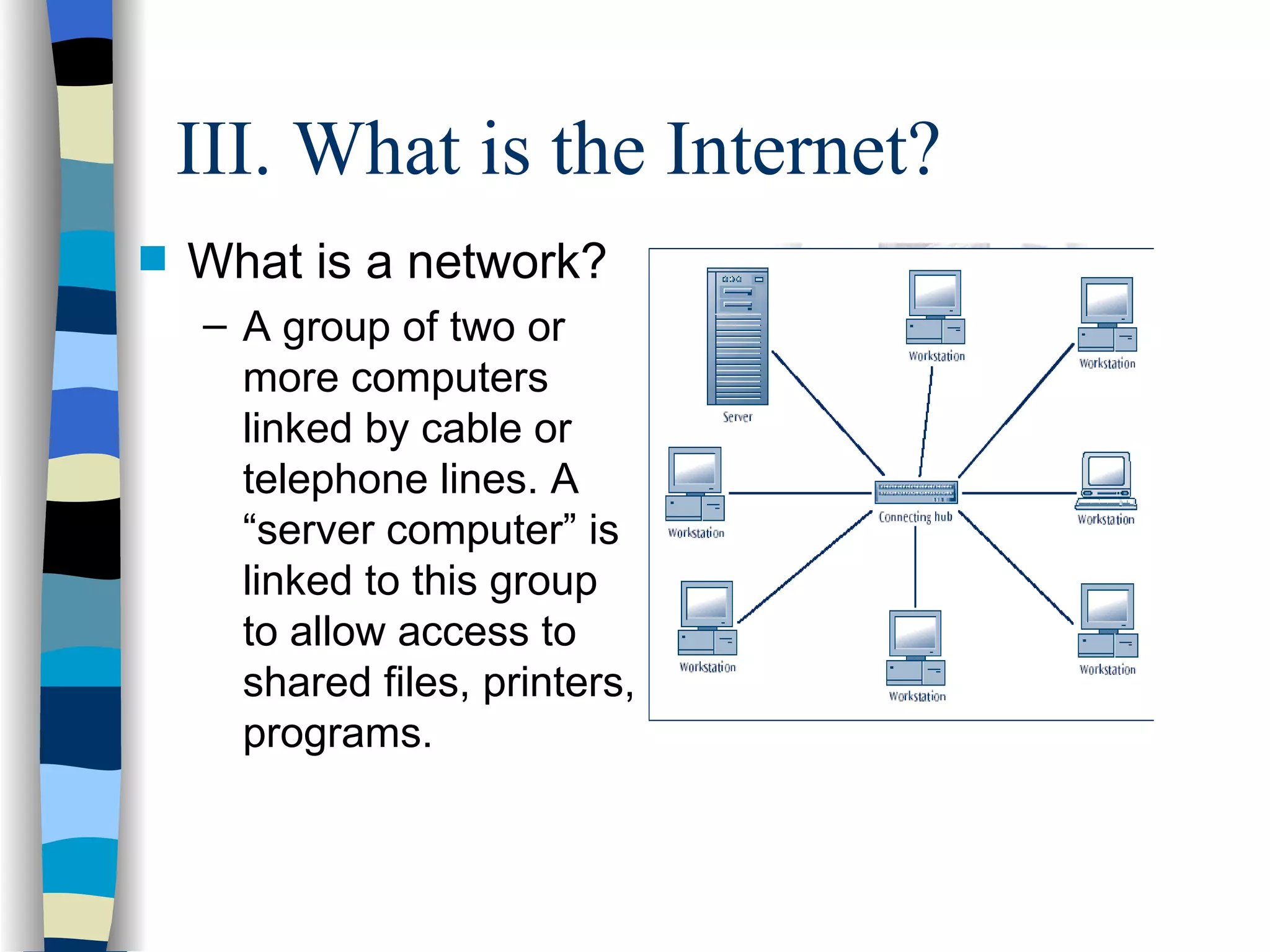
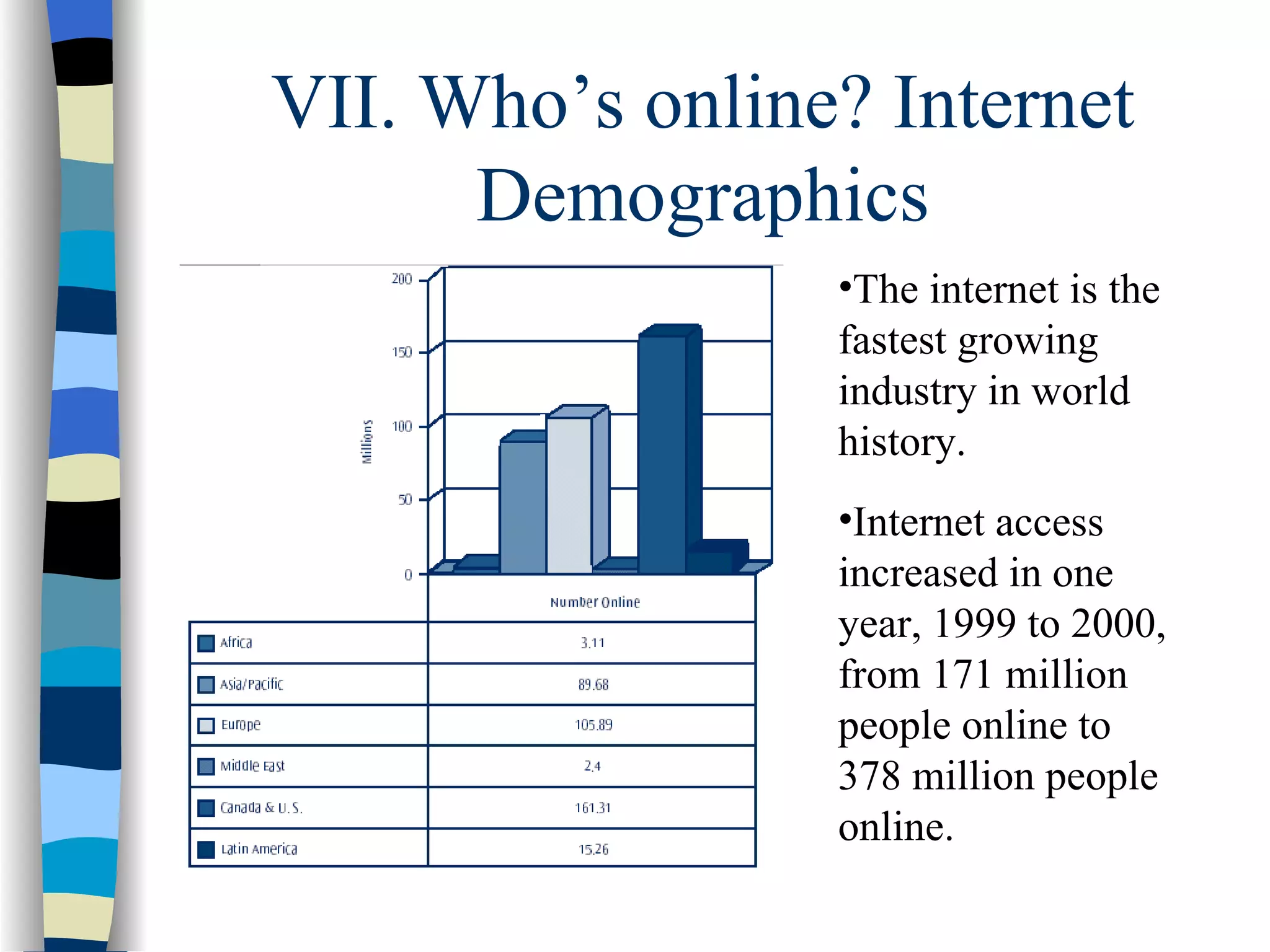
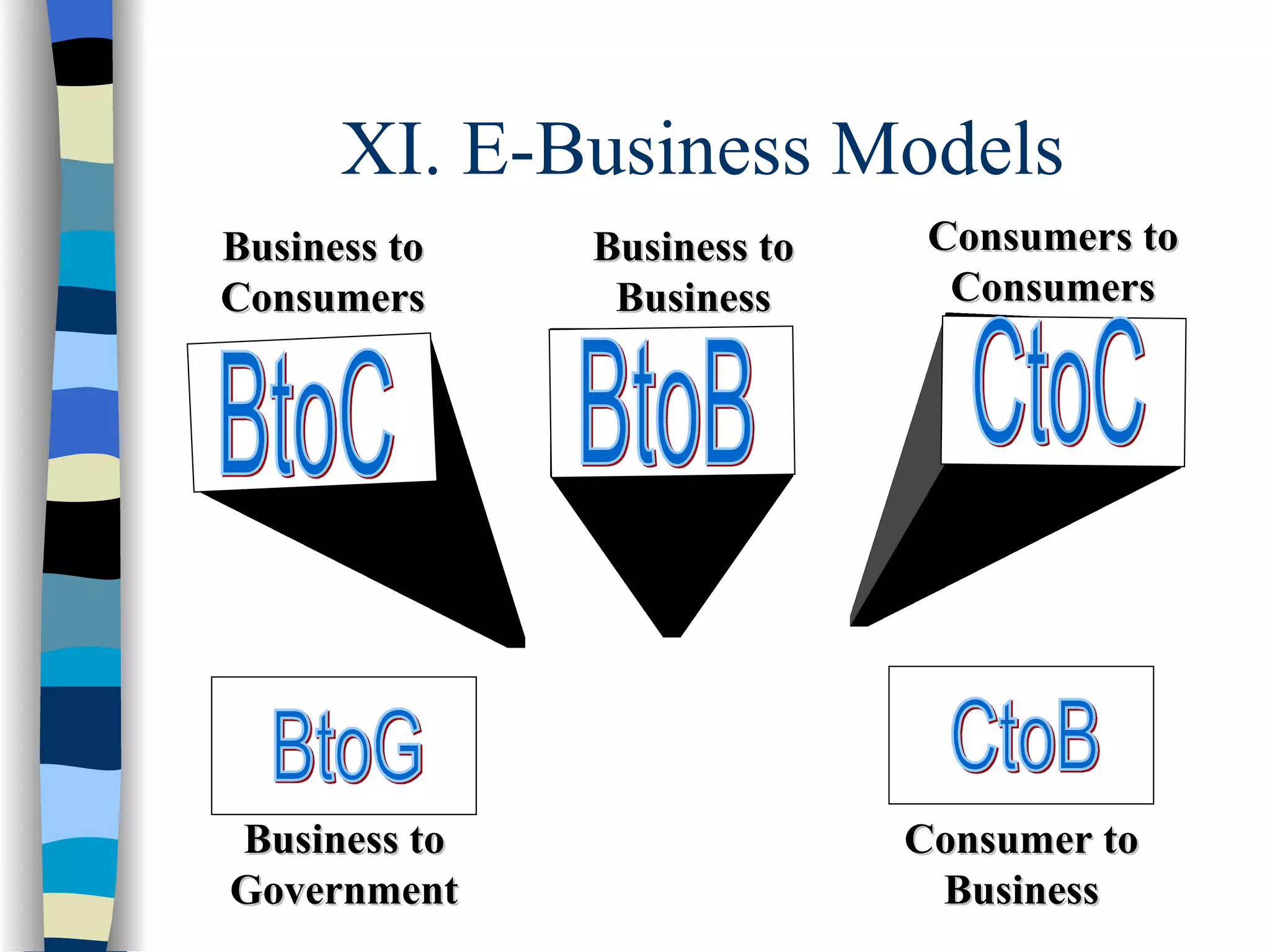
This document provides an overview of electronic commerce and e-business basics. It discusses the difference between traditional commerce involving physical marketplaces versus electronic commerce conducted over telecommunications networks. The chapter then covers the history of e-commerce beginning in the 1960s-1970s with banking EFT and business EDI networks. It describes how the internet functions as a public network connecting private networks using TCP/IP protocols. The development of the World Wide Web in 1989 is discussed as improving information sharing through hypertext links. Advantages of the WWW for users and types of e-business models are summarized.