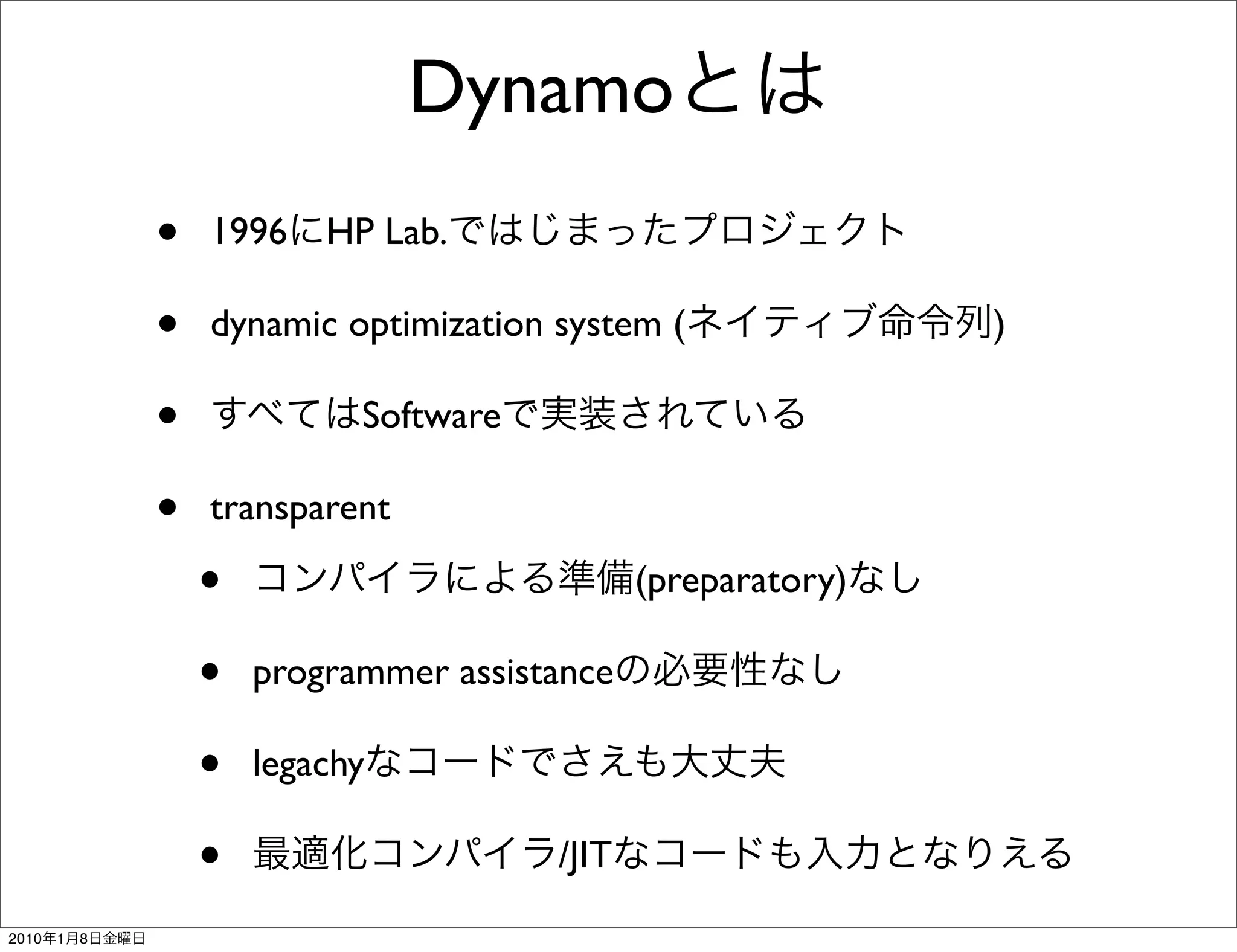
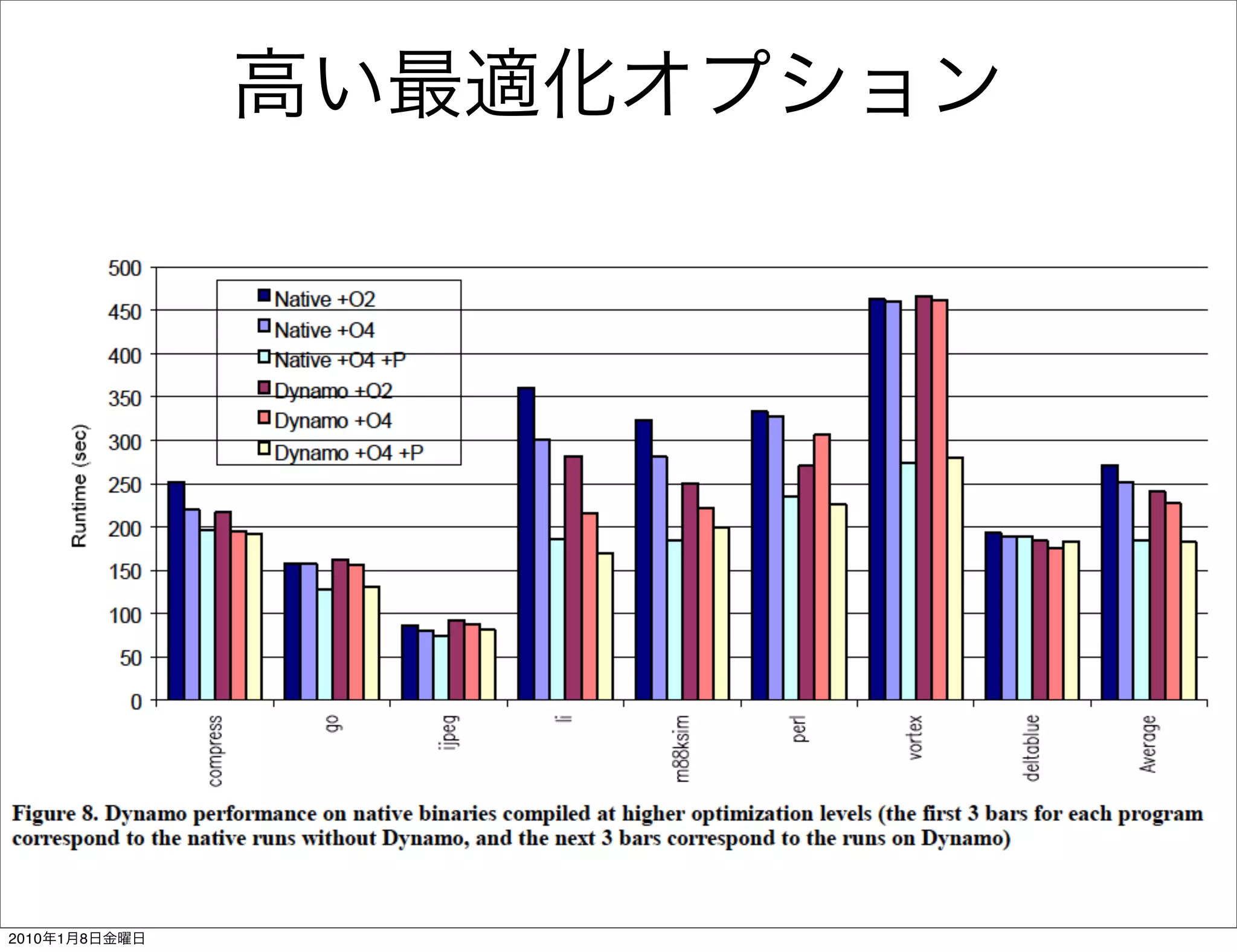
- Dynamo is a dynamic optimization system developed at HP Labs in 1996 that performs dynamic binary translation and optimization at runtime.
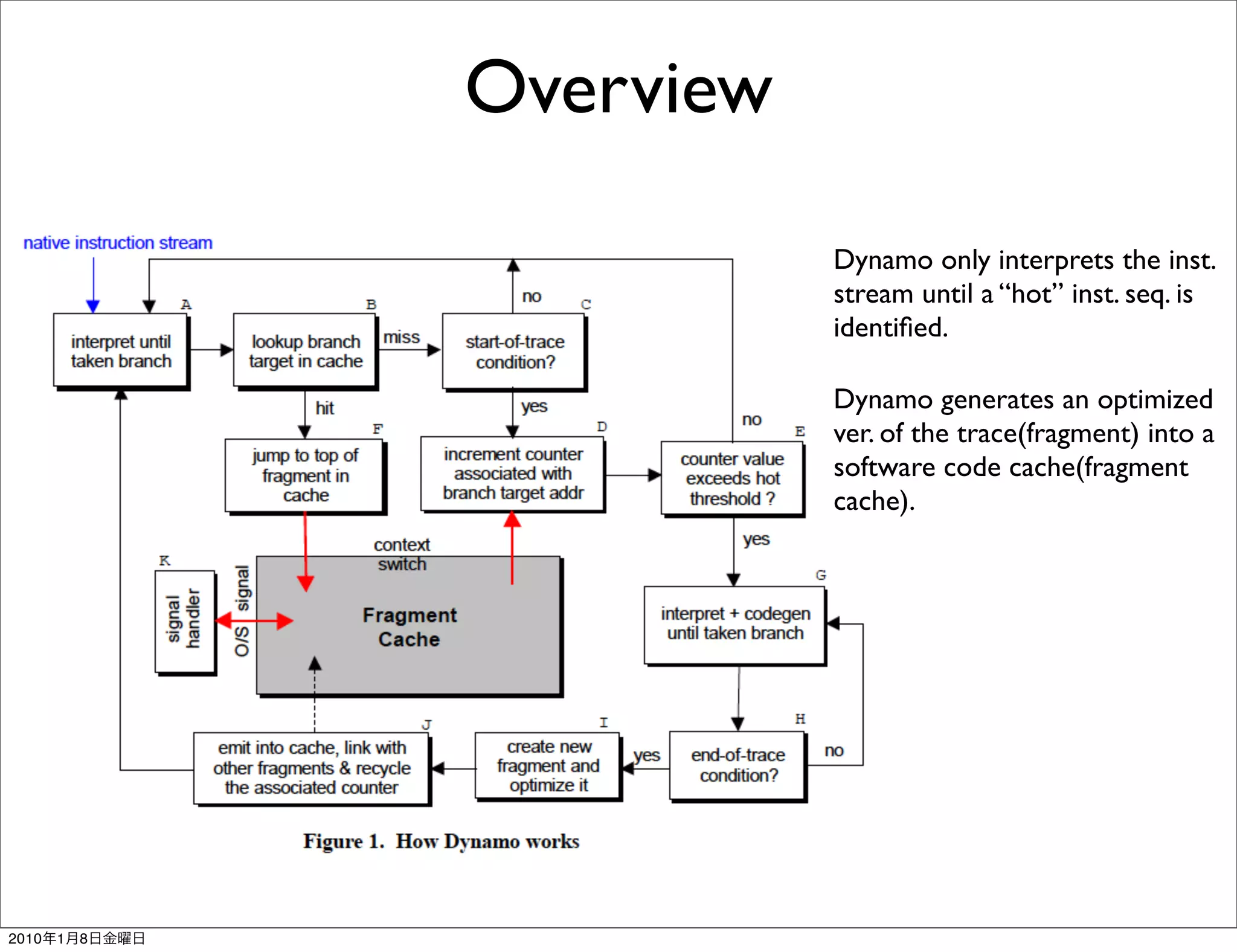
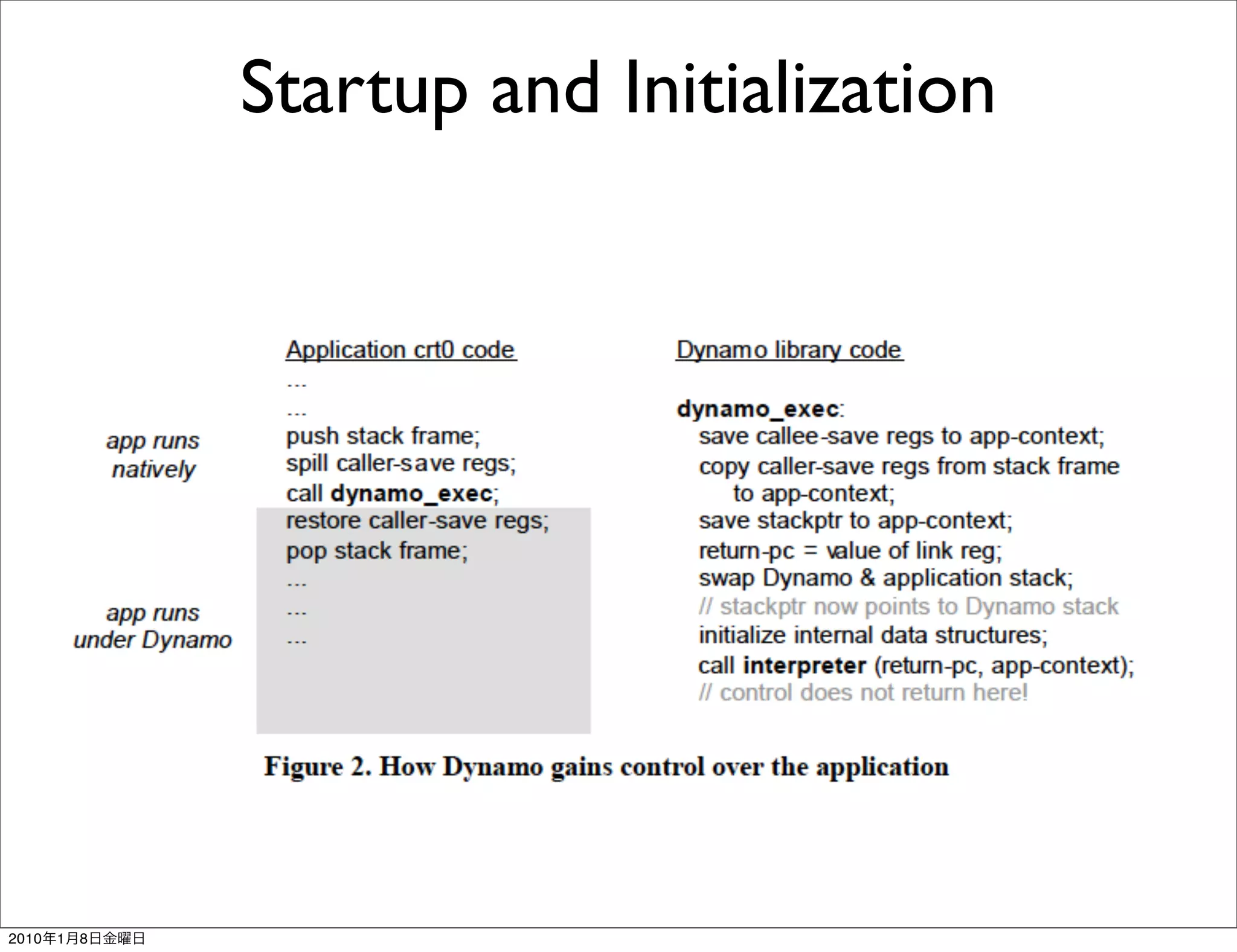
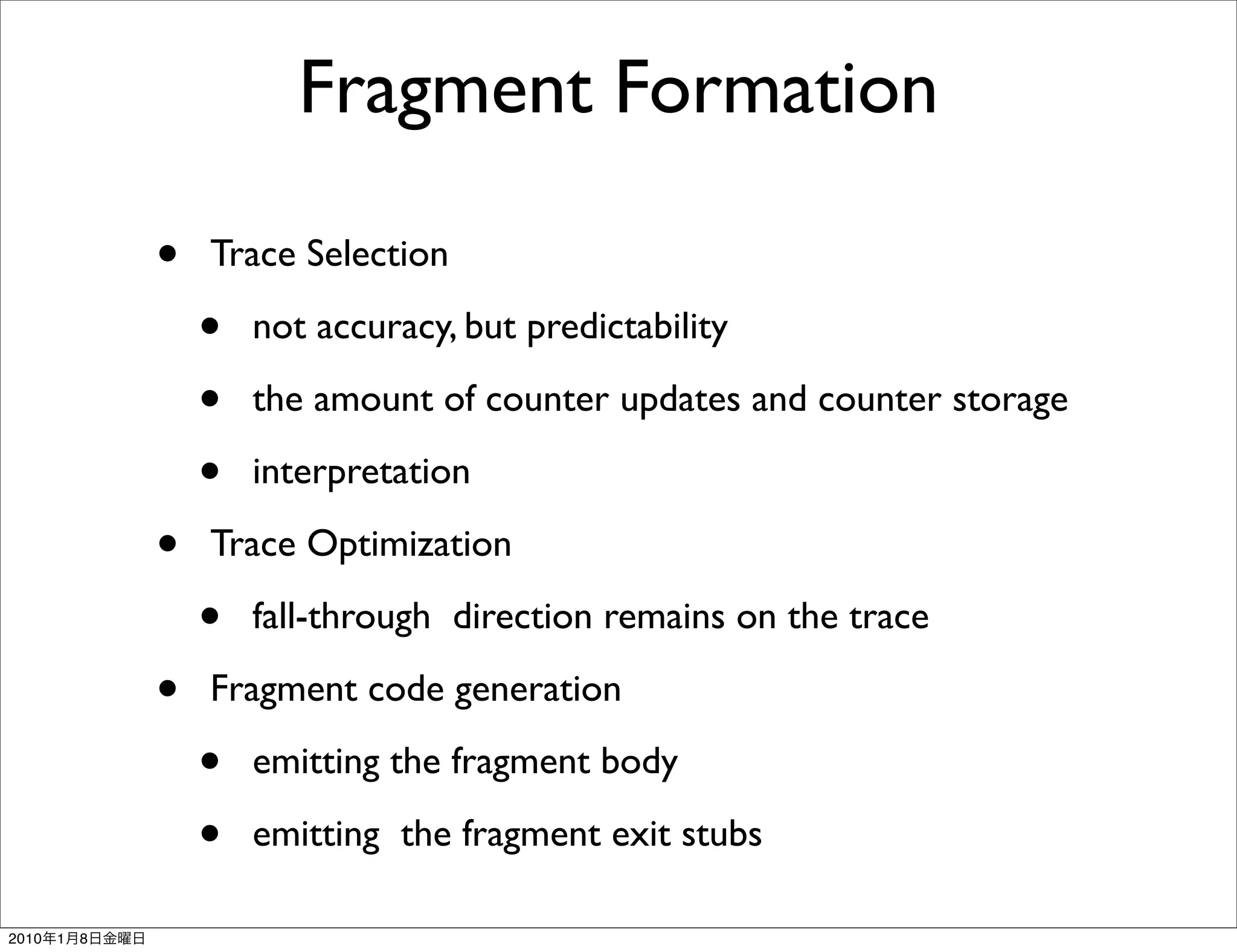
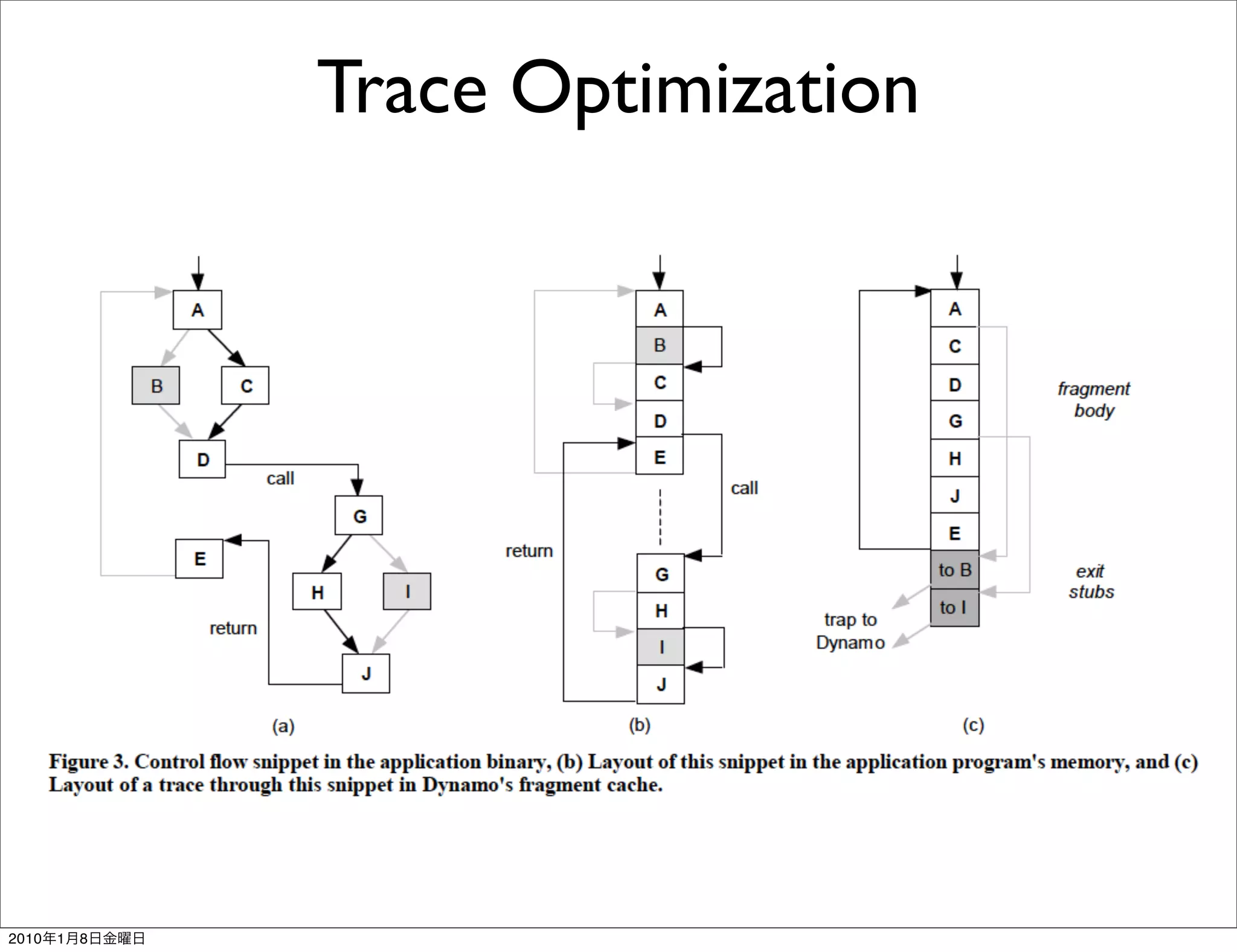
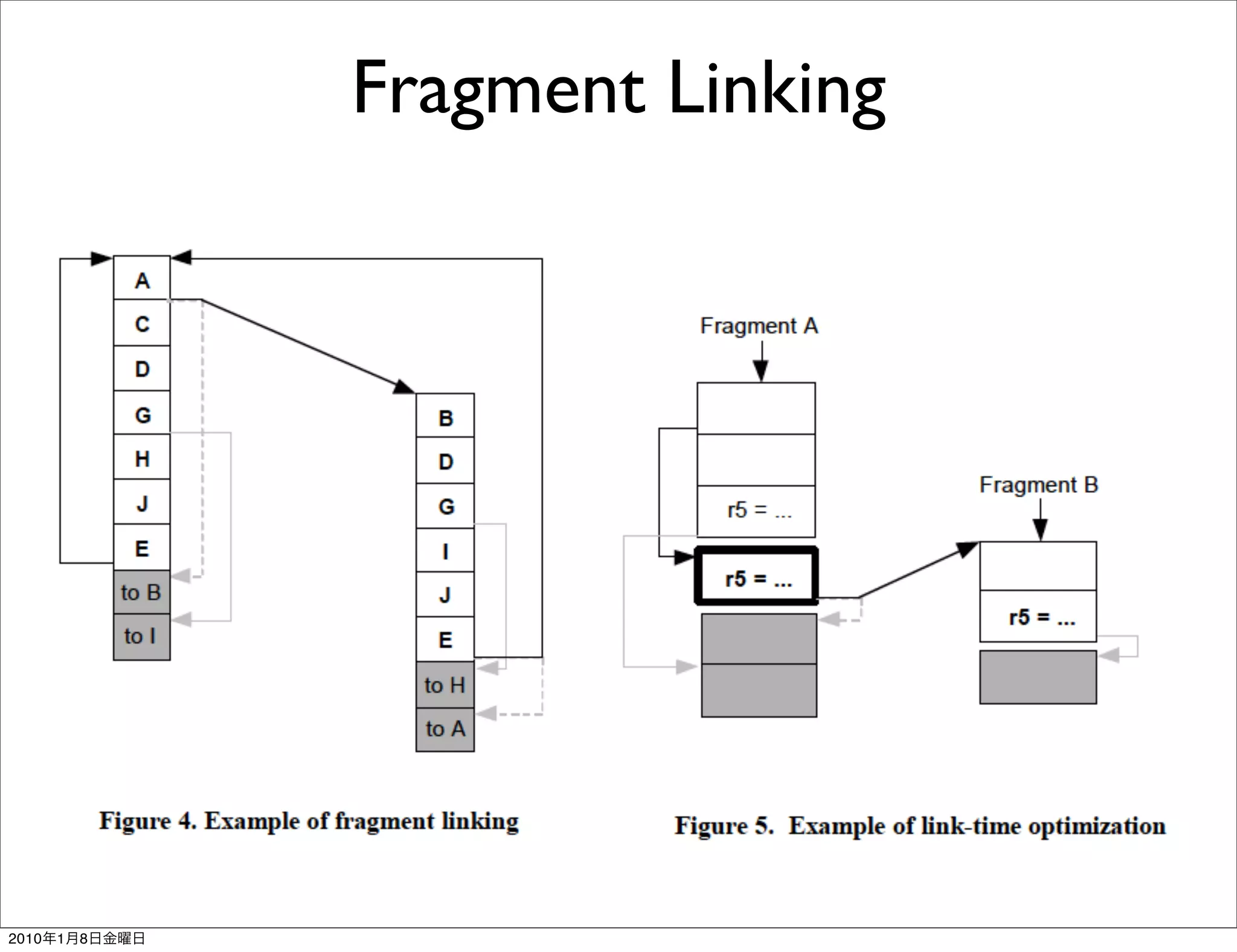
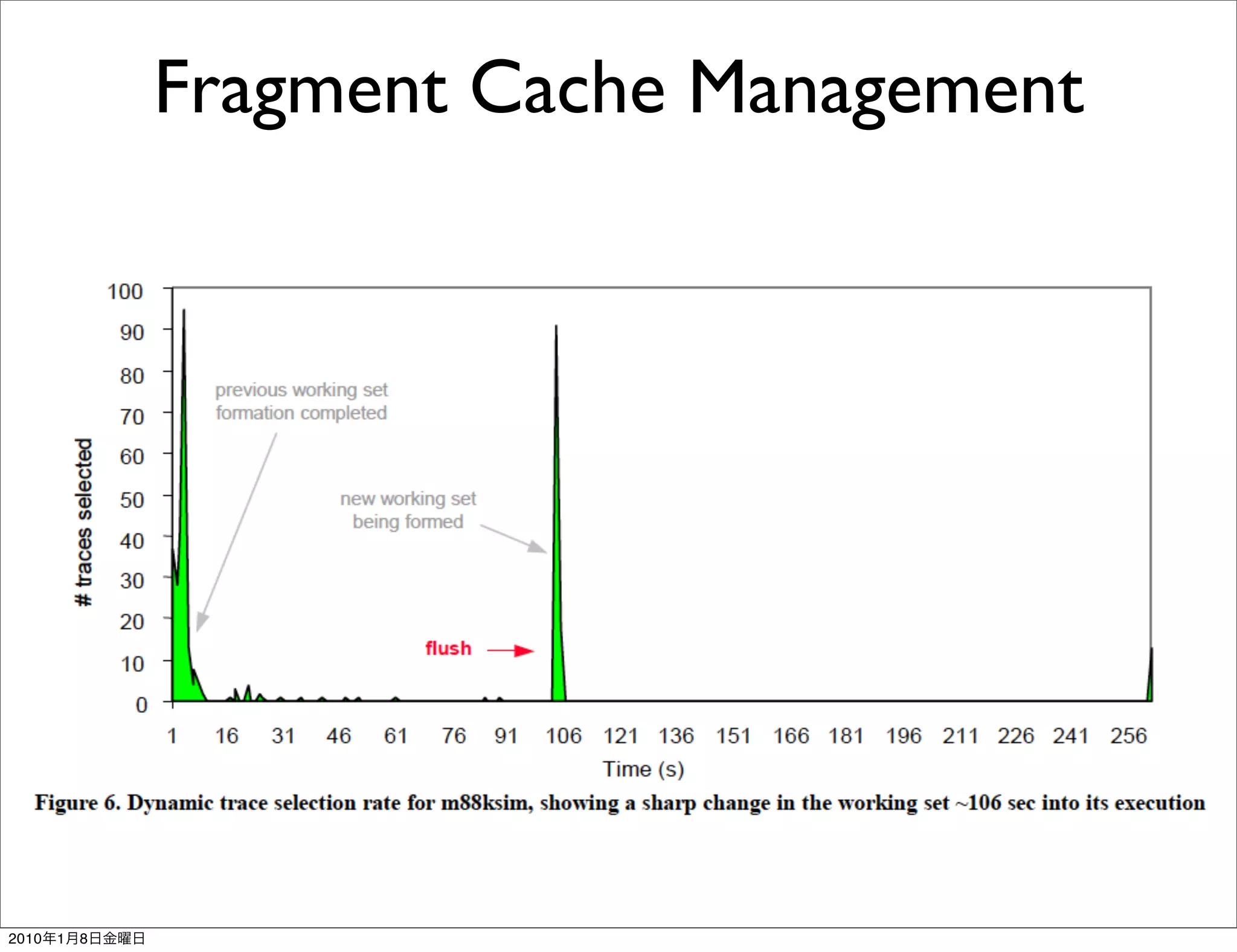
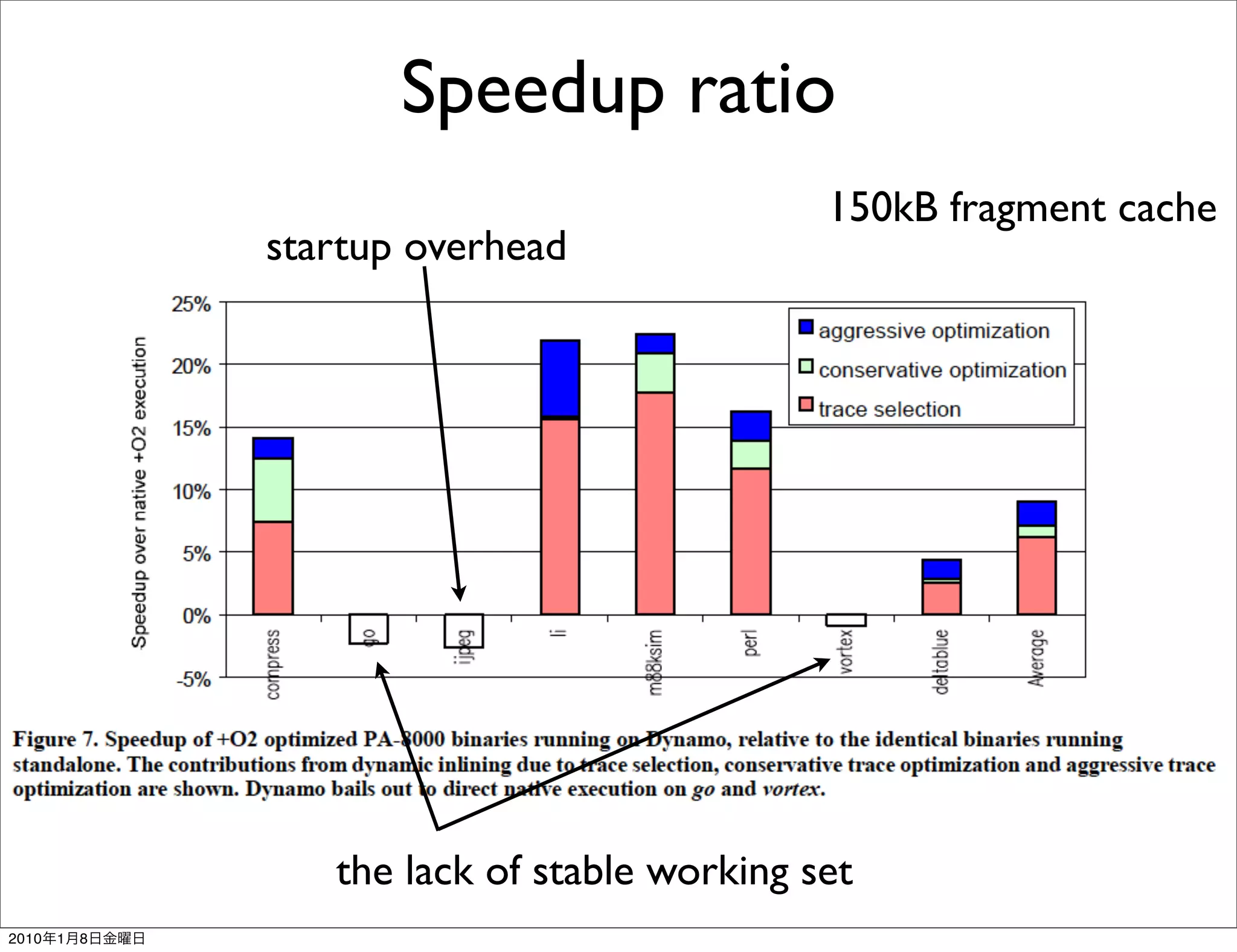
- It works transparently by initially interpreting the instruction stream until hot instruction sequences, or traces, are identified. Then it generates optimized versions of the traces and stores them in a software code cache called the fragment cache.
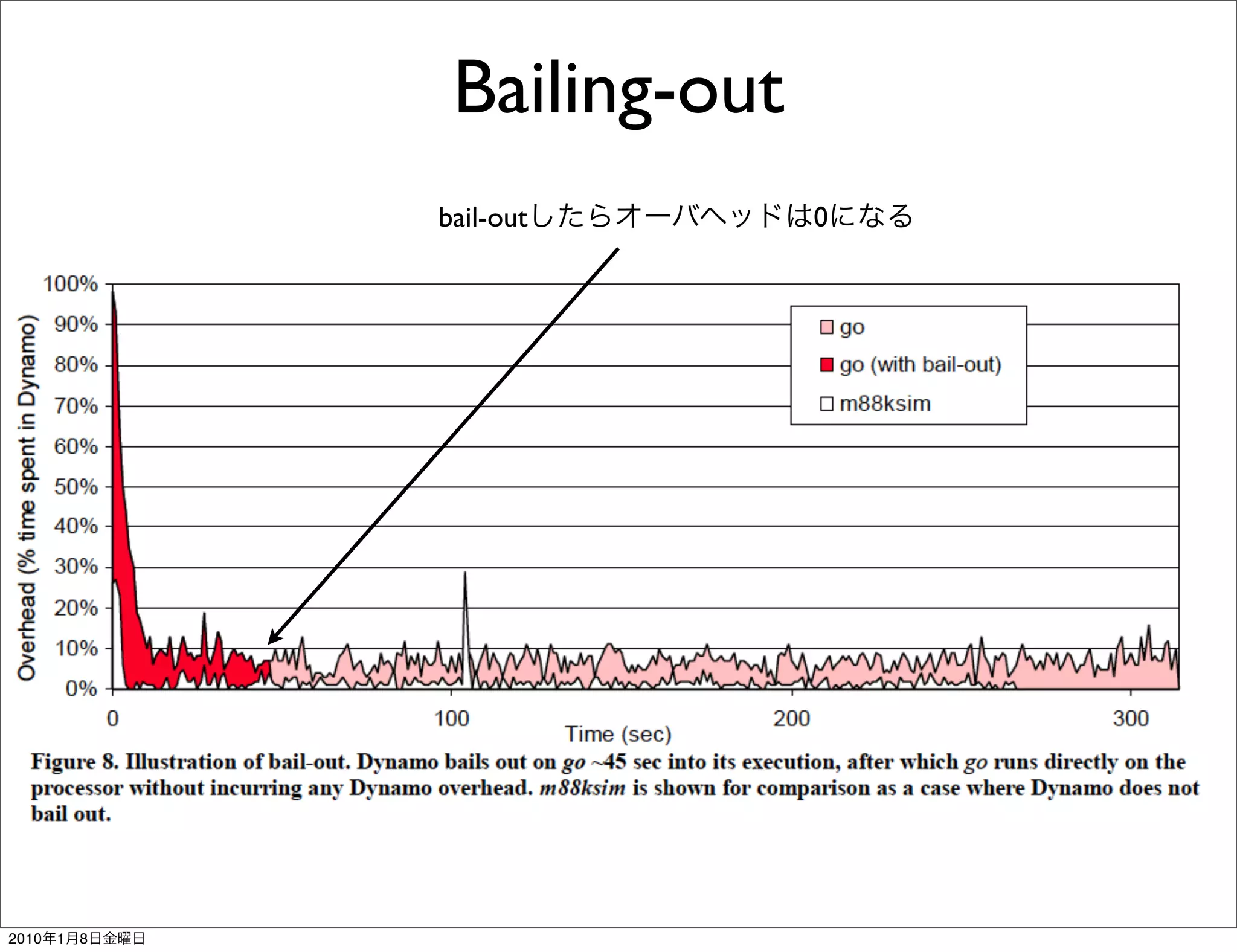
- Key aspects of how Dynamo works include trace selection and formation, trace optimization, fragment linking and management, handling signals and exceptions, and mechanisms for "bailing out" of optimized code back to interpretation if optimizations cannot be applied.